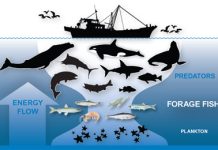
In the vast tapestry of life on Earth, animals are not just inhabitants; they are essential threads that weave the intricate fabric of our ecosystems. When we talk about animals definition in a biological context, we refer to multicellular, eukaryotic organisms that share certain key characteristics, such as the need for food from other living beings, the ability to move, and a complex responsiveness to their environment. But these creatures are far more than just definitions in a textbook. They are dynamic players in the grand ecological theater, each performing roles that are crucial for the survival and health of their habitats.
Consider the ecosystems, those vibrant communities where living organisms interact with their physical environment in a delicate dance of balance and dependency. Animals are pivotal in these systems, acting as consumers, pollinators, decomposers, and more. From the majestic elephant that roams the savannahs to the tiny bee buzzing from flower to flower, their actions have profound implications on ecological dynamics. Imagine the world without the rhythmic song of birds or the silent, industrious work of earthworms; the balance would be disrupted, cascading into unforeseen consequences for all life forms.
This blog delves into the interdependence between animals and other elements of ecosystems, exploring everything from their symbiotic relationships to the devastating impacts of extinction. As humans, our actions significantly influence these natural networks, often with detrimental effects. Yet, there is hope through conservation efforts, which remind us of our responsibility to protect these invaluable creatures.
Join us as we embark on this exploration, gaining insights into the indispensable roles animals play in ecosystems. Understanding the animals definition not only enriches our knowledge but also deepens our connection to the natural world, urging us to cherish and safeguard it for future generations.
Introduction to Animals and Ecosystems
Defining Animals in the Biological Context
In the vast tapestry of life on Earth, animals hold a pivotal role, serving as essential threads that weave the intricate web of ecosystems. But what precisely defines these remarkable creatures? Scientifically, animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms that belong to the biological kingdom Animalia. Unlike plants, animals are heterotrophic, meaning they rely on other organisms for sustenance. This reliance forms the foundation of numerous food chains and intricate ecological interactions.
Animals are characterized by their ability to move voluntarily, a trait that sets them apart from most other life forms. This motility allows them to hunt, forage, escape predators, and explore their environments, driving the dynamic balance within ecosystems. Additionally, animals possess specialized tissues and organs, such as muscles and nerves, which facilitate complex behaviors and responses to their surroundings.
Moreover, animals reproduce primarily through sexual means, contributing to genetic diversity and the adaptability of populations. However, some species also exhibit asexual reproduction, showcasing the incredible versatility within the animal kingdom. Animals are generally divided into two main groups: invertebrates, which lack a backbone, and vertebrates, which possess one. This classification underscores the diversity of forms and functions that animals exhibit.
The animals definition extends beyond mere biological traits; it encompasses their roles as consumers, pollinators, decomposers, and more. Each animal species, from the tiniest ant to the largest whale, plays a unique and essential role in maintaining ecological equilibrium. Understanding what constitutes an animal in the biological context helps us appreciate the complexity and significance of these organisms in the natural world.
Overview of Ecosystems and Their Components
Ecosystems are dynamic systems comprising living organisms interacting with each other and their physical environment. They range from the smallest puddle to expansive forests, each hosting a unique assembly of life forms and environmental conditions. An ecosystem’s health and functionality are dependent on the intricate relationships between its biotic (living) and abiotic (non-living) components.
Biotic components include all living organisms within an ecosystem—plants, animals, fungi, and microorganisms. Each of these plays a role that is critical to the ecosystem’s overall health. For instance, plants, as primary producers, harness solar energy through photosynthesis to create organic materials that serve as food for other organisms. Animals, acting as consumers, drive the flow of energy and matter through the food web.
Abiotic components encompass the physical and chemical aspects of an ecosystem, such as sunlight, water, soil, temperature, and nutrients. These non-living elements provide the essential conditions and resources that support life. For example, water is crucial for cellular processes, while soil provides nutrients necessary for plant growth.
The interaction between biotic and abiotic components forms the foundation of ecosystems, fostering cycles of energy and matter that sustain life. Animals contribute to these cycles in multifaceted ways, from pollination and seed dispersal to decomposition and nutrient cycling. Their activities help maintain the structure and functionality of ecosystems.
Understanding ecosystems and their components allows us to grasp how interconnected and interdependent life is. Each organism, including humans, influences and is influenced by the ecosystem it inhabits. Recognizing the essential roles of animals within these systems is crucial for conservation efforts and the sustainable management of natural resources.
