In the mysterious cloak of night, when the world is often perceived as silent and asleep, an entirely different cast of characters comes to life. These are the nocturnal animals, creatures whose lives unfold under the moonlight, offering a fascinating glimpse into the wonders of nature that often go unnoticed. From the stealthy owl to the echolocating bat, these nighttime dwellers have adapted in remarkable ways, not only to survive but to thrive in environments where others would falter. But beyond their intriguing lifestyles, what benefits do these creatures bring to our world?
In this blog, we delve into the surprising benefits of nocturnal animals—those you might not have considered before. Imagine enhancing your night vision skills; these creatures have perfected the art, influencing advancements in human technology. Their role in maintaining biodiversity is crucial, acting as linchpins in the delicate balance of ecosystems and food chains. The unique communication methods of nocturnal animals, such as the silent flight of owls and the sonar-like echolocation of bats, reveal a world of interaction beyond human perception.
Moreover, by studying the sleep patterns and behaviors of these night-dwellers, we gain insights that could revolutionize our understanding of human health. Their influence extends into the cultural realm, inspiring art, literature, and film with their mystique and symbolism. As we explore these aspects, it becomes clear that embracing the wonders of the night offers more than just a peek into another world—it enriches our own in countless ways.
Join us on this nocturnal journey as we uncover the hidden benefits that these creatures bring, reshaping our understanding and appreciation of the night and the remarkable beings that call it home.
Enhanced Night Vision Skills
Nocturnal animals, creatures that thrive in the darkness, possess an extraordinary set of adaptations that allow them to navigate and hunt effectively in low-light environments. These adaptations are not only fascinating but also contribute significantly to their survival and efficiency as predators or prey. In this section, we delve into the remarkable characteristics that enhance the night vision skills of nocturnal animals and explore how these adaptations have influenced human technology.
Adaptations for Low Light Environments
The ability of nocturnal animals to see in the dark is nothing short of incredible. These creatures have evolved over millennia to develop specialized features that enable them to function optimally when the sun sets. One of the most crucial adaptations is their enhanced eyesight. Unlike diurnal animals, nocturnal species have retinas rich in rod cells, which are more sensitive to light and allow for better vision in dimly lit conditions. This adaptation is particularly evident in animals like owls, whose large eyes can capture even the faintest glimmers of light, providing them with a keen sense of sight at night.
Moreover, the tapetum lucidum, a reflective layer behind the retina, is another adaptation that significantly boosts night vision. This structure reflects light that passes through the retina back into the eyes, effectively giving nocturnal animals a second chance to detect any photons that might have been missed. This is why many nocturnal animals, such as cats and foxes, have eyes that seem to glow when caught in headlights or a flashlight beam.
In addition to their enhanced eyesight, many nocturnal animals rely on other senses to navigate the darkness. Bats, for instance, use echolocation, emitting high-frequency sounds that bounce off objects and return to the animal, helping them map their surroundings with pinpoint accuracy. This sophisticated form of bio-sonar allows bats to hunt efficiently, even in complete darkness, ensuring they can locate and capture their prey with ease.
Nocturnal animals’ adaptations for low-light environments are not only fascinating but also vital for their roles within ecosystems. By dominating the night, these animals maintain a balance in the food chain, ensuring that various species do not overlap in their resource consumption, thereby promoting biodiversity.

An owl demonstrating its glowing eyes due to the tapetum lucidum
Impact on Human Technology
The remarkable adaptations of nocturnal animals have not gone unnoticed by humans. In fact, they have significantly influenced the development of various technologies, particularly in the field of optics and sensory equipment. The study of nocturnal animals has inspired innovations that enhance human capabilities, especially in situations where visibility is limited.
One of the most direct influences is seen in the development of night vision technology. Scientists and engineers have studied the unique eye structures of nocturnal animals to create devices that amplify low light and allow humans to see in the dark. These technologies are widely used in military operations, search and rescue missions, and wildlife observation, providing humans with the ability to function effectively in environments where natural light is scarce.
Furthermore, the concept of echolocation has been adapted into sonar technology, which is extensively used in maritime navigation and exploration. By mimicking the way bats use sound waves to understand their surroundings, humans have developed sonar systems that can map ocean floors, detect submarines, and even assist in fishing by locating schools of fish.
