When you think of small animals surviving the harshest corners of our planet, it might seem like a plot straight out of a nature documentary. Yet, these tiny creatures, from the Arctic tundra to the scorching deserts, and even the lush, dense tropical rainforests, have mastered the art of adaptation. It’s fascinating how nature’s most diminutive beings have developed incredible strategies not just to survive, but to thrive in extreme climates that seem uninhabitable.
Imagine a world where a tiny rodent can endure the biting cold of the Arctic with clever insulation and camouflage techniques, or where a small desert creature employs ingenious water conservation strategies to stay hydrated. These adaptations are not only a testament to nature’s ingenuity but also highlight the critical role that small animals play in maintaining the delicate balance of ecosystems. As we journey through this blog, we’ll uncover the remarkable ways these animals adapt to their environments, diving into their behavioral, physiological, and ecological marvels.
In this exploration, we won’t just celebrate the resilience of these tiny titans; we’ll also reflect on the broader implications of their survival tactics. What can we, as humans, learn from their ability to adapt? How can their resilience inspire us to tackle our own challenges? And perhaps most importantly, why is it vital to foster an appreciation for biodiversity and conservation? Join me as we delve into the extraordinary world of small animals and their awe-inspiring adaptations, showcasing that even the smallest creatures can have the biggest impact on our understanding of life and survival.
Introduction to Animal Adaptations
Definition and Importance of Adaptations
In the grand tapestry of nature, small animals are remarkable examples of life’s ability to thrive against all odds. As we delve into the world of animal adaptations, it is essential to first understand what adaptations are and why they are crucial for survival. Adaptations are the physical or behavioral characteristics that have evolved over time, enabling species to better survive and reproduce in their specific environments. These adaptations might include physical traits like fur thickness or behavioral strategies such as migration.
The importance of adaptations cannot be overstated. They are nature’s way of ensuring that species can cope with and flourish in the diverse and often challenging habitats they inhabit. For small animals, which are often at the mercy of larger predators and harsh environmental conditions, these adaptations are vital. They allow these creatures to find food, escape predators, and reproduce in climates that range from the frigid Arctic tundra to the sweltering deserts.
Understanding these adaptations not only highlights the resilience and ingenuity of small animals but also provides insight into the intricate balance of ecosystems. Each adaptation plays a role in the survival of the species, contributing to the broader tapestry of biodiversity.
Overview of Extreme Climates
When we talk about extreme climates, we refer to environments that pose significant challenges to life due to their harsh conditions. These climates test the limits of survival and require innovative adaptations from the creatures that inhabit them. Let’s explore some of these extreme climates:
- Arctic Climates: Characterized by freezing temperatures, limited vegetation, and long, dark winters, the Arctic is a formidable environment. Animals here must develop thick insulation, such as blubber or fur, and often have white or grey coloring for camouflage against the snow and ice.
- Desert Environments: On the other end of the spectrum, deserts are known for their scorching temperatures and scarce water resources. Animals in these areas have evolved to conserve water efficiently and often display nocturnal behaviors to avoid the daytime heat.
- Tropical Rainforests: These lush environments present their own set of challenges, such as high humidity and dense vegetation. Animals in rainforests have adaptations that allow them to move through thick foliage and exploit the diverse food sources available.
- High-Altitude Regions: At high altitudes, oxygen levels are low, and temperatures can fluctuate dramatically. Animals living in these regions develop physiological adaptations to cope with reduced oxygen and survive the cold.
Each of these extreme climates presents unique challenges, and the small animals that inhabit them have developed fascinating adaptations to thrive. By studying these adaptations, we gain a deeper appreciation for the resilience of life and the delicate balance of ecosystems.

Various small animals showcasing their adaptations in extreme climates
Adaptations to Arctic Climates
The Arctic is an unforgiving environment, where temperatures plummet to extreme lows and survival becomes a daily challenge. Yet, in this icy expanse, small animals have evolved remarkable adaptations that allow them to thrive. These adaptations are both physical and behavioral, enabling them to navigate the harsh conditions with finesse.
Insulation and Camouflage Techniques
In the Arctic, maintaining body heat is crucial for survival. Small animals have developed sophisticated insulation techniques to combat the biting cold. One of the primary methods is through thick fur or feathers, which create a layer of air that acts as insulation, trapping body heat. Animals like the Arctic fox and the snowshoe hare boast dense, fluffy coats that are not only warm but also serve as excellent camouflage against the snowy backdrop.
The Arctic fox, for instance, changes its coat color with the seasons, donning a white coat in winter to blend seamlessly with the snow and a brownish coat in the summer to match the tundra. This ability to alter their appearance is a critical survival tactic, reducing the risk of predation.