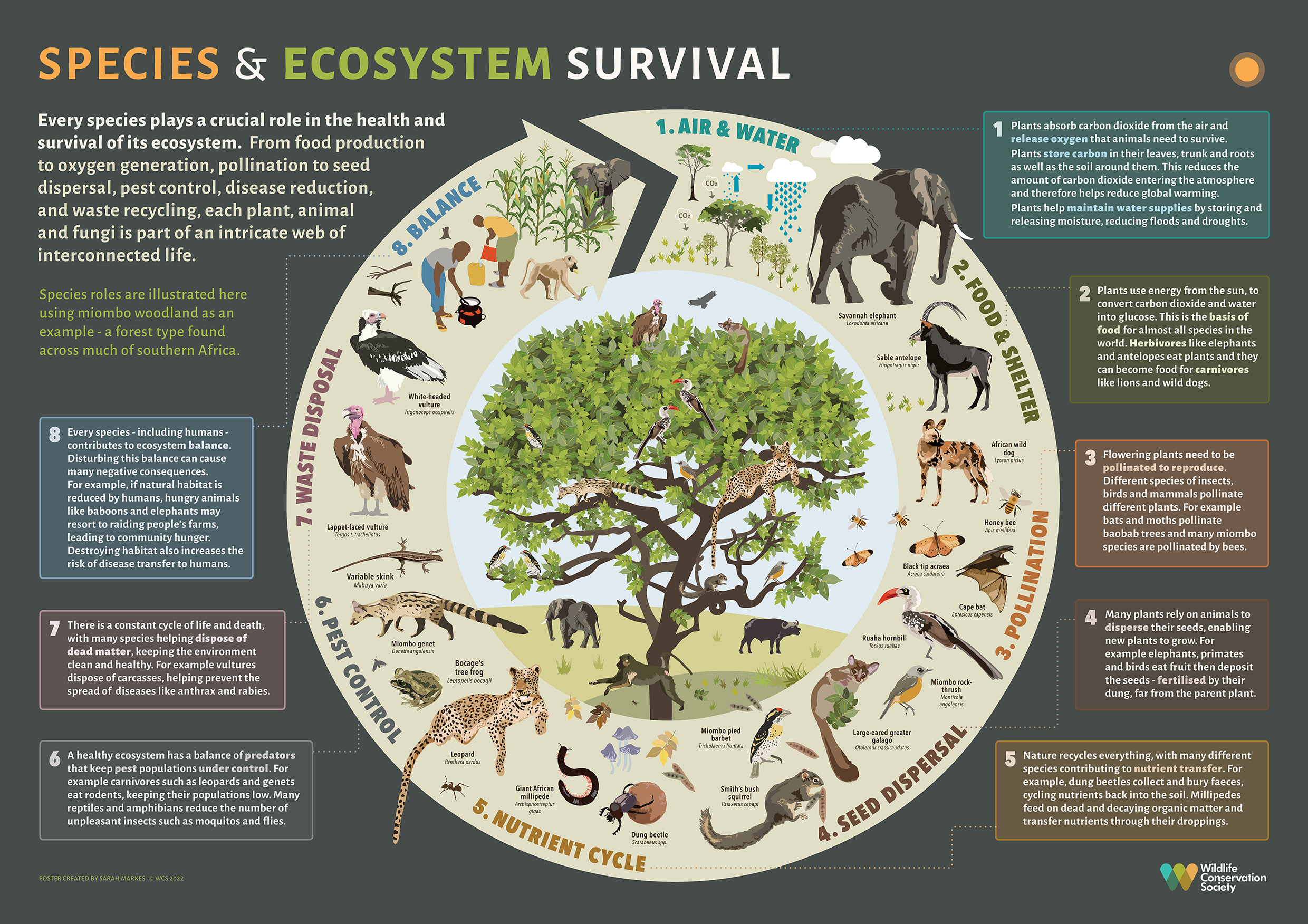
A vibrant ecosystem showcasing the diversity of life
By delving into the animals definition and the components of ecosystems, we can begin to appreciate the complexity and beauty of the natural world. This understanding is vital for fostering a harmonious relationship with our environment and ensuring the longevity of the planet’s diverse ecosystems.