In addition to these direct technological applications, the study of nocturnal animals continues to inspire further research in the fields of biology and robotics. For instance, scientists are exploring how the neural processing of sensory information in nocturnal animals can be applied to improve the design and function of autonomous vehicles and drones, enabling them to operate more efficiently in low-light conditions.
The profound impact of nocturnal animals on technology underscores the importance of understanding and preserving these creatures. As we unravel the mysteries of their adaptations, we not only gain insights into the wonders of nature but also find new ways to enhance our own capabilities, bridging the gap between the natural and technological worlds.

Modern night vision goggles inspired by the adaptations of nocturnal animals
In summary, the enhanced night vision skills of nocturnal animals are a testament to the wonders of evolution and adaptation. Their ability to thrive in low-light environments has not only ensured their survival but also provided humanity with a wealth of knowledge that continues to shape our technological advancements. As we explore the mysteries of the night, it becomes increasingly clear that these creatures hold the key to unlocking new frontiers in science and technology.
Contribution to Biodiversity
The role of nocturnal animals in biodiversity is a testament to the intricate and interconnected web of life that unfolds under the cover of darkness. These creatures, which include a variety of species such as bats, owls, and even certain primates like night monkeys, play a critical role in maintaining the delicate balance of ecosystems around the world. Their unique adaptations and behaviors allow them to occupy ecological niches that diurnal, or daytime, animals cannot, thus enhancing overall biodiversity.
Role in Ecosystem Balance
Nocturnal animals are vital to the ecosystem balance as they fulfill roles that are crucial for maintaining the health and stability of their environments. For instance, many nocturnal predators help control the populations of insects and small mammals, which could otherwise reach levels that might be detrimental to plant life and agricultural crops. Owls, for example, are efficient hunters of rodents. Their silent flight and keen hearing make them effective nighttime predators, ensuring that rodent populations do not spiral out of control.
Bats, another fascinating group of nocturnal animals, contribute significantly to ecosystems by acting as pollinators and seed dispersers. Certain bat species feed on nectar, transferring pollen from one flower to another, thereby aiding in plant reproduction. Others consume fruit and subsequently disperse seeds through their droppings, facilitating the growth of new plants in various areas. This natural process is indispensable for the health of many ecosystems, particularly in tropical regions where bats are primary pollinators for numerous plant species.

An owl demonstrating silent flight during a night hunt
Furthermore, the presence of nocturnal animals can indicate the health of an ecosystem. A diverse population of nocturnal species often suggests a robust environment that can support various life forms. Their interactions with other organisms—whether as predators, prey, or competitors—help to sustain the dynamic equilibrium that is essential for ecosystem resilience.
Importance in Food Chains
In terms of food chains, nocturnal animals often occupy key positions, acting as both predators and prey. This dual role is essential for the transfer of energy through an ecosystem. For example, small nocturnal mammals such as shrews and mice are prey for larger nocturnal predators like foxes and owls. This predation is crucial for controlling the populations of these small mammals, which, if left unchecked, could lead to overgrazing and depletion of vegetation.
Conversely, nocturnal animals like bats and certain nocturnal birds also serve as crucial predators, managing insect populations. Many bat species consume vast quantities of insects each night, which helps to control pest populations and reduce the spread of diseases that insects can carry. This insectivorous behavior is not only beneficial for the ecosystems they inhabit but also for human agriculture, as it reduces the need for chemical pesticides.

Bats helping control insect populations at night
The dynamics of these food chains are complex and highlight the importance of nocturnal animals in sustaining ecological processes. By participating in various trophic levels, they ensure that energy is cycled efficiently and that ecosystems remain balanced. This balance is vital for the survival of countless other species, including humans, who rely on healthy ecosystems for resources such as clean air, water, and food.
In summary, the contribution of nocturnal animals to biodiversity is profound. They play indispensable roles in ecosystem balance and food chains, ensuring that natural processes continue to function smoothly. By doing so, they not only support the biodiversity of their habitats but also provide invaluable services that extend far beyond the veil of night.
Unique Communication Methods
The world of nocturnal animals is a fascinating realm of mystery and adaptation, particularly when it comes to how these creatures communicate in the dark. These animals have developed unique methods to interact with their environment and each other. Among the most intriguing are the echolocation abilities of bats and the silent flight of owls, both of which highlight the incredible adaptations necessary for survival in the night.