Another intriguing adaptation is the presence of subcutaneous fat in many Arctic animals. This layer of fat provides an additional thermal barrier and serves as an energy reserve during scarce times. It’s fascinating to observe how these small creatures have fine-tuned their physiology to withstand the Arctic’s challenges.
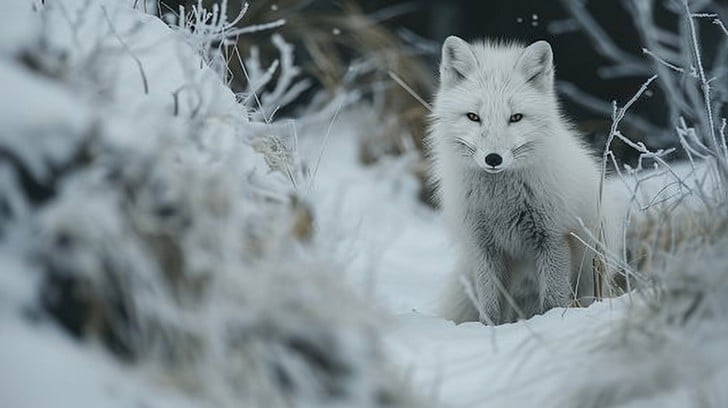

An Arctic fox with its winter coat blending into the snowy environment
Behavioral Adaptations for Cold Survival
Aside from physical adaptations, the survival of small animals in the Arctic heavily relies on their behaviors. Many species adopt hibernation or torpor, a state of reduced metabolic activity, to conserve energy during the coldest months. The Arctic ground squirrel, for example, enters a hibernation state where its body temperature drops significantly, allowing it to survive without food until the weather becomes more favorable.
Social behaviors also play a crucial role in surviving the Arctic climate. Some small animals, like lemmings, form communal nests during the winter, huddling together to share warmth. This social insulation is a clever strategy to combat the cold and ensure mutual survival.
Moreover, small animals such as the ptarmigan practice daily routines and movements that minimize energy expenditure. They often seek shelter in snow burrows or under rocks where temperatures are slightly warmer and remain inactive during the coldest parts of the day.
While these adaptations may seem extraordinary, they are a testament to the resilience and ingenuity of small animals. The Arctic environment, with its relentless cold and stark beauty, challenges these creatures, yet they persist, showcasing nature’s incredible ability to adapt and thrive against the odds.
Survival in Desert Environments
Deserts are some of the most extreme and challenging environments on Earth, characterized by their arid conditions, intense heat during the day, and often surprisingly cold nights. Despite these harsh conditions, many small animals have developed incredible adaptations to not only survive but thrive in these environments. In this section, we’ll explore the fascinating strategies these creatures employ to conserve water and regulate their body temperature through nocturnal and burrowing habits.
Water Conservation Strategies
In the unforgiving desert landscape, water is a scarce and precious resource. Small animals have evolved exceptional water conservation strategies that enable them to make the most of the limited moisture available. Many of these adaptations are physiological, allowing these creatures to survive on minimal water intake.
One of the most remarkable adaptations is the ability of some small animals to extract water from their food. For instance, the kangaroo rat, a desert-dwelling rodent, can metabolize water from the seeds it consumes, allowing it to stay hydrated without ever drinking liquid water. This adaptation is crucial in an environment where water sources are often miles apart.
Moreover, small animals like the fennec fox have developed highly efficient kidneys that concentrate urine, minimizing water loss. The fennec fox’s kidneys are so effective that it can thrive without drinking water for extended periods. This physiological feature is complemented by behavioral adaptations such as spending the hottest part of the day in cool burrows, reducing the need for water to regulate body temperature.