The Role of Animals in Ecosystems
Animals play an essential role in ecosystems, acting as dynamic participants in a variety of processes that sustain ecological balance. Understanding the different functions they serve provides a clearer perspective on how interconnected life on Earth truly is. In this section, we’ll explore the roles of animals as consumers, pollinators, seed dispersers, and contributors to decomposition and nutrient cycling.
Animals as Consumers: Herbivores, Carnivores, and Omnivores
Animals are primarily distinguished by their roles as consumers within the ecosystem. They are categorized into three main types based on their dietary habits: herbivores, carnivores, and omnivores. Each group plays a unique part in maintaining the flow of energy through the food chain.
Herbivores are animals that consume plants as their primary food source. They play a crucial role in controlling plant populations and facilitating the transfer of energy from the sun (captured via photosynthesis in plants) to higher trophic levels. Common examples include deer, rabbits, and caterpillars. By feeding on plants, herbivores also help in shaping plant community structures and enhancing biodiversity.
Carnivores are predators that primarily eat other animals. They are vital in regulating prey populations and maintaining the health of ecosystems. By controlling the number of herbivores, carnivores ensure that plant life is not over-consumed, thus preserving habitats. Lions, wolves, and hawks are typical examples of carnivores. Their presence in an ecosystem often indicates a balanced food web, as they tend to be at the top of the food chain.
Omnivores consume both plants and animals, providing versatility in their ecological roles. They can adapt to various food sources, thus thriving in diverse environments. This adaptability helps in stabilizing ecosystems, especially when food availability fluctuates. Humans, bears, and crows exemplify omnivores. Their dietary flexibility allows them to fill multiple ecological niches, contributing to ecosystem resilience.
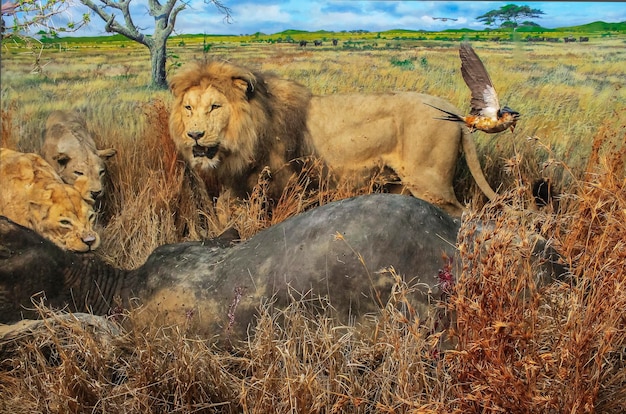

A lion showcasing its role as a top predator in the savannah ecosystem
Animals as Pollinators and Seed Dispersers
Animals also play a pivotal role in the reproduction of plants through pollination and seed dispersal. These processes are essential for plant diversity and ecosystem health.
Pollinators, such as bees, butterflies, and certain birds, facilitate the transfer of pollen from one flower to another, enabling fertilization and the production of seeds. This process is crucial for the reproduction of many plant species, including those that form the basis of human agriculture. The decline of pollinator populations is a significant concern, as it directly affects food security and ecosystem stability.
Seed dispersers include a variety of animals, such as birds, mammals, and even insects, that transport seeds away from the parent plant. This dispersal helps in reducing competition among seedlings and promotes genetic diversity. Animals like squirrels, who bury nuts, or birds that eat fruit and excrete seeds elsewhere, contribute to the spread of plants across different areas, fostering ecosystem diversity.
