Embarking on a journey into the heart of the wilderness, we find ourselves captivated by the myriad of wild animals that roam our planet. These fascinating creatures, from the majestic lions of the savannah to the stealthy snow leopards of the Himalayas, are not just the stars of wildlife documentaries but are vital cogs in the intricate machinery of our ecosystems. Understanding wild animals goes beyond mere fascination; it is about recognizing their roles and relationships within the natural world.
What exactly defines a wild animal? Unlike their domesticated counterparts, these creatures live independently of human intervention, thriving in natural habitats that range from dense forests to arid deserts and icy polar regions. This guide is your gateway to exploring the wondrous diversity of wild animals. We delve into various species, offering a comprehensive list that includes the name of wild animals, accompanied by vivid descriptions and captivating images—like a gallery showcasing 5 wild animals pictures—to bring these creatures to life.
Our exploration will take us through the rich tapestry of habitats where these animals dwell, examining their unique behaviors and adaptations. From the survival strategies that ensure their continuity to the complex social structures they form, each section reveals the intricacies of life in the wild. Furthermore, we address the pressing threats these animals face and the conservation efforts in place to protect them, emphasizing the critical role each of us plays in safeguarding their future.
As we embark on this enlightening journey, we invite you to not only learn about wild animals but to be inspired to act. Together, let’s celebrate the beauty and importance of these magnificent creatures and commit to preserving their rightful place in the world.
Introduction to Wild Animals
What Defines a Wild Animal?
Wild animals are an integral part of our planet’s biodiversity. But what exactly defines a wild animal? At its core, a wild animal is one that lives independently of humans in natural environments, such as forests, oceans, deserts, or savannahs. These creatures have not been domesticated or tamed and typically rely on their instincts and the ecological systems around them for survival. Wild animals can encompass a broad range of species, including mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and insects.
The distinction between wild and domestic animals is significant, as domesticated animals have been bred and raised under human control, often for specific purposes like companionship, labor, or food. In contrast, wild animals maintain their natural behaviors and survival strategies without direct human intervention. This independence is a defining characteristic of their existence and is crucial for maintaining the natural balance within ecosystems.
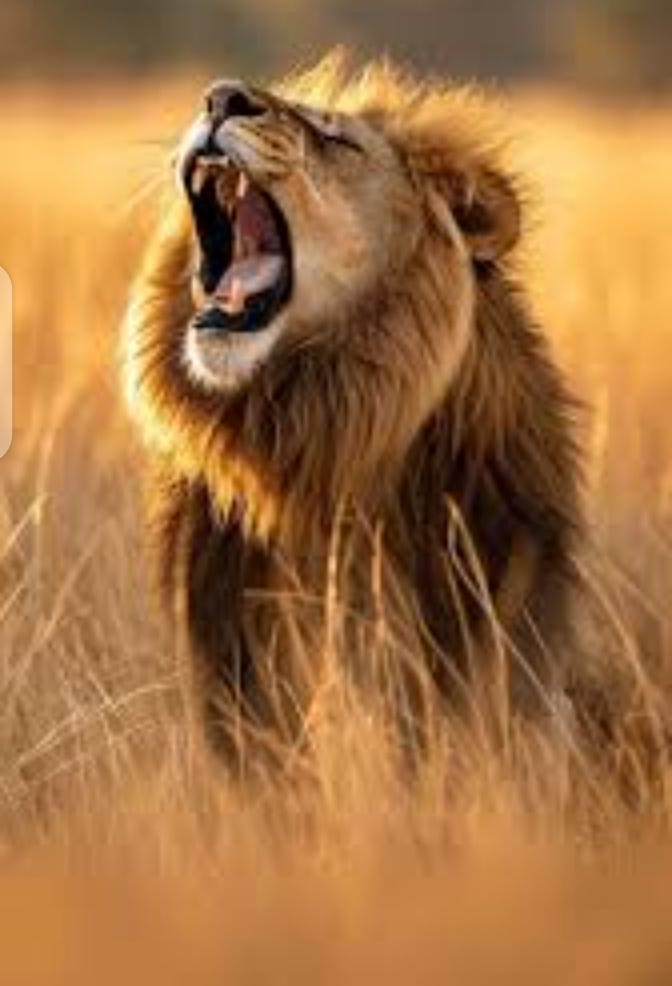

A majestic lion roaring in the savannah showcasing the wilds raw power
Importance of Studying Wild Animals
Studying wild animals is not just a scientific endeavor; it is a vital part of understanding the complex web of life on Earth. Wild animals play critical roles in ecosystems, contributing to ecological balance through predator-prey relationships, seed dispersal, and pollination. Understanding these roles helps us appreciate the interconnectedness of life and the importance of preserving it.