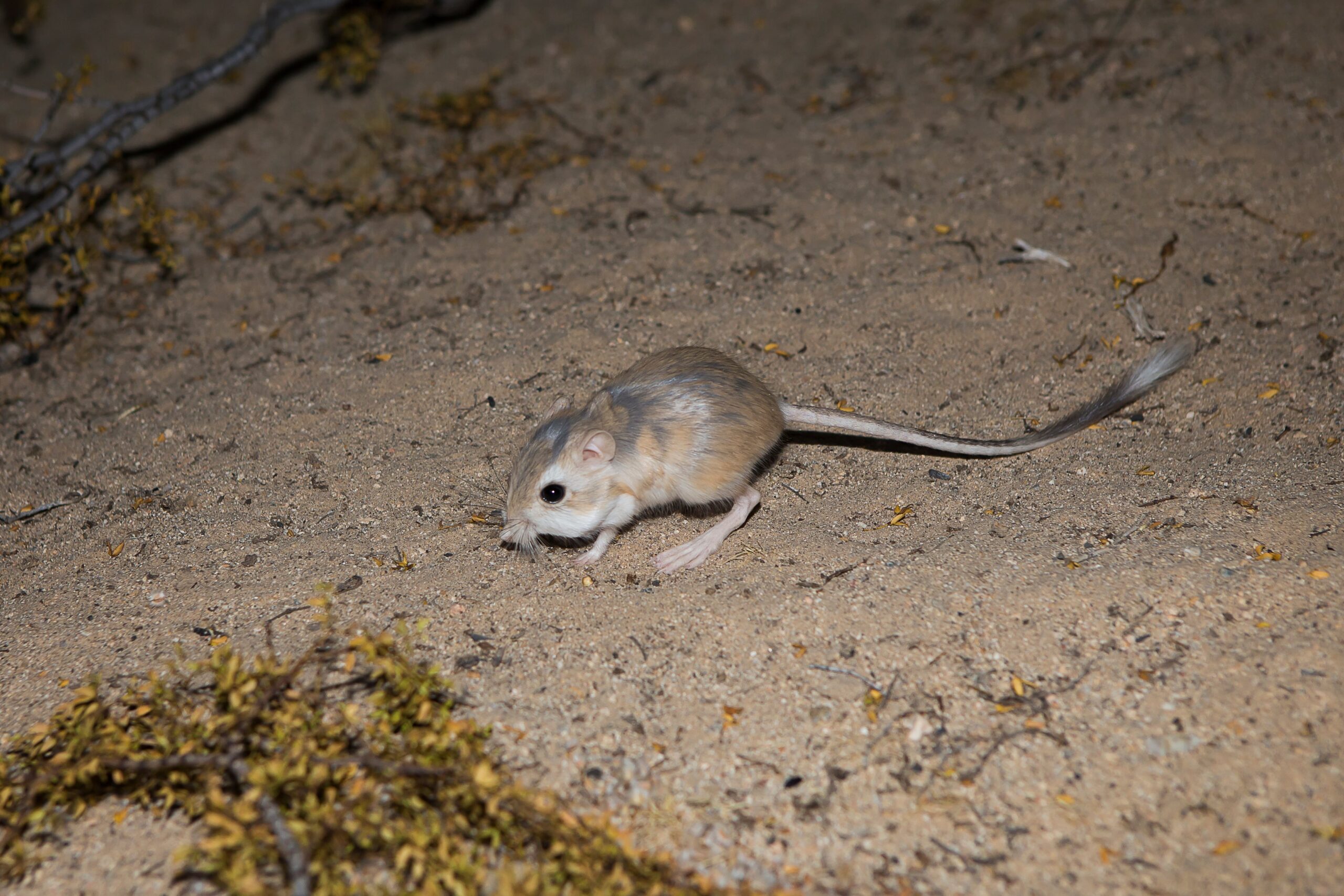

A kangaroo rat thriving in its desert habitat
Nocturnal and Burrowing Habits
The intense heat of the desert daytime can be lethal for small animals. To cope with these conditions, many species have adopted nocturnal habits, becoming active during the cooler night hours. This behavioral adaptation not only helps them avoid the scorching sun but also reduces water loss through evaporation.
For example, the desert hedgehog emerges from its burrow under the cover of darkness to forage for food. By being active at night, it avoids the extreme daytime temperatures and conserves precious moisture. Similarly, the jerboa, a small rodent found in North African and Asian deserts, also exhibits nocturnal behavior, using its long legs to hop across the sand in search of insects and seeds.
In addition to being nocturnal, many small desert animals are expert burrowers. Burrowing provides a cooler and more stable environment compared to the surface. The burrows offer protection from predators and help maintain a consistent microclimate that is less subject to the extreme temperature fluctuations of the desert surface.
The desert tortoise, for example, digs burrows that not only provide shelter from heat but also help in conserving moisture. These burrows can be several feet deep, allowing the tortoise to escape the extreme temperatures above ground.