Echolocation in Bats
Bats, perhaps the most iconic of all nocturnal animals, have developed an extraordinary method of navigation and communication: echolocation. This process allows bats to “see” with their ears, using sound waves to detect objects and prey in the dark. By emitting high-frequency sound pulses, bats can interpret the echoes that bounce back to them from various surfaces. This ability is crucial, as it allows them to hunt with precision and avoid obstacles even in complete darkness.
The mechanics of echolocation are akin to the sonar technology used in submarines. When a bat emits a sound wave, it travels through the air until it hits an object and bounces back as an echo. By analyzing the time delay and frequency change of the returning echo, bats can ascertain the size, shape, distance, and even the texture of the object.
This biological sonar is not only a marvel of nature but has also inspired human technology. Devices like sonar and radar take cues from this natural phenomenon, highlighting the impact of nocturnal animals on technological advancements. The study of bat echolocation has also led to innovations in robotics and navigation systems, demonstrating how observing nature can lead to breakthroughs in human technology.
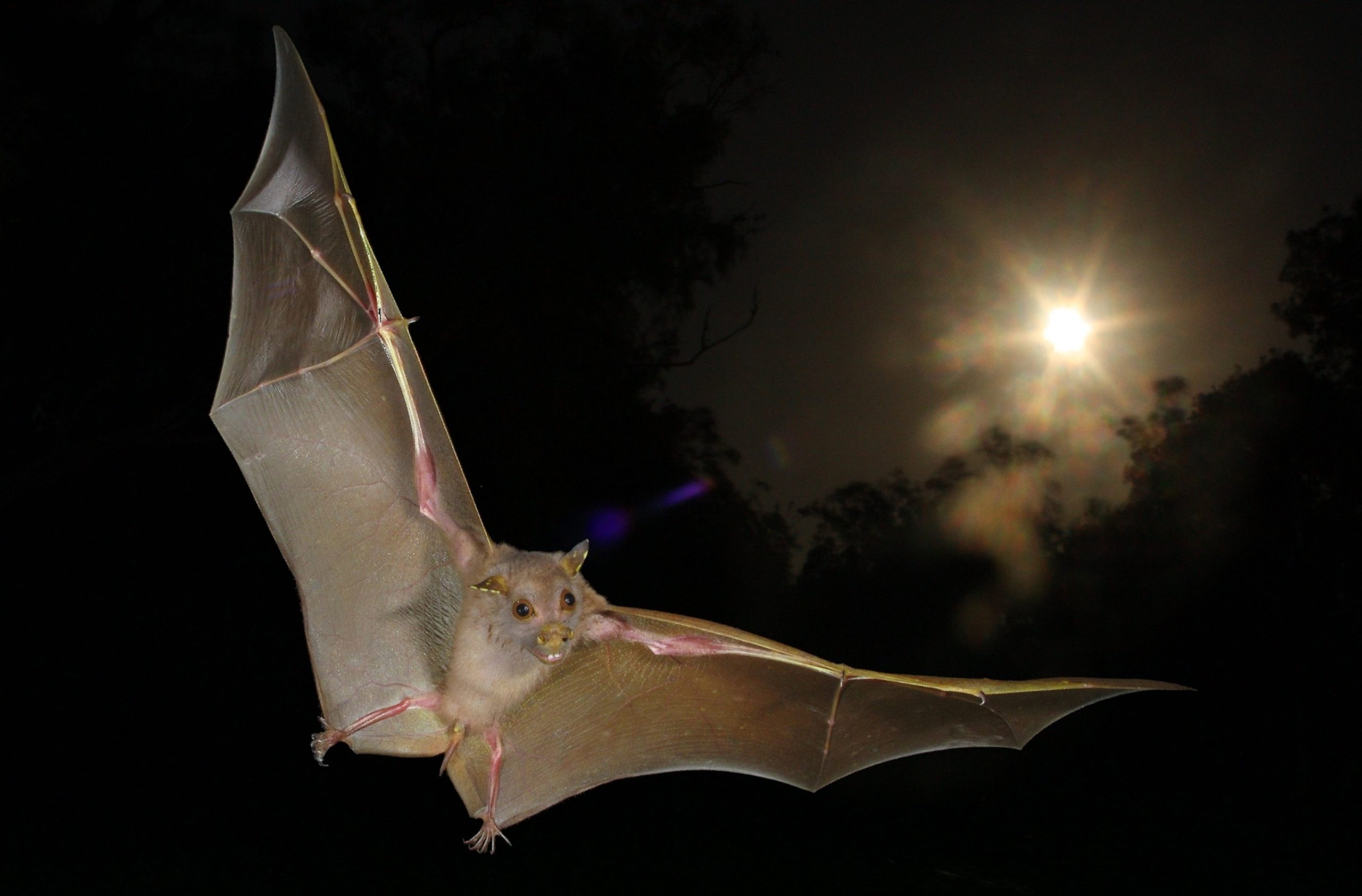

Bats using echolocation to navigate and hunt at night
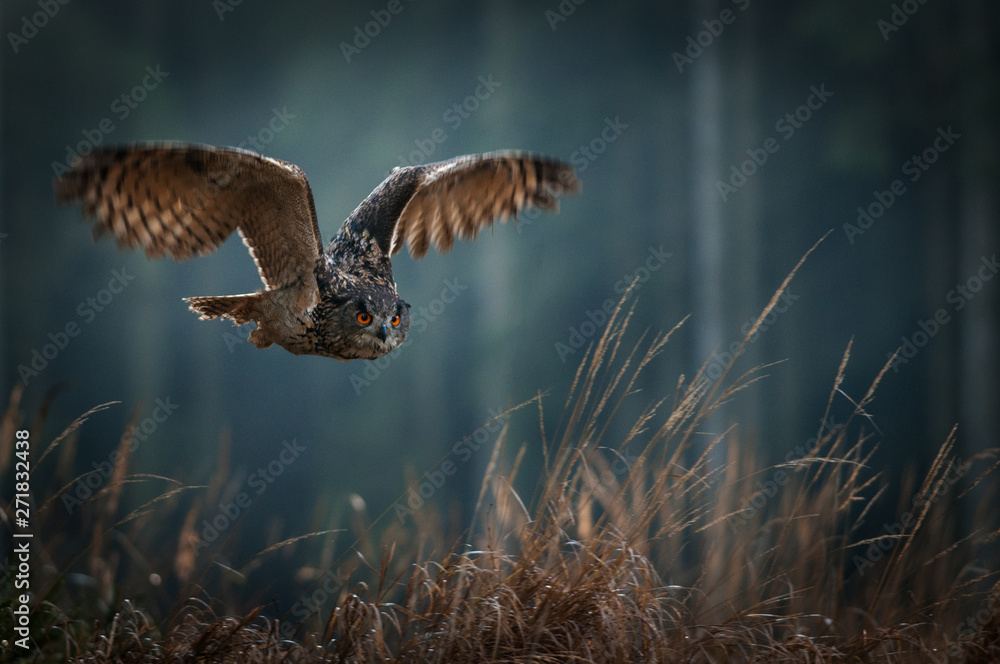
Silent Flight in Owls
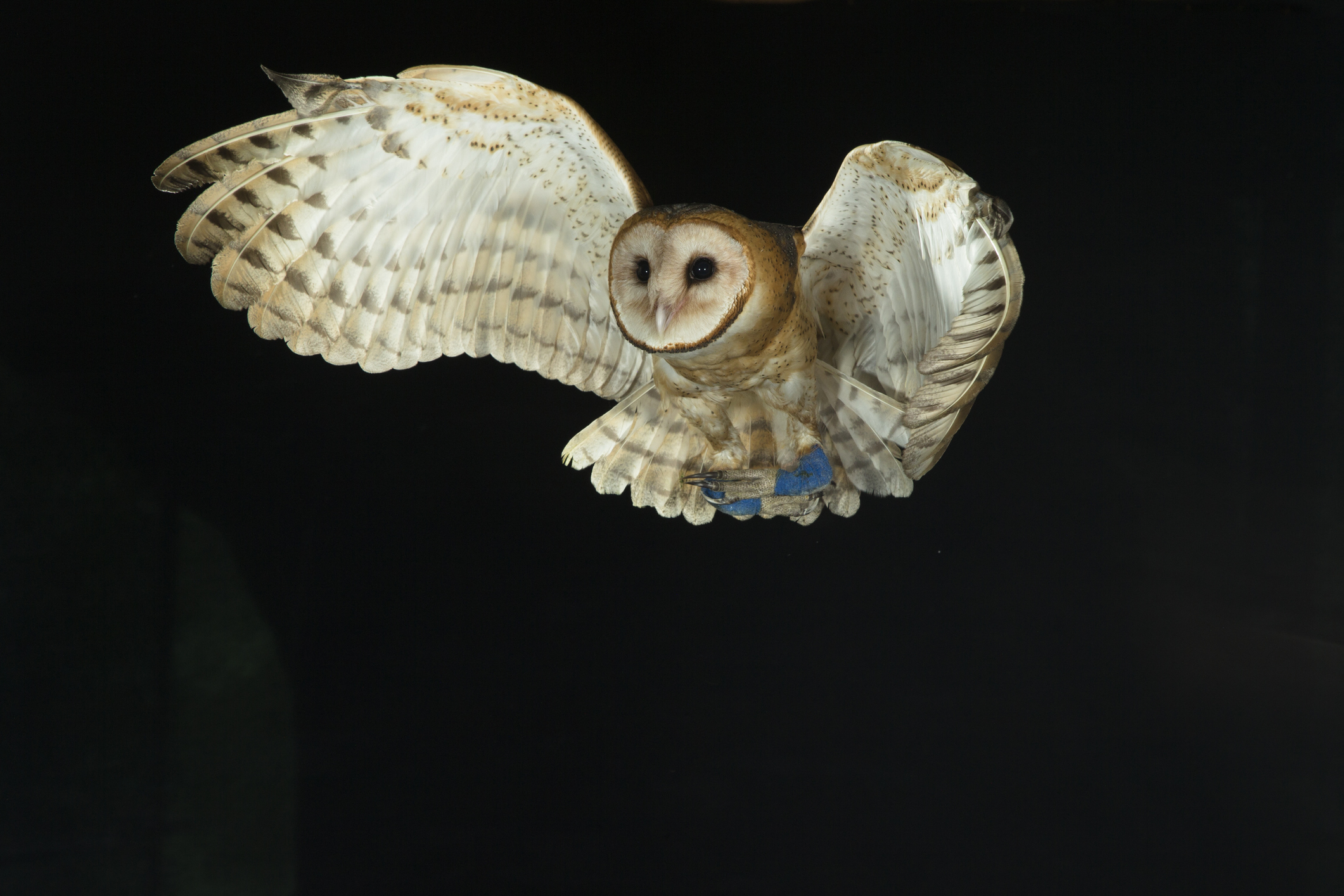
Another remarkable communication and hunting adaptation among nocturnal animals is the silent flight of owls. Unlike other birds, owls have evolved to fly almost silently, an adaptation that gives them a predatory advantage in the dark. This stealthy flight is made possible by unique feather structures that reduce turbulence and noise.
The leading edges of an owl’s primary feathers have serrated edges, breaking up the turbulence into smaller currents, which muffles the sound of their flight. Additionally, the velvety texture of their feathers absorbs sound frequencies, further enhancing their silent approach. This adaptation not only aids in hunting but also allows owls to listen for the faint noises made by their prey, such as the rustling of a mouse in the underbrush.
Silent flight is crucial for owls as it allows them to approach prey without being detected. This adaptation has piqued the interest of engineers and designers, particularly in the field of aerodynamics and noise reduction. The study of owl flight has influenced the design of quieter aircraft and wind turbines, showcasing how these nocturnal animals continue to inspire human innovation.