Moreover, research on wild animals provides insights into evolution, adaptation, and survival strategies. These studies can reveal how species have evolved over time to fit their ecological niches and can inform conservation efforts. For example, understanding migration patterns and breeding habits can lead to more effective wildlife protection measures.
Studying wild animals also brings attention to the threats they face, such as habitat destruction, climate change, and poaching. By highlighting these challenges, conservationists and policymakers can develop strategies to mitigate them, ensuring that future generations can enjoy a world rich in biodiversity.
Furthermore, wild animals inspire creativity and curiosity. They are subjects of art, literature, and folklore across cultures, symbolizing everything from strength and freedom to mystery and wisdom. By studying them, we not only gain a deeper understanding of the natural world but also enrich our cultural and intellectual heritage.
In conclusion, the importance of studying wild animals extends beyond mere observation; it is about fostering a deeper connection with the planet we call home. As we learn more about these incredible creatures, we also learn about our role in protecting them and ensuring that the natural world remains vibrant and diverse for generations to come.
Different Types of Wild Animals
In the vast and varied tapestry of life on Earth, wild animals represent the untamed, natural inhabitants of our planet. This section delves into the diverse types that make up the animal kingdom, exploring their unique characteristics and roles within the ecosystem. From mammals to insects, each group offers fascinating insights into the adaptability and complexity of life in the wild.
Mammals in the Wild
Mammals are a class of warm-blooded animals characterized by the presence of mammary glands, which females use to nourish their young. In the wild, mammals are incredibly diverse, ranging from the majestic elephants to the elusive snow leopards.
- Characteristics and Adaptations: Most mammals have body hair or fur, which provides insulation in various climates. They possess a high level of intelligence, with complex brain structures that allow for intricate social behaviors and problem-solving capabilities.
- Diverse Habitats: Mammals are found in nearly every habitat on Earth. For instance, the African elephant roams the savannahs, while the polar bear is adapted to the frigid Arctic ice. Each species is uniquely adapted to its environment, whether it’s through specialized hunting techniques or migratory patterns.
- Examples and Fun Facts: The blue whale, the largest animal on Earth, is a marine mammal that can weigh up to 200 tons. Meanwhile, the platypus is a fascinating monotreme, a subgroup of mammals that lay eggs instead of giving live birth.
Birds of the Wilderness
Birds are among the most visible and studied groups of wild animals, known for their ability to soar the skies and traverse vast distances.
- Physical Attributes: Birds are characterized by their feathered bodies, wings, and beaks. Their lightweight skeletal structure and powerful flight muscles enable many species to migrate across continents.
- Ecosystem Roles: Birds play critical roles in ecosystems as pollinators, seed dispersers, and predators of insects and small animals. The hummingbird, for example, is crucial for pollinating many plant species, while birds of prey help control rodent populations.
- Migration and Navigation: Many bird species undertake long migrations, guided by the sun, stars, and Earth’s magnetic field. The Arctic tern is known for its annual pole-to-pole journey, covering more than 44,000 miles.