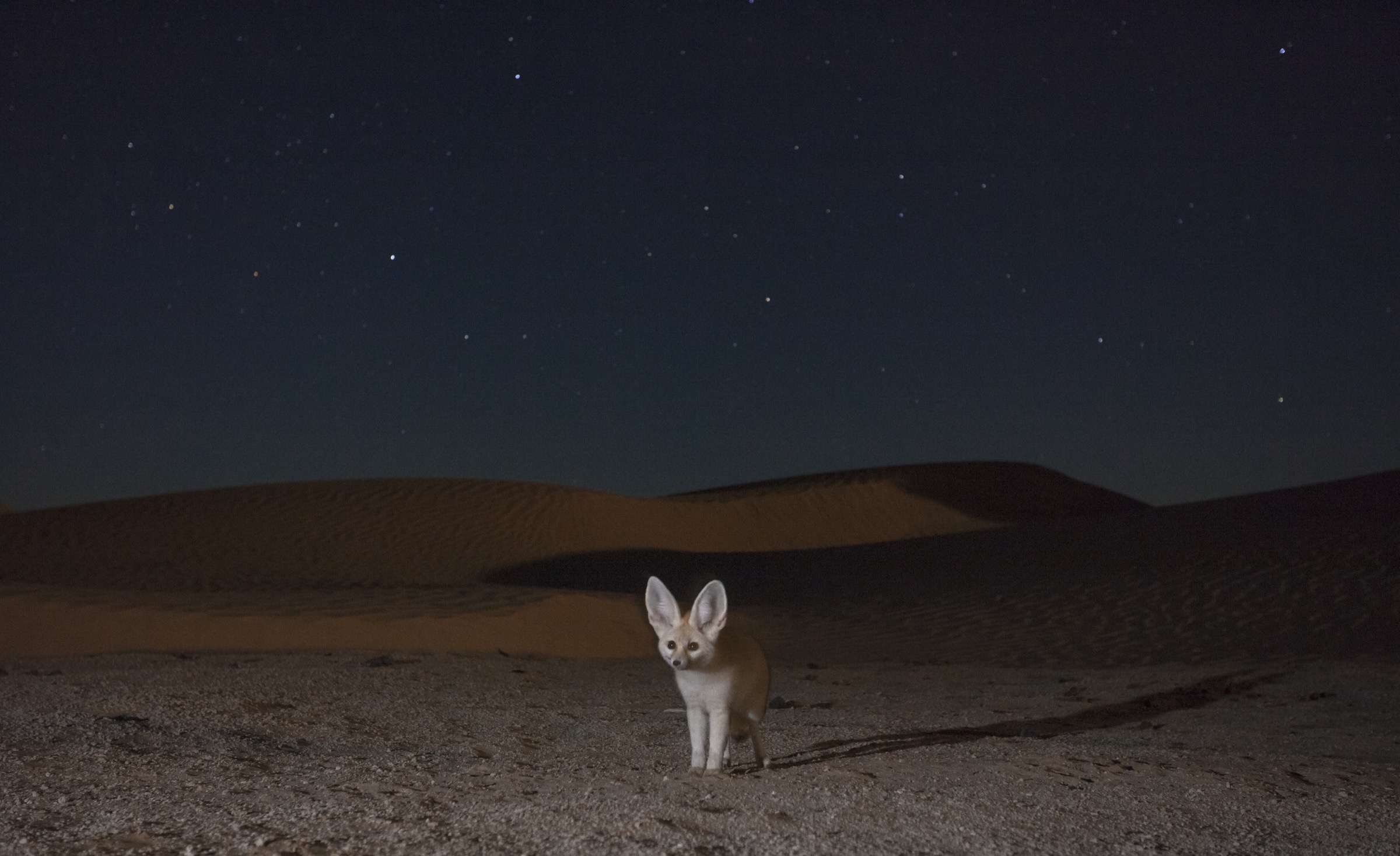

A fennec fox exploring the desert at night
Through a combination of physiological and behavioral adaptations, small animals in desert environments showcase their incredible resilience and ingenuity. These strategies not only highlight the adaptability of life but also underscore the importance of conserving these unique ecosystems and the biodiversity they support.
Tropical Rainforest Adaptations
Navigating Dense Vegetation and High Humidity
The tropical rainforest, a lush and vibrant ecosystem, presents unique challenges for the small animals that inhabit it. These creatures must skillfully navigate through dense vegetation and cope with consistently high levels of humidity. The rainforest is a complex web of life, with towering trees, thick underbrush, and a canopy that filters sunlight, creating a world of dappled shadows and rich biodiversity.
Small animals, such as frogs, insects, and small mammals, have developed remarkable adaptations to thrive in these conditions. For example, many amphibians, like the poison dart frog, possess bright coloration that not only serves as a warning to predators but also helps them blend into the vibrant environment. Their skin secretes toxins that deter predators, allowing them to move freely through the forest without constant threat.