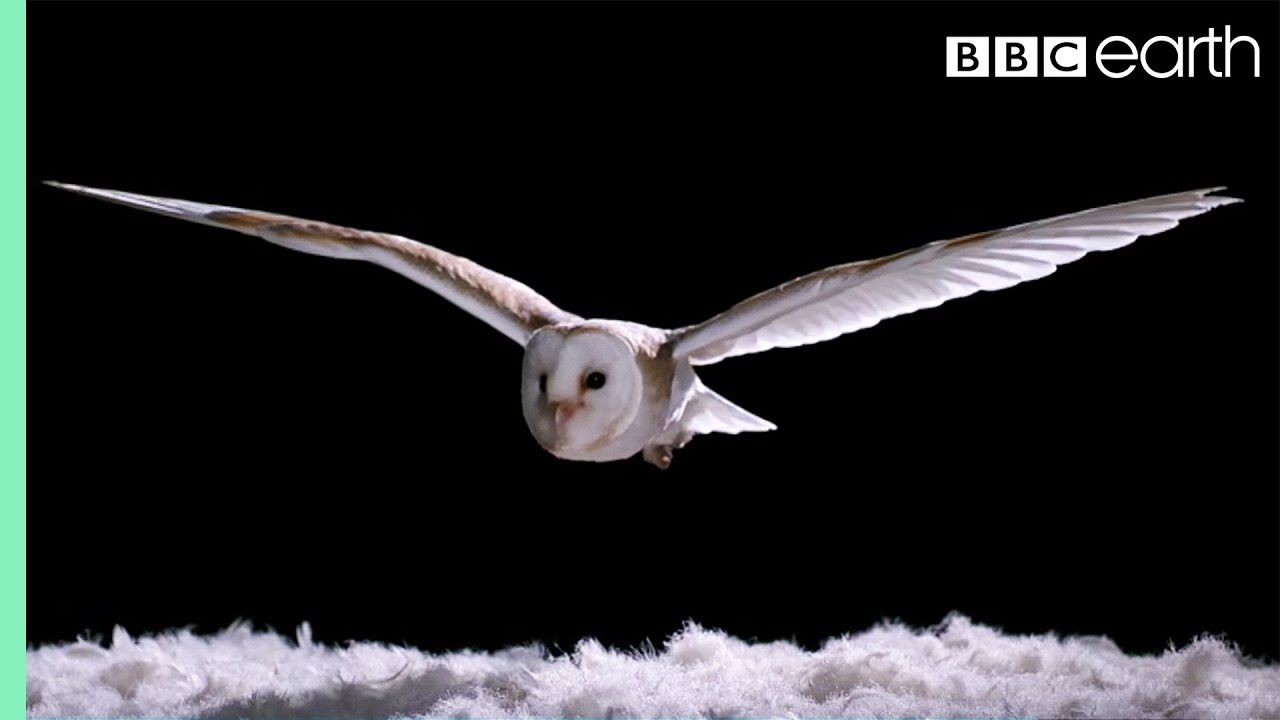

Owl demonstrating silent flight at night
In essence, the communication methods of bats and owls reflect the incredible adaptability and resilience of nocturnal animals. Their unique abilities not only ensure their survival but also offer valuable insights and inspiration for technological advancements in our world. By embracing and understanding these creatures’ capabilities, we can appreciate the intricate tapestry of life that thrives under the cover of darkness.
Insights from Nocturnal Behavior
The enigmatic world of nocturnal animals opens up an array of fascinating insights into behavioral patterns that are crucial not only for understanding animal ecology but also for drawing parallels with human health and behavior. These creatures, active primarily during the night, exhibit unique adaptations and behaviors that have intrigued scientists and nature enthusiasts alike. Let’s delve into how their sleep patterns and nocturnal activities offer enlightening perspectives.
Studying Sleep Patterns
The study of sleep patterns in nocturnal animals provides a window into the diverse strategies animals adopt to thrive in darkness. Unlike diurnal animals, nocturnal species have evolved to take advantage of the night, avoiding competition and predation while exploiting the cover of darkness for hunting and foraging. This shift in activity cycles has led to significant physiological and behavioral adaptations.
For instance, bats, one of the most recognized nocturnal creatures, have a sleep pattern that involves long periods of rest during the day, followed by active foraging at night. Their sleep architecture, characterized by unique phases and durations, offers insights into the flexibility and adaptability of sleep in mammals. Similarly, owls exhibit fascinating nocturnal behaviors, with their sleep being interspersed with various hunting activities at night. This has intrigued researchers studying the evolutionary benefits of such sleep patterns.