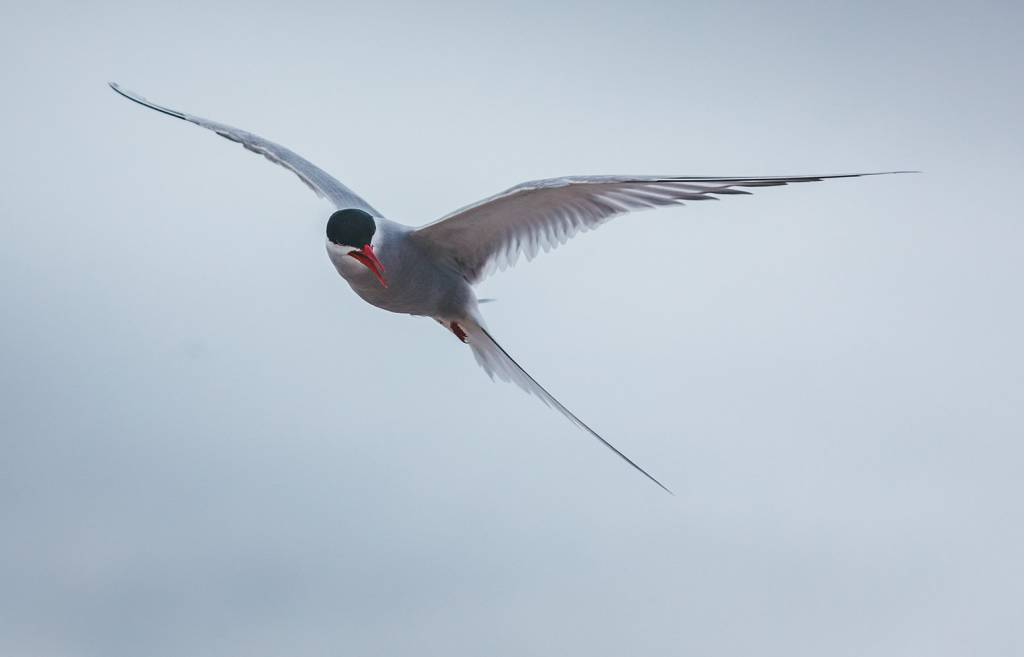

Arctic tern during its impressive migration
Reptiles and Amphibians in Nature
Reptiles and amphibians are often grouped together, yet they are distinct in many ways and inhabit a range of environments.
- Reptilian Traits: Reptiles, such as snakes, lizards, and turtles, are ectothermic, relying on external heat sources to regulate their body temperatures. They have scales or scutes and lay eggs, often on land.
- Amphibian Characteristics: Amphibians, including frogs, toads, and salamanders, typically have a dual life stage, living both in water and on land. They have moist skin that assists in respiration and often undergo metamorphosis from larval to adult stages.
- Conservation Concerns: Both groups face significant threats from habitat loss, climate change, and diseases such as the chytrid fungus affecting amphibians globally. Conservation efforts are crucial to protect these vital components of biodiversity.

A vibrant tree frog in its rainforest habitat
Insects and Their Role in the Ecosystem
Insects are the most numerous and diverse group of animals on the planet, playing indispensable roles in maintaining ecological balance.
- Diversity and Abundance: Insects include a wide variety of species such as beetles, butterflies, bees, and ants. Their sheer numbers and diversity allow them to inhabit almost every environment, from rainforests to deserts.
- Ecological Importance: Insects are vital for pollination, decomposition, and serving as a food source for numerous other animals. Bees, for example, are essential pollinators for many crops and wild plants, while dung beetles help recycle nutrients back into the soil.
- Challenges and Conservation: Insect populations are declining due to pesticide use, habitat destruction, and climate change. Protecting insect habitats and reducing chemical use are crucial steps in conserving these invaluable creatures.