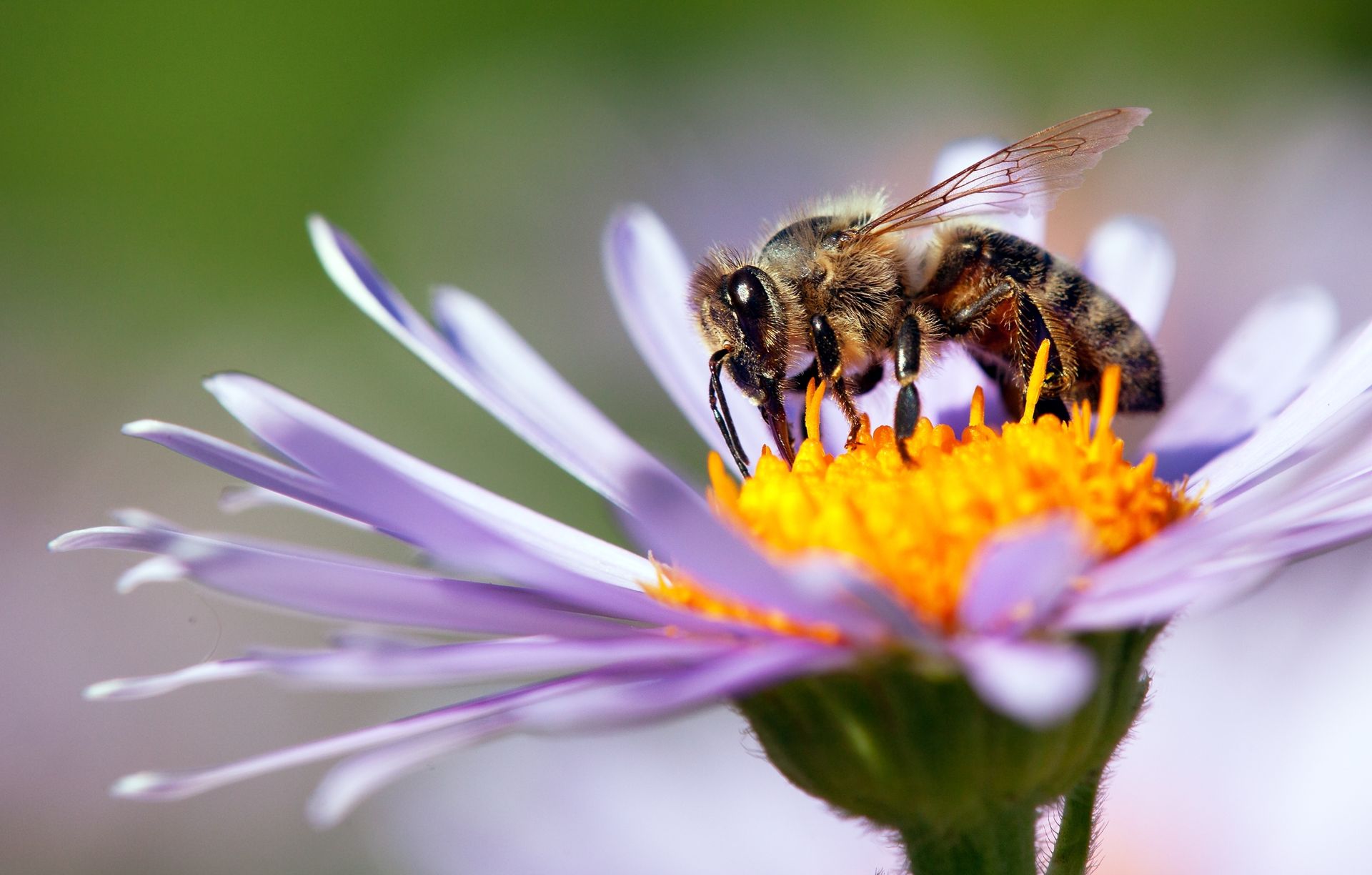

A bee engaging in pollination a crucial ecological process
Animals in Decomposition and Nutrient Cycling
Decomposition is a vital ecosystem process, and animals play a crucial role in breaking down organic matter. This process is essential for nutrient cycling, which replenishes the soil and supports plant growth.
Decomposers such as insects, fungi, and some mammals, break down dead organic matter, returning essential nutrients to the soil. This process is critical for the sustainability of ecosystems, as it ensures the continuous availability of nutrients necessary for plant growth. For example, earthworms and dung beetles process organic material, improving soil structure and fertility.
Scavengers, including vultures and hyenas, consume dead animals, preventing the accumulation of carrion and promoting a cleaner environment. Their activities help in the recycling of nutrients and support the overall health of the ecosystem.