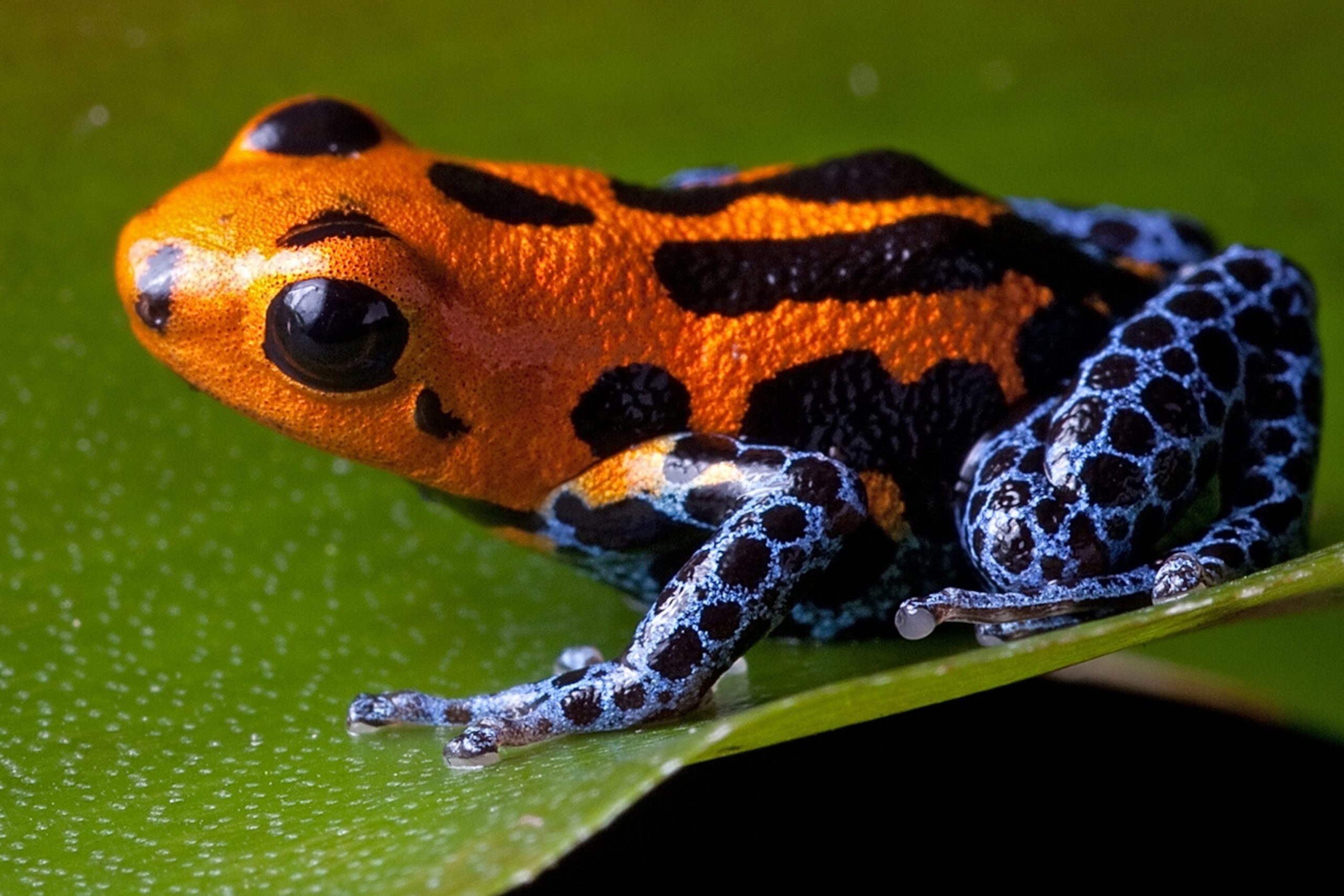

A brilliantly colored poison dart frog perched on a leaf
High humidity levels in the rainforest can be both a blessing and a curse. While the moisture supports a wide variety of plant life, it also poses a risk of fungal infections for small animals. To combat this, many creatures have developed specialized skin or fur that repels water and prevents disease. For instance, the coati, a small mammal related to raccoons, has a sleek coat that sheds water efficiently, allowing it to move through the wet underbrush with ease.
In addition to physical adaptations, many small animals have developed behavioral strategies to navigate the rainforest. Arboreal animals, like certain species of monkeys and lizards, have evolved prehensile tails and strong limbs to swing from branch to branch, avoiding the dangers on the forest floor. This not only helps them find food but also escape predators lurking below.
Unique Feeding and Reproductive Strategies
The abundance of life in tropical rainforests offers a buffet of food options, yet it also demands unique feeding strategies from small animals. Many species have specialized diets that allow them to exploit specific niches, minimizing competition for resources. The leafcutter ant, for example, harvests leaves not for direct consumption, but to cultivate fungus gardens, which serve as their primary food source. This symbiotic relationship is a testament to the ingenuity of small animals in utilizing available resources.

Leafcutter ants diligently transporting leaves for their fungus gardens
Reproductive strategies in the rainforest are equally fascinating. The sheer density of life means that finding a mate can be both challenging and competitive. Many small animals have developed unique courtship rituals or rely on environmental cues to ensure successful reproduction. The glass frog, for instance, lays its eggs on leaves overhanging streams. Once the eggs hatch, the tadpoles drop into the water below, a strategy that helps protect the young from terrestrial predators.
Additionally, some small animals exhibit brood parasitism, where one species lays its eggs in the nest of another, leaving the host to care for the offspring. This strategy is seen in certain birds and insects and highlights the diverse approaches to survival in the rainforest.