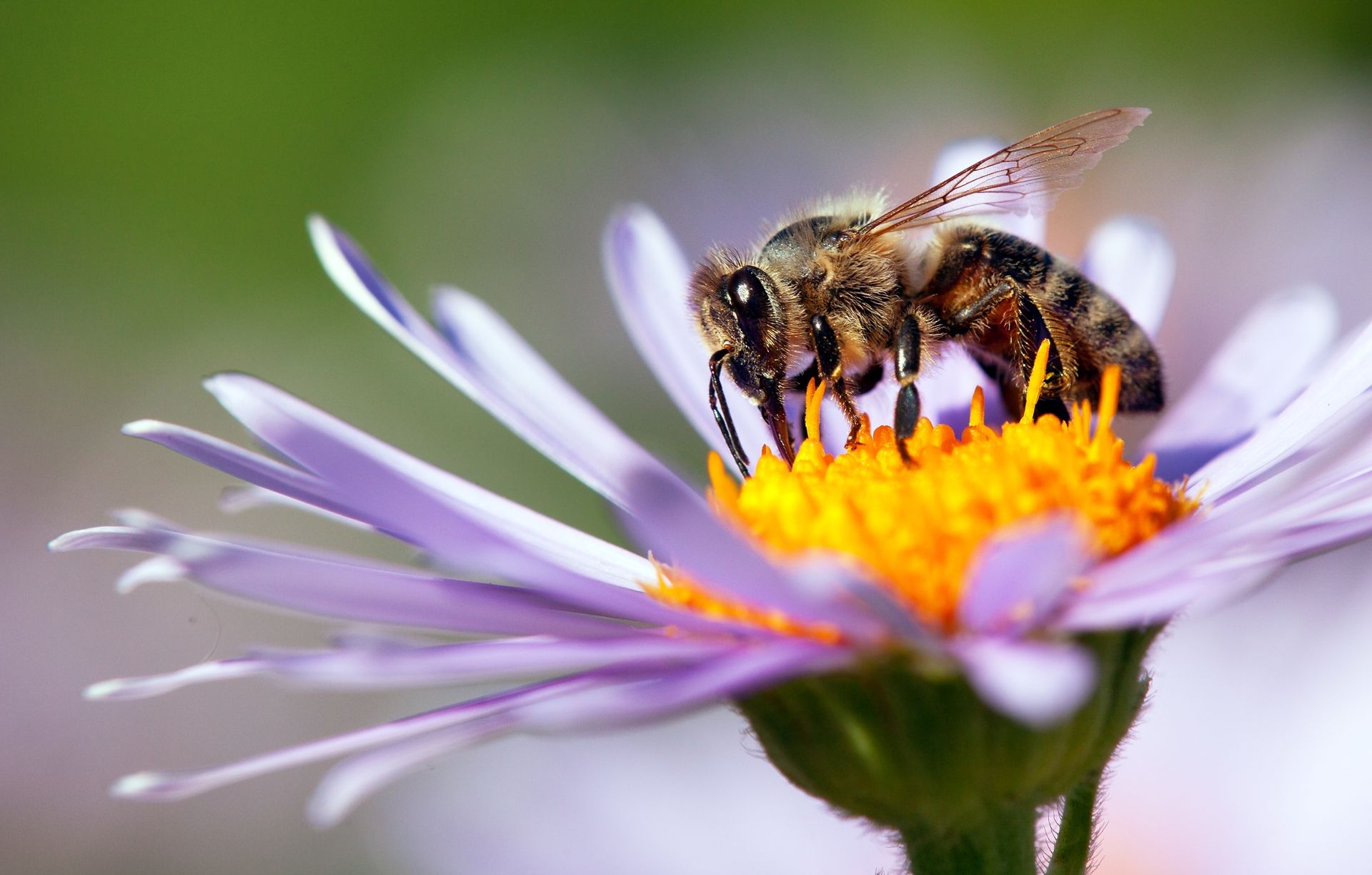

A honeybee fulfilling its role as a pollinator
In understanding the variety of wild animals, we gain insight into the intricate web of life that sustains our world. Each group, from the largest mammals to the smallest insects, contributes to the rich diversity of life on Earth, underscoring the importance of conserving these treasures for future generations.