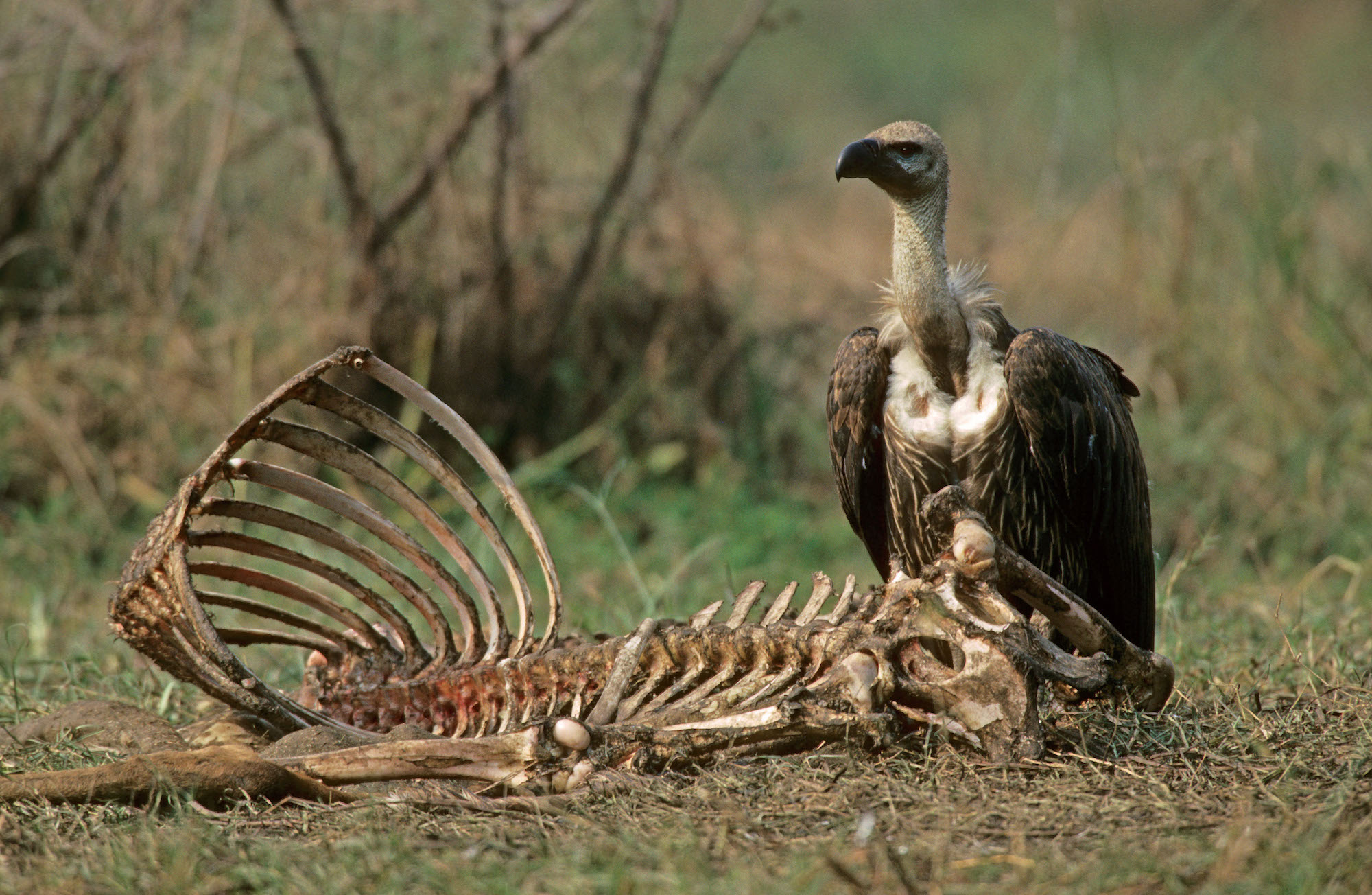

A vulture contributing to nutrient cycling by feeding on carrion
In conclusion, animals are indispensable components of ecosystems, serving multiple roles that contribute to ecological balance and health. Their activities as consumers, pollinators, seed dispersers, and decomposers illustrate the complexity and interdependence of life on Earth. Understanding the animals definition in this context underscores their importance and the need to preserve biodiversity for the planet’s overall well-being.
The Interdependence of Animals and Other Ecosystem Elements
In the grand tapestry of life on Earth, animals do not exist in isolation. They are intricately woven into the fabric of ecosystems, interacting with myriad elements and playing pivotal roles that maintain ecological balance. This interdependence is a testament to their significance in sustaining life and biodiversity.
Symbiotic Relationships: Mutualism, Commensalism, and Parasitism
Symbiosis is a fascinating concept in ecology where different species live together in close association, often for mutual benefit. Understanding these relationships is crucial when discussing the animals definition within ecosystems.
Mutualism is a win-win situation. Both parties benefit from the relationship, like bees and flowers. Bees collect nectar for food, and in the process, they pollinate flowers, aiding in their reproduction. This mutualistic interaction is essential for the survival of many plant species and the animals that depend on them for food.