The adaptability of small animals in the tropical rainforest showcases the incredible diversity of life on our planet. Their ability to navigate and thrive in such a challenging environment is a testament to nature’s resilience and ingenuity. As we explore these adaptations, it becomes clear that small animals play a crucial role in maintaining the delicate balance of the rainforest ecosystem.
High-Altitude Adaptations
Physiological Adjustments to Low Oxygen Levels
High-altitude environments present unique challenges to small animals. One of the most significant is the low oxygen levels, which require remarkable physiological adaptations for survival. At higher elevations, the air is thinner, meaning there is less oxygen available for respiration. Small animals, despite their size, have developed ingenious ways to cope with these conditions.
Many small animals living in high-altitude areas have evolved enhanced respiratory systems. For instance, species like the Andean mouse have larger lungs relative to their body size. This adaptation allows them to take in more air with each breath, maximizing the oxygen they can extract. Additionally, some species exhibit a higher concentration of hemoglobin in their blood. Hemoglobin is the protein responsible for transporting oxygen, and having more of it means these animals can carry more oxygen to their tissues, even when it’s scarce in the environment.
Moreover, small animals at high altitudes often have an increased number of red blood cells. This adaptation is crucial because it allows for more efficient oxygen transport throughout the body. Interestingly, some species can even adjust the number of red blood cells they produce depending on the altitude they are currently inhabiting, showcasing a remarkable level of physiological flexibility.
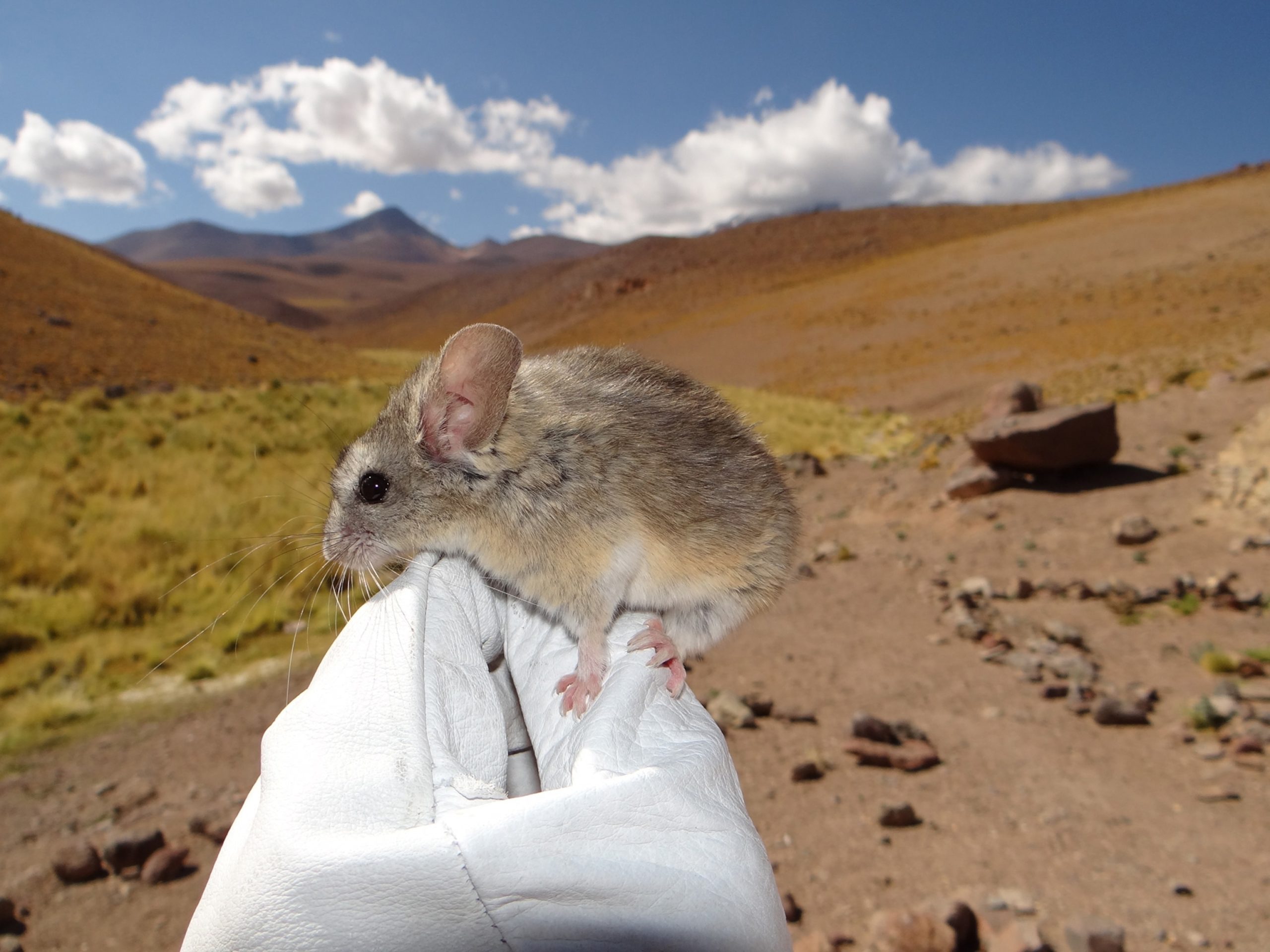

The Andean mouse adapted to high altitudes
Another fascinating adaptation seen in small animals like the pika is the ability to slow down their metabolism. By reducing their metabolic rate, these animals require less oxygen for basic bodily functions, which is vital in an environment where every breath counts. This metabolic flexibility not only helps in oxygen conservation but also in energy conservation, allowing them to survive in environments where food might also be scarce.