Habitats of Wild Animals
Understanding the diverse habitats of wild animals is crucial for appreciating their adaptability and the ecological roles they play. Habitats not only define the living conditions of these animals but also influence their behavior, diet, and survival strategies.
Forests and Their Inhabitants
Forests are among the most biologically rich ecosystems on Earth, providing shelter and sustenance to a myriad of wild animals. These lush environments are divided into various types, including tropical rainforests, temperate forests, and boreal forests, each hosting unique wildlife.
Tropical Rainforests are known for their dense canopy and high biodiversity. They are home to some of the most fascinating species, such as jaguars, sloths, and a variety of primates like orangutans and gibbons. The lush vegetation offers abundant food sources and hiding spots, making it an ideal habitat for survival.

A majestic jaguar prowling through the tropical rainforest
In temperate forests, you can find animals like deer, foxes, and a range of bird species such as owls and woodpeckers. These forests experience distinct seasons, which influence the behavior and life cycles of the wildlife residing there.
Boreal forests, also known as taigas, are characterized by coniferous trees and are home to species adapted to colder climates. Animals like bears, wolves, and lynxes thrive in these environments, where they have evolved to withstand harsh winters.
Desert Wildlife
Deserts present one of the most challenging habitats for wild animals, with extreme temperatures and scarce water resources. Despite these harsh conditions, deserts are teeming with life, showcasing some of the most remarkable adaptations.
Animals like camels, fennec foxes, and various reptiles have evolved to survive with minimal water. Camels, often referred to as the “ships of the desert,” can travel long distances without hydration, storing fat in their humps that metabolizes into water.
Nocturnal species, such as the desert fox and various rodents, avoid the scorching sun by being active during cooler nights. These adaptations allow them to conserve energy and water, vital for survival in such arid conditions.
Marine and Aquatic Life
The oceans and freshwater bodies are some of the most expansive habitats on Earth, supporting a diverse array of wild animals. Marine environments, from coral reefs to the deep sea, are bustling with life. Species such as dolphins, whales, and a myriad of fish call these waters home.
Coral reefs, often dubbed the “rainforests of the sea,” are vibrant ecosystems teeming with biodiversity. They support numerous species, including sea turtles, sharks, and colorful fish, all of which contribute to the intricate food web.

A vibrant coral reef bustling with marine life
Freshwater habitats like rivers, lakes, and wetlands are vital for species such as otters, beavers, and numerous amphibians. These environments provide essential resources for breeding, feeding, and shelter.
Polar Regions and Arctic Animals
The polar regions, encompassing the Arctic and Antarctic, are characterized by extreme cold and icy landscapes. Despite these harsh conditions, they are home to some of the most iconic wild animals, showcasing extraordinary adaptations.
In the Arctic, animals like polar bears, arctic foxes, and walruses have adapted to the freezing temperatures. Polar bears, for instance, have thick fur and a layer of blubber to insulate against the cold, while their large paws are perfect for navigating ice and swimming in icy waters.
The Antarctic is primarily inhabited by marine wildlife such as penguins, seals, and krill, which form the base of the food chain. Penguins, with their streamlined bodies and insulating layers of fat, are perfectly suited to the icy waters where they forage for fish.
Each of these habitats plays a critical role in maintaining the ecological balance and supporting the biodiversity of wild animals. Understanding these environments helps us appreciate the complexity of nature and the adaptive prowess of wildlife. As we continue to explore and learn about these habitats, it is imperative to advocate for their conservation to ensure the survival of the myriad species that call them home.
Behavior and Adaptations
Understanding the behavior and adaptations of wild animals is crucial to appreciating their resilience and intricate survival mechanisms. These creatures have evolved over millions of years, developing unique strategies to thrive in diverse and often harsh environments. This section delves into the fascinating world of survival strategies, communication, social structures, and migration patterns that define the essence of wild animals.