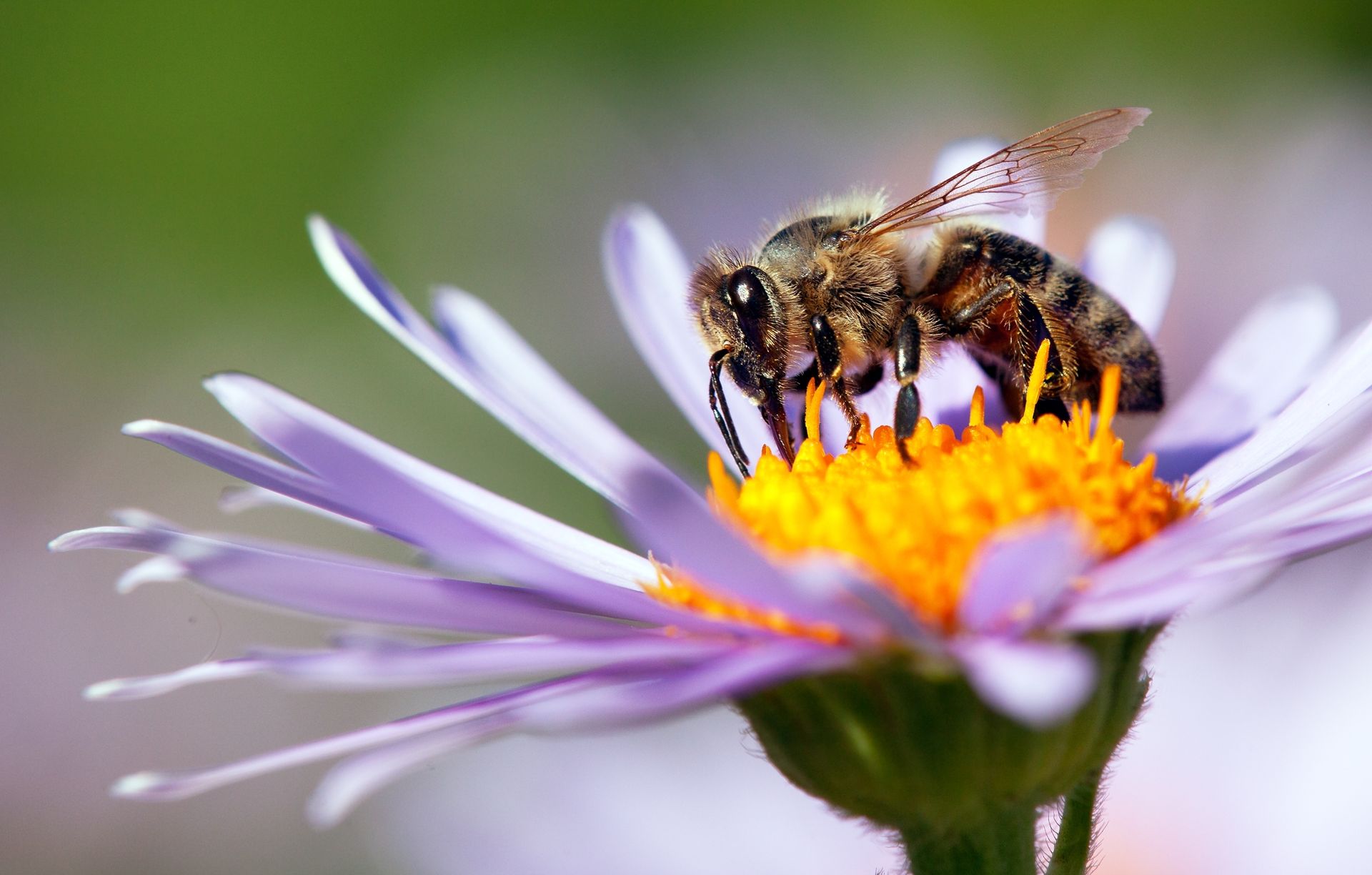

A bee pollinating a flower showcasing mutualism in nature
In commensalism, one species benefits while the other is neither helped nor harmed. An example is barnacles attaching to the shell of a turtle. The barnacles gain mobility to access food, while the turtle remains unaffected. This relationship demonstrates how some animals find innovative ways to survive and thrive without harming their hosts.
Parasitism presents a different dynamic, where one organism benefits at the expense of another. Parasites like ticks and fleas feed on their hosts, often causing harm. While seemingly detrimental, parasitism plays a role in controlling population sizes and maintaining ecosystem health by preventing any one species from dominating.