Coping with Temperature Extremes
High-altitude regions are notorious for their temperature extremes. These areas can be blisteringly hot during the day and freezing cold at night. Small animals living in such environments have developed a variety of strategies to cope with these drastic changes.
One common adaptation is the development of thick fur or feathers to provide insulation against the cold. For instance, the Himalayan marmot has a dense coat that helps retain body heat during frigid nights. This fur is often layered, with a soft undercoat to trap heat close to the body and a coarser outer layer to protect against wind and moisture.
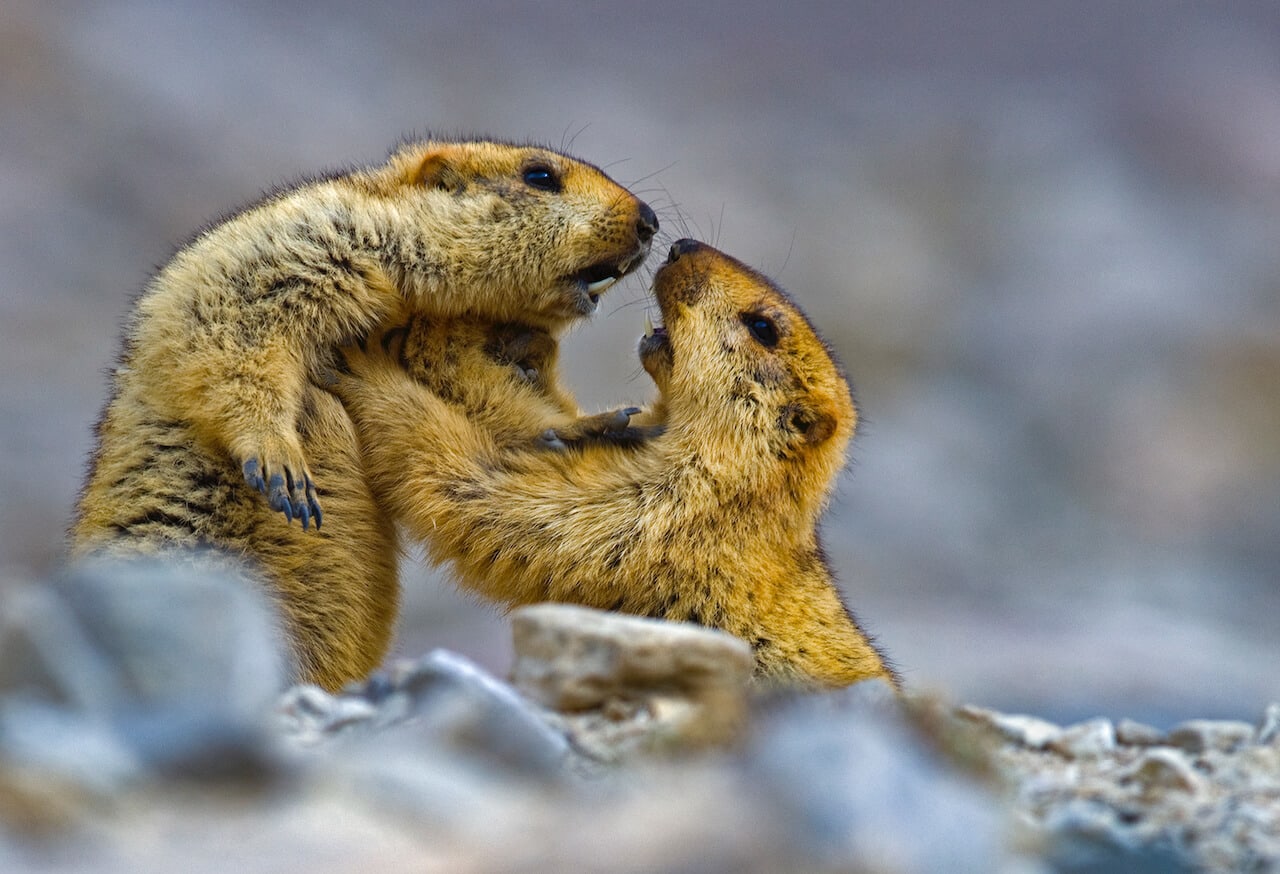

The Himalayan marmot equipped with thick fur for insulation
In addition to physical adaptations, behavioral strategies are also crucial for survival. Many small animals in high-altitude environments are crepuscular, meaning they are most active during the cooler parts of the day—dawn and dusk. This behavior helps them avoid the extremes of midday heat and nighttime cold. Some species, like certain ground squirrels, engage in hibernation or torpor during the coldest months, significantly reducing their energy requirements and allowing them to survive on limited resources.