Moreover, the study of nocturnal animals extends our understanding of circadian rhythms—the internal body clocks that regulate sleep-wake cycles. In these animals, the circadian rhythm is often shifted to align with nighttime activity, providing a natural model to study how shifts in these rhythms can affect physiology and behavior. Such research is invaluable, especially when considering the implications for humans who work night shifts or suffer from sleep disorders.

Implications for Human Health
Exploring the behaviors of nocturnal animals has far-reaching implications for human health, particularly in understanding sleep disorders and mental health conditions. The adaptability of these animals to live nocturnally offers clues to how humans might better manage disrupted sleep patterns or adapt to irregular work schedules.
One significant area of research is the impact of light exposure on circadian rhythms. Nocturnal animals, such as night monkeys, are sensitive to minimal light levels and have developed acute night vision to navigate the dark. Studying how these animals perceive and react to light can give insights into how artificial lighting affects human sleep patterns and overall health.
Furthermore, the behaviors of these animals have inspired therapeutic approaches in treating human sleep disorders. By observing how these animals manage the balance between activity and rest, researchers have developed strategies that encourage better sleep hygiene and help in the treatment of insomnia and other sleep-related issues.
Another interesting aspect is the influence of nocturnal behavior on mood and mental health. The natural night activity of these animals provides a unique framework for studying the effects of darkness on mood and psychological well-being. This is particularly relevant in understanding conditions like Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD), where lack of daylight leads to depression in some individuals.
In essence, the behavioral patterns of nocturnal animals offer profound insights into our own health and well-being. They teach us about the resilience and adaptability of life, challenging us to rethink our understanding of sleep, activity, and health in the context of our 24-hour world. As we continue to uncover the mysteries of these creatures of the night, we not only enhance our appreciation for their role in the ecosystem but also gain valuable knowledge that could improve human life.

In examining the nocturnal world, we find that the nighttime behaviors of animals are not just about survival; they are a testament to the intricate balance of nature and the interconnectedness of all living beings.
Cultural and Artistic Influence
The realm of nocturnal animals extends far beyond the biological and ecological; it delves deeply into the tapestry of human culture and artistry. These creatures have long captured the human imagination, serving as powerful symbols and inspirations across various artistic and cultural mediums. From ancient myths to contemporary films, nocturnal animals have woven themselves into the fabric of our stories, symbols, and creative expressions.
Symbolism in Art and Literature
In art and literature, nocturnal animals frequently embody mystery, transformation, and the unknown. Their active presence in the night, a time often associated with dreams and subconscious thoughts, makes them ideal symbols for the unseen and the mystical. For instance, owls have long been revered as symbols of wisdom and knowledge, a nod to their keen vision in the darkness. This symbolism is prevalent in ancient Greek mythology, where the owl is associated with Athena, the goddess of wisdom.
In literature, nocturnal animals often appear as metaphors for deeper human experiences. Edgar Allan Poe, known for his dark and gothic tales, frequently used ravens and other night creatures to symbolize death and the macabre. His famous poem “The Raven” is a quintessential example, where the bird becomes a harbinger of doom and a symbol of unending sorrow. The use of nocturnal animals in such contexts underscores their role as bridges between the known and the unknown.
The symbolism of nocturnal animals also finds expression in visual arts. Many painters and sculptors have used these creatures to evoke a sense of wonder or foreboding. The mysterious allure of the night, coupled with the enigmatic nature of these animals, provides rich material for artists exploring themes of duality and the hidden aspects of reality.
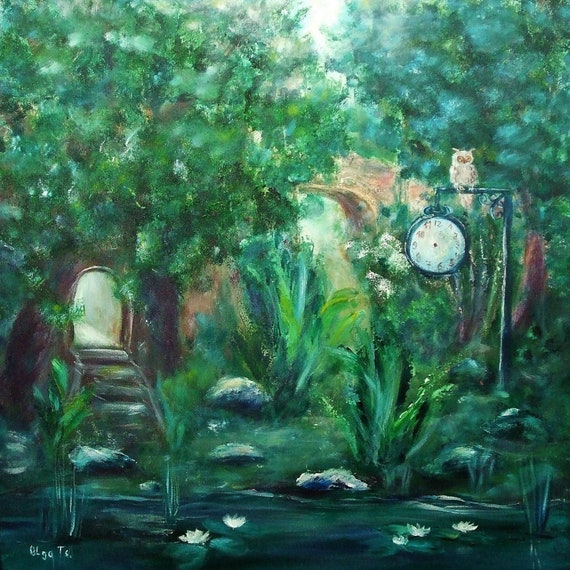

A painting depicting an owl symbolizing wisdom and mystery in a mystical forest setting
Inspiration in Film and Media
The influence of nocturnal animals is perhaps most vividly seen in film and media. These creatures have inspired filmmakers to explore themes of fear, survival, and transformation. The 2016 film “Nocturnal Animals,” directed by Tom Ford, is a direct nod to these themes. While the film itself doesn’t center around actual animals, its title and narrative structure reflect the duality and tension often associated with the nocturnal. The film’s plot, weaving between reality and fiction, mirrors the dual nature of night and day—an exploration of the conscious and subconscious.