The Impact of Animal Extinction on Ecosystem Balance
The extinction of animal species can have catastrophic effects on ecosystem balance. Animals serve as vital cogs in the ecological machinery, and their loss can lead to a domino effect, disrupting food webs and ecological processes.
Consider the case of apex predators, such as wolves. Their extinction in certain regions has led to overpopulation of prey species, like deer, which in turn overgraze vegetation. This overgrazing can lead to habitat degradation, affecting other species and leading to further imbalances. Such occurrences underscore the importance of each species and its role within the ecosystem.
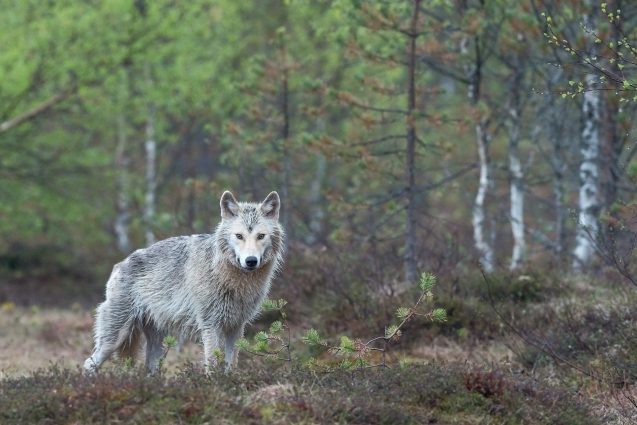

A wolf in its natural habitat highlighting the role of apex predators
Moreover, the extinction of pollinators like bees could severely impact plant reproduction, leading to reduced plant diversity and availability of food for herbivores. This chain reaction can affect entire ecosystems, demonstrating the interconnectedness of life forms.
Efforts to conserve animal populations and prevent extinction are not just about saving individual species but about preserving the intricate web of life that sustains ecosystems. Understanding the animals definition and their roles helps us appreciate the delicate balance of nature and the urgent need for conservation.
By exploring these symbiotic relationships and the consequences of animal extinction, we gain a deeper insight into the critical role animals play in maintaining the health and stability of ecosystems worldwide.
Human Influence on Animal Populations and Ecosystems
Habitat Destruction and Its Effects on Animals
The rapid expansion of human activities has led to significant habitat destruction, posing a severe threat to animal populations worldwide. Urban development, agriculture, logging, and mining are major contributors to the degradation and fragmentation of natural habitats. When forests are cleared, wetlands drained, or grasslands converted to farms, the intricate balance of ecosystems is disturbed, often leading to catastrophic consequences for the animals that inhabit them.
Deforestation, for instance, has a profound impact on biodiversity. Tropical rainforests, which cover only about 7% of the Earth’s surface, are home to more than half of the world’s species. The loss of these forests not only reduces the number of available habitats but also disrupts the complex web of interactions among species. For example, the orangutans of Borneo and Sumatra are critically endangered due to the extensive logging and palm oil plantations that have decimated their natural habitat.

Deforestation leading to habitat loss for countless species
Similarly, the draining of wetlands for agriculture or urban development has led to the decline of many amphibian and bird species. Wetlands serve as breeding grounds and provide essential resources for these animals. As these areas disappear, so do the species that rely on them for survival.
The effects of habitat destruction on animals are not limited to loss of home and resources. Fragmented habitats can lead to genetic isolation, where animal populations become too small and separated to maintain healthy genetic diversity. This can increase the vulnerability of species to disease and reduce their ability to adapt to environmental changes.
Moreover, animals forced into smaller habitats often face increased competition for dwindling resources, leading to heightened stress and reduced reproductive success. Predators may also find it harder to hunt, while prey species become more susceptible to becoming easy targets due to limited refuge options.
Conservation Efforts and Their Importance
In response to the escalating threat of habitat destruction, conservation efforts have become a vital tool in preserving animal populations and the ecosystems they inhabit. These efforts range from establishing protected areas and wildlife reserves to implementing species-specific recovery plans and legislative measures aimed at curbing human impact on natural habitats.
Protected areas, such as national parks and reserves, play a crucial role in conserving biodiversity. By safeguarding large swaths of habitat, these areas provide a refuge for countless species, allowing them to thrive without the constant pressure of human encroachment. Conservationists often emphasize the importance of creating corridors between fragmented habitats to enable the movement of species and maintain genetic diversity.