Survival Strategies in the Wild
Wild animals exhibit a remarkable array of survival strategies that are essential for their continued existence in nature. These strategies can be broadly categorized into physical adaptations, behavioral tactics, and reproductive methods.
Physical Adaptations: Many wild animals have developed physical features that aid in their survival. For instance, the camouflage of a chameleon, which allows it to blend into its surroundings, is a classic example of an adaptation that helps avoid predators. Similarly, the thick fur of polar bears insulates them against the extreme cold of the Arctic.

Behavioral Tactics: Some animals rely on specific behaviors to survive. For example, meerkats in the Kalahari Desert have sentinels that watch for predators while the rest forage for food. This cooperative behavior increases their chances of survival. Additionally, nocturnal animals like owls and bats come out at night to hunt, avoiding competition with diurnal predators.
Reproductive Methods: High reproductive rates can be another survival strategy. Species like rabbits and rodents reproduce quickly, ensuring that at least some offspring survive predation and environmental challenges.
Animal Communication and Social Structures
Communication is pivotal in the social dynamics of many wild animals. It facilitates mating, hunting, and establishing social hierarchies.
Communication Methods: Animals communicate through vocalizations, body language, and chemical signals. For instance, wolves use howls to coordinate hunting and establish territory. Dolphins, on the other hand, use a complex system of clicks and whistles to communicate with their pod.

Social Structures: Social structures in wild animals can vary significantly. Some animals, like lions, live in prides with defined roles for each member, enhancing their hunting efficiency and protection. Elephants, known for their matriarchal social structure, rely on the leadership of the oldest female to guide their herd in search of food and water.
Non-verbal Communication: Body language is another critical aspect. For instance, the peacock’s display of its vibrant tail feathers is both a mating ritual and a deterrent to predators. Chemical signals, such as pheromones, are used by insects like ants to navigate and communicate within their colonies.
Migration Patterns and Reasons
Migration is a phenomenon observed in many species of wild animals, serving as a critical survival mechanism.
Why Animals Migrate: Migration usually occurs in response to seasonal changes, food availability, or breeding purposes. For example, wildebeests in Africa undertake a massive migration annually across the Serengeti in search of greener pastures and water. This migration is one of the most spectacular natural events in the world.

Types of Migration: There are different types of migration, including altitudinal migration seen in mountain species, where animals move to lower elevations during winter. Birds, such as the Arctic Tern, undertake long-distance migrations from the Arctic to the Antarctic, covering thousands of miles annually.
Challenges of Migration: Migration is fraught with challenges, including predation, extreme weather conditions, and human-induced obstacles like habitat destruction. Despite these challenges, migration remains a testament to the resilience and endurance of wild animals.
In conclusion, the behavior and adaptations of wild animals are a testament to their resilience and ability to thrive in a constantly changing world. Understanding these aspects not only enriches our knowledge but also underscores the importance of conserving these magnificent creatures and their habitats.
Conservation and Protection
Threats to Wild Animal Populations
Wild animals face numerous threats that have significantly impacted their populations worldwide. The challenges they encounter are complex and interwoven, making conservation efforts crucial for their survival.
One of the most pressing threats is habitat loss. As human populations expand, natural habitats are being destroyed to make way for agriculture, urban development, and infrastructure projects. This destruction not only reduces the available space for wild animals to live and thrive but also fragments their habitats, isolating populations and making it harder for them to find food, mates, and shelter.
Poaching and illegal wildlife trade are also major concerns. Many wild animals are hunted for their fur, bones, and other body parts, which are highly valued in black markets. This illegal trade has driven some species to the brink of extinction, as seen with the African elephant and the rhinoceros. The demand for exotic pets further exacerbates the problem, with animals being captured and sold globally, often resulting in high mortality rates during transportation.
