In the ever-evolving landscape of agriculture, the role of farm animals is undergoing a fascinating transformation. As we delve into the future of farm animals within modern farming, we find ourselves at the intersection of tradition and innovation. Historically, these animals have been the backbone of agriculture, providing not only food but also labor and companionship. But what are farm animals in today’s context? They are still the same essential contributors, yet their roles are being redefined through technological advancements and sustainable practices.
Imagine a farm where automation and robotics seamlessly manage daily tasks, ensuring efficiency and precision. This is not just a vision—it’s a reality taking shape. The advent of Precision Livestock Farming is revolutionizing how farmers interact with their livestock, using data-driven approaches to enhance productivity and animal welfare. As we explore these technological leaps, we also recognize the shift towards more sustainable practices, like organic and free-range farming, which prioritize the ethical treatment and welfare of animals.
Moreover, the future holds exciting prospects in animal nutrition and health. Advances in feed technology and veterinary science are paving the way for healthier livestock, reducing disease risks, and promoting longevity. In parallel, biotechnology is playing a pivotal role in animal breeding, from genetic engineering to cloning, promising to enhance livestock traits and resilience.
As we journey through this blog, we’ll uncover how these innovations are shaping a new era for farm animals, ensuring they remain integral to agriculture while aligning with modern ethical and environmental standards. Whether you’re intrigued by the idea of natural farm animals or fascinated by the potential of biotechnology, this exploration offers a compelling glimpse into the future of farming. Join us as we navigate this dynamic landscape, where tradition meets technology, and the well-being of farm animals is at the forefront of agricultural progress.
Introduction to Modern Farming
As we stand on the cusp of an agricultural revolution, modern farming practices are rapidly transforming how we view and manage farm animals. These changes are not just about efficiency and productivity; they encompass a broader vision that includes sustainability, animal welfare, and technological innovation. In this section, we will delve into the evolution of farming practices and the critical role that farm animals play in agriculture today.
The Evolution of Farming Practices
Farming has always been the backbone of human civilization, but the way we farm has undergone significant changes over the centuries. From the days of simple subsistence farming to today’s complex and technologically advanced operations, the evolution of farming practices reflects our growing understanding of agriculture and its impact on the environment.
In the past, farming was primarily manual labor, heavily reliant on human and animal power. Farmers worked tirelessly with basic tools to cultivate the land and raise animals for food, fiber, and labor. However, as the Industrial Revolution swept through the 18th and 19th centuries, machinery began to replace manual labor, leading to increased productivity and the birth of modern agriculture.
The 20th century brought further advancements with the introduction of chemical fertilizers, pesticides, and genetically modified organisms (GMOs). These innovations allowed for higher yields but also raised concerns about environmental impact and sustainability. The latter part of the century saw a shift towards more sustainable practices, such as integrated pest management and organic farming, which aim to balance productivity with ecological health.
Today, the focus is on precision agriculture, where technology such as GPS, drones, and data analytics are used to optimize every aspect of farming. This precision allows farmers to monitor and manage crops and livestock with unprecedented accuracy, reducing waste and improving yields. The incorporation of automation and robotics into farming practices has further streamlined operations, allowing for more efficient management of resources and labor.