A protected wildlife conservation area promoting biodiversity
Conservation organizations also work tirelessly to restore degraded habitats. Reforestation projects, for instance, aim to replant native trees and rebuild ecosystems that have been lost to deforestation. Such initiatives not only benefit animals but also help combat climate change by increasing carbon sequestration.
In addition to habitat protection and restoration, conservation efforts often involve community engagement and education. By raising awareness of the importance of biodiversity and the role of animals in ecosystems, conservationists hope to foster a sense of stewardship among local communities. Empowering people to become active participants in conservation can lead to more sustainable land-use practices and a reduction in activities that harm ecosystems.
Moreover, many countries have enacted laws and regulations to protect endangered species and their habitats. International agreements, such as the Convention on Biological Diversity, further emphasize the global commitment to preserving the Earth’s natural heritage.
In conclusion, while human activities have undeniably impacted animal populations and ecosystems, ongoing conservation efforts offer a glimmer of hope. By understanding the animals definition and their crucial role in maintaining ecological balance, we can better appreciate the importance of conserving both species and habitats. These efforts are essential not only for the survival of countless species but for the health and sustainability of our planet as a whole.
Conclusion: The Essential Role of Animals in Sustaining Ecosystems
The intricate tapestry of life on Earth is woven with countless threads, many of which are spun by the diverse array of animals that inhabit our planet. Each species, no matter how small or seemingly insignificant, plays a crucial role in maintaining the balance and health of ecosystems. This animals definition encompasses their roles as consumers, pollinators, decomposers, and participants in complex symbiotic relationships. Through these roles, animals are indispensable to the functioning and sustainability of ecosystems.
One of the primary contributions of animals to ecosystems is their role as consumers. Herbivores, carnivores, and omnivores all participate in the food web, transferring energy from one level to another. This energy transfer is vital for the survival of other organisms. For example, herbivores consume plants, which are primary producers, and in turn, are prey for carnivores and omnivores. This chain ensures the flow of energy and nutrients, supporting a diverse array of life forms.
Moreover, animals serve as pollinators and seed dispersers, facilitating plant reproduction and the spread of various species across landscapes. Bees, butterflies, birds, and bats are just a few examples of pollinators that enable plants to reproduce and bear fruit. Without these animals, many plants would struggle to survive, leading to a decline in plant biodiversity and the collapse of ecosystems that rely on these plants for food and shelter.
In the cycle of life and death, animals also play a critical role in decomposition and nutrient cycling. Scavengers and decomposers, such as vultures, insects, and microorganisms, break down dead organic material, returning essential nutrients to the soil. This process enriches the soil, promoting plant growth and sustaining the primary producers in the ecosystem.
The interdependence of animals with other ecosystem elements often manifests in symbiotic relationships. Mutualism, commensalism, and parasitism illustrate the complex interactions that sustain ecosystems. For instance, the mutualistic relationship between bees and flowers benefits both parties, as bees obtain nectar while pollinating the plants. These interactions highlight the interconnectedness of life and the delicate balance that sustains biodiversity.
However, when species face extinction due to natural or anthropogenic causes, the impact on ecosystem balance can be profound. The loss of a single species can trigger a cascade of effects, destabilizing food webs and leading to further extinctions. This underscores the importance of conserving animal populations to maintain ecological equilibrium.
Human activities, such as habitat destruction, pollution, and climate change, have severely impacted animal populations and ecosystems. It is imperative to implement conservation efforts to protect these vital components of our natural world. Conservation not only preserves biodiversity but also ensures the continued provision of ecosystem services that humans rely on, such as clean air, water, and fertile soil.
In conclusion, the animals definition extends beyond mere classification and characteristics; it encompasses their pivotal roles in ecosystems. Animals are not just inhabitants of our planet; they are architects of the natural world, shaping and sustaining the environments we depend on. As stewards of the Earth, it is our responsibility to understand, appreciate, and protect these incredible creatures, ensuring that the intricate web of life they support remains vibrant for generations to come.

A diverse range of animals contribute to the vibrancy and balance of ecosystems
WildWhiskers is a dedicated news platform for animal lovers around the world. From heartwarming stories about pets to the wild journeys of animals in nature, we bring you fun, thoughtful, and adorable content every day. With the slogan “Tiny Tails, Big Stories!”, WildWhiskers is more than just a news site — it’s a community for animal enthusiasts, a place to discover, learn, and share your love for the animal kingdom. Join WildWhiskers and open your heart to the small but magical lives of animals around us!