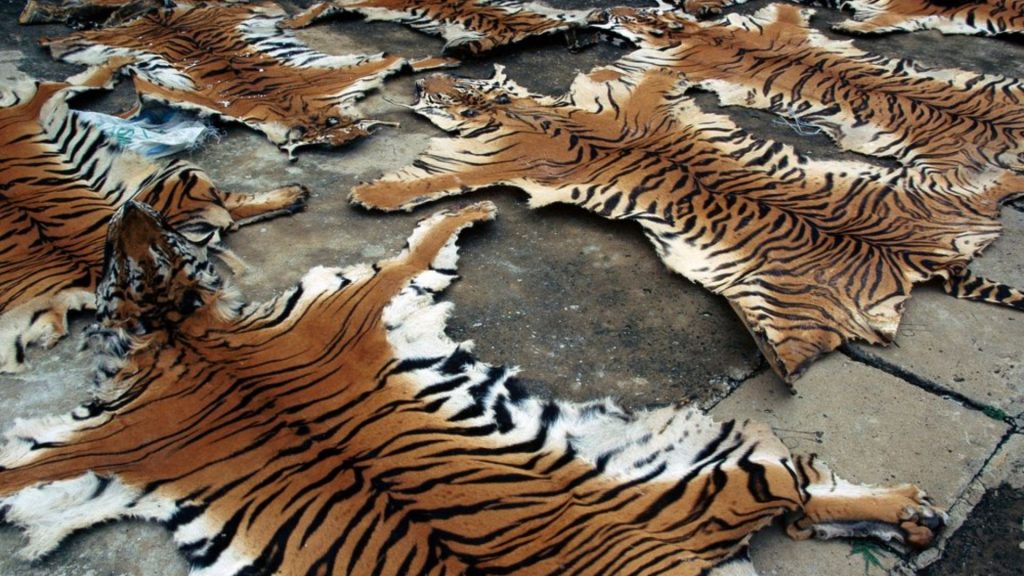

Poaching is a major threat to wild animal populations
Climate change is another significant threat, altering habitats and food availability. Rising temperatures, changing precipitation patterns, and more frequent extreme weather events affect the delicate balance of ecosystems. For instance, polar bears are losing their ice habitats due to melting Arctic ice, impacting their ability to hunt seals, their primary food source.
Human-wildlife conflict also poses a serious threat. As humans encroach on wild animal habitats, encounters become more frequent, leading to conflicts. These conflicts often result in the killing of wild animals to protect human lives and property, further reducing their populations.
Efforts in Wildlife Conservation
In response to these threats, numerous efforts have been made globally to conserve and protect wild animals. Conservation strategies focus on protecting habitats, enforcing laws, and raising awareness about the importance of biodiversity.
Protected areas, such as national parks and wildlife sanctuaries, are one of the most effective ways to conserve wild animals. These areas provide safe havens where animals can live without the threat of habitat destruction and poaching. Governments and non-governmental organizations (NGOs) work together to establish and manage these protected areas, ensuring they are adequately staffed and funded.
International agreements like the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES) aim to regulate and monitor the trade of wild animals and their products. By implementing strict regulations, CITES helps to ensure that international trade does not threaten the survival of wild animal populations.
Conservation organizations also employ community-based conservation approaches, involving local communities in conservation efforts. By providing education and alternative livelihoods, these initiatives help communities understand the value of protecting wild animals and reduce their reliance on activities that harm wildlife.
Technological advancements have also played a role in conservation, with satellite tracking and drones being used to monitor animal movements and detect poaching activities. This data-driven approach allows conservationists to make informed decisions and implement targeted strategies to protect endangered species.
How Individuals Can Help
Individuals play a crucial role in the conservation and protection of wild animals. By making conscious choices and supporting conservation efforts, each person can contribute to the preservation of biodiversity.
One of the simplest ways to help is by supporting conservation organizations through donations or volunteer work. These organizations often rely on public support to fund their initiatives and carry out their mission of protecting wild animals.
Raising awareness about the threats facing wild animals is another impactful action. By spreading information through social media, community events, or educational programs, individuals can encourage others to join the cause and make a collective impact.