Bats, another prominent member of the list of nocturnal animals, have been central to the creation of iconic characters such as Batman. This superhero, operating under the cover of night, draws on the bat’s nocturnal nature to symbolize strength, mystery, and the fight against darkness. The cast of nocturnal animals like bats in such roles highlights the cultural fascination with creatures that thrive in the dark.
Nocturnal animals have also made their mark in animation and children’s media, often portrayed as quirky, wise, or misunderstood characters. This representation helps demystify these creatures, making them more relatable and less fearsome to younger audiences. The use of these animals in storytelling serves to bridge the gap between human and animal worlds, fostering a greater appreciation for biodiversity and the natural world.

A movie scene featuring a batthemed superhero symbolizing mystery and strength
In conclusion, the cultural and artistic influence of nocturnal animals is profound and multifaceted. These creatures continue to inspire artists, writers, and filmmakers, serving as powerful symbols and sources of creativity. Their presence in art and media not only enriches our cultural narratives but also encourages us to explore the mysteries of the night, embracing the wonders that the darkness holds.
Conclusion: Embracing the Night’s Wonders
As we reach the culmination of our exploration into the world of nocturnal animals, it’s clear that these creatures offer far more than their mysterious allure. Their adaptations and roles in nature paint a vivid picture of survival and symbiosis that resonates throughout the animal kingdom. From the enhanced night vision skills that have inspired human technology to their significant contributions to biodiversity, these animals are integral to maintaining the balance of ecosystems.
Nocturnal animals, with their unique communication methods like the echolocation in bats and the silent flight of owls, showcase nature’s ingenuity. These adaptations not only aid in their survival but also provide valuable insights into behavioral and biological sciences. Moreover, studying their nocturnal habits sheds light on sleep patterns and has potential implications for human health, offering lessons that transcend the boundaries of species.
Beyond their ecological importance, nocturnal animals have left an indelible mark on human culture and arts. Their presence in literature, art, and media reflects our fascination with the night and its inhabitants. The symbolism of these creatures often represents mystery, wisdom, and transformation, themes that resonate deeply within the human psyche.
The film “Nocturnal Animals,” directed by Tom Ford, further exemplifies how the concept has permeated popular culture. With a gripping narrative that intertwines reality and fiction, it mirrors the complexity and duality often associated with these night dwellers.

In embracing the wonders of the night, we find ourselves more connected to the natural world. The nocturnal animals list is a testament to the adaptability and diversity of life on Earth. As we continue to study and protect these creatures, we not only preserve their habitats but also safeguard the delicate balance of our planet’s ecosystems.
At WildWhiskers, we celebrate these tiny tails and big stories that enrich our understanding and appreciation of the animal kingdom. We invite you to continue exploring and sharing the magic of nocturnal animals and all wildlife around us. Join us in this journey to discover, learn, and cherish the lives of these extraordinary creatures.
In recognizing the contributions and beauty of nocturnal animals, we not only honor their place in the natural world but also reflect on our own relationship with nature. Let us continue to embrace the wonders of the night, finding inspiration in the darkness and marveling at the secrets it holds.

A serene view of nocturnal animals thriving in their natural habitat under the moonlight
Remember, WildWhiskers is your go-to platform for all things animal-related, providing daily doses of heartwarming stories and fascinating insights. With us, you’re not just a reader—you’re part of a community that values the incredible lives of animals worldwide. So, open your heart to the wonders of the night and the enchanting world of nocturnal animals.