Small animals also utilize their environment cleverly to manage temperature extremes. Burrowing into the ground or seeking shelter in rocky crevices can provide a more stable microclimate, offering protection from both the heat and the cold. These natural shelters can maintain a relatively constant temperature compared to the outside environment, which is critical for the survival of small animals in such demanding climates.
In summary, the high-altitude adaptations of small animals are a testament to their resilience and ingenuity. Through a combination of physiological changes and behavioral strategies, these creatures have successfully carved out a niche in some of the planet’s most challenging environments. Their ability to adapt and thrive under such conditions not only highlights the incredible diversity of life but also underscores the importance of conserving these unique ecosystems and the small animals that inhabit them.
Celebrating Nature’s Resilience
Nature’s resilience is a testament to the incredible diversity and adaptability of life on Earth. Small animals, in particular, demonstrate a remarkable ability to survive and thrive in some of the harshest environments, offering valuable insights into the importance of biodiversity and conservation.
The Importance of Biodiversity and Conservation
Biodiversity is the variety of life found on our planet, encompassing the different species, genetic variations, and ecosystems that make up the natural world. The role of small animals in maintaining biodiversity is crucial. These creatures, often unnoticed, play significant roles in ecosystems, contributing to nutrient cycling, pollination, and the food web. For instance, bees, which are small but mighty, are essential pollinators for many crops and wild plants.
Conserving biodiversity is not just about preserving individual species but maintaining the complex web of life that supports human well-being. Small animals are key players in this web. Frogs, for example, help control insect populations, while earthworms enhance soil fertility. The loss of such species could lead to cascading effects that disrupt ecosystems and ultimately affect human societies.
Conservation efforts aim to protect these intricate relationships. By safeguarding habitats and implementing sustainable practices, we ensure that small animals continue to fulfill their ecological roles. Initiatives like creating wildlife corridors, reducing pesticide usage, and supporting conservation organizations are vital steps in preserving biodiversity.

Small animals thriving in their natural habitats
What We Can Learn from Small Animals
Small animals offer profound lessons in adaptability and resilience. Despite their size, they have evolved numerous strategies to overcome environmental challenges. For example, the Arctic fox’s white fur provides camouflage in the snow, while its thick coat offers insulation against freezing temperatures. Similarly, desert-dwelling creatures like the fennec fox have large ears that dissipate heat and help them stay cool.
These adaptations highlight the importance of flexibility and innovation in the face of adversity. In our rapidly changing world, where climate change and habitat destruction pose significant threats, the ability to adapt is more crucial than ever. Observing how small animals navigate their environments can inspire human innovation in fields like technology and engineering, where biomimicry—drawing inspiration from nature’s solutions—is gaining traction.
Moreover, small animals teach us about the value of resourcefulness. Many species have developed efficient ways to utilize limited resources. For instance, certain desert rodents can extract water from seeds, demonstrating how to survive with minimal inputs. This kind of efficiency could inform sustainable practices in agriculture and resource management.
In celebrating the resilience of small animals, we also recognize the interconnectedness of all life. Their survival strategies remind us of the delicate balance that sustains ecosystems and the need for concerted efforts to maintain that balance. By valuing and protecting small animals, we contribute to a healthier, more resilient planet.

Small animals adapting to diverse environments
By exploring the world of small animals, we can develop a deeper appreciation for the natural world and our place within it. Their stories of survival and adaptation serve as a powerful reminder of nature’s ingenuity and the urgent need to preserve it for future generations.
WildWhiskers is a dedicated news platform for animal lovers around the world. From heartwarming stories about pets to the wild journeys of animals in nature, we bring you fun, thoughtful, and adorable content every day. With the slogan “Tiny Tails, Big Stories!”, WildWhiskers is more than just a news site — it’s a community for animal enthusiasts, a place to discover, learn, and share your love for the animal kingdom. Join WildWhiskers and open your heart to the small but magical lives of animals around us!