Responsible consumer choices can also make a difference. By avoiding products made from endangered species and opting for sustainable, ethically sourced goods, consumers can reduce the demand for wildlife products. Additionally, supporting eco-friendly companies and initiatives helps promote practices that protect wild animals and their habitats.
Finally, individuals can advocate for stronger environmental policies by engaging in activism and advocacy efforts. Writing to local representatives, participating in campaigns, and voting for leaders committed to conservation can drive policy changes that protect wild animals and their environments.
By understanding the threats to wild animals and taking proactive steps, both collectively and individually, we can ensure a future where these magnificent creatures continue to thrive in their natural habitats. The responsibility lies with us to protect the wild animals and preserve the incredible biodiversity of our planet.
Conclusion: The Future of Wild Animals and Our Role in It
As we venture into the future, the fate of wild animals is intricately tied to our actions and choices. The rich tapestry of life on Earth is woven with the presence of these majestic creatures, each playing a pivotal role in maintaining ecological balance. Understanding the importance of wild animals is not just about appreciating their beauty or diversity but acknowledging their critical role in the ecosystem.
The Challenges Ahead
The 21st century presents numerous challenges for wild animals. From rampant deforestation to climate change, these factors are contributing to the decline of animal populations worldwide. Human activities such as poaching and habitat destruction are pushing many species to the brink of extinction. The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) has listed thousands of species as threatened, highlighting the urgent need for action.
Moreover, the expansion of urban areas encroaches on wildlife habitats, leading to increased human-wildlife conflicts. This not only endangers animals but also poses a threat to human safety. The delicate balance that sustains life on Earth is at risk, and the loss of wild animals would have profound consequences on biodiversity and ecosystem health.
Our Role in Conservation
In light of these challenges, it becomes imperative for us to play an active role in the conservation of wild animals. Governments, non-governmental organizations, and individuals must collaborate to create effective strategies that ensure the protection and preservation of wildlife.
- Protected Areas and Sanctuaries: Establishing and maintaining national parks and wildlife reserves is crucial. These protected areas serve as safe havens for endangered species, allowing them to thrive without the threat of human interference.
- Sustainable Practices: Adopting sustainable agricultural and industrial practices can reduce habitat destruction. By minimizing pollution and using resources responsibly, we can significantly reduce our ecological footprint.
- Education and Awareness: Educating the public about the importance of wild animals and the threats they face is vital. Awareness campaigns can inspire people to take action, whether by supporting conservation initiatives or altering their consumption habits.
- Legislation and Policy: Strong legal frameworks are necessary to combat illegal wildlife trade and ensure that conservation efforts are enforced. Governments must prioritize wildlife protection in their policies and allocate sufficient resources for enforcement.
How Individuals Can Help
Every individual has the power to make a difference. Simple actions such as reducing waste, choosing sustainable products, and supporting wildlife conservation organizations can have a significant impact. Volunteering for local conservation projects or participating in citizen science initiatives are great ways to contribute.
Additionally, educating oneself and others about wild animals and their habitats fosters a deeper connection and appreciation for the natural world. This understanding can empower communities to advocate for positive change and support efforts to preserve wildlife for future generations.
A Call to Action
As stewards of the planet, it is our responsibility to ensure that future generations inherit a world rich in biodiversity, where wild animals continue to roam free. Let us embrace our role in this global mission and take decisive action to protect the incredible diversity of life on Earth. The future of wild animals depends on us, and together, we can safeguard their existence.
By joining forces and committing to conservation, we can create a sustainable future where humans and wild animals coexist in harmony. Let’s protect our wild friends!
WildWhiskers is a dedicated news platform for animal lovers around the world. From heartwarming stories about pets to the wild journeys of animals in nature, we bring you fun, thoughtful, and adorable content every day. With the slogan “Tiny Tails, Big Stories!”, WildWhiskers is more than just a news site — it’s a community for animal enthusiasts, a place to discover, learn, and share your love for the animal kingdom. Join WildWhiskers and open your heart to the small but magical lives of animals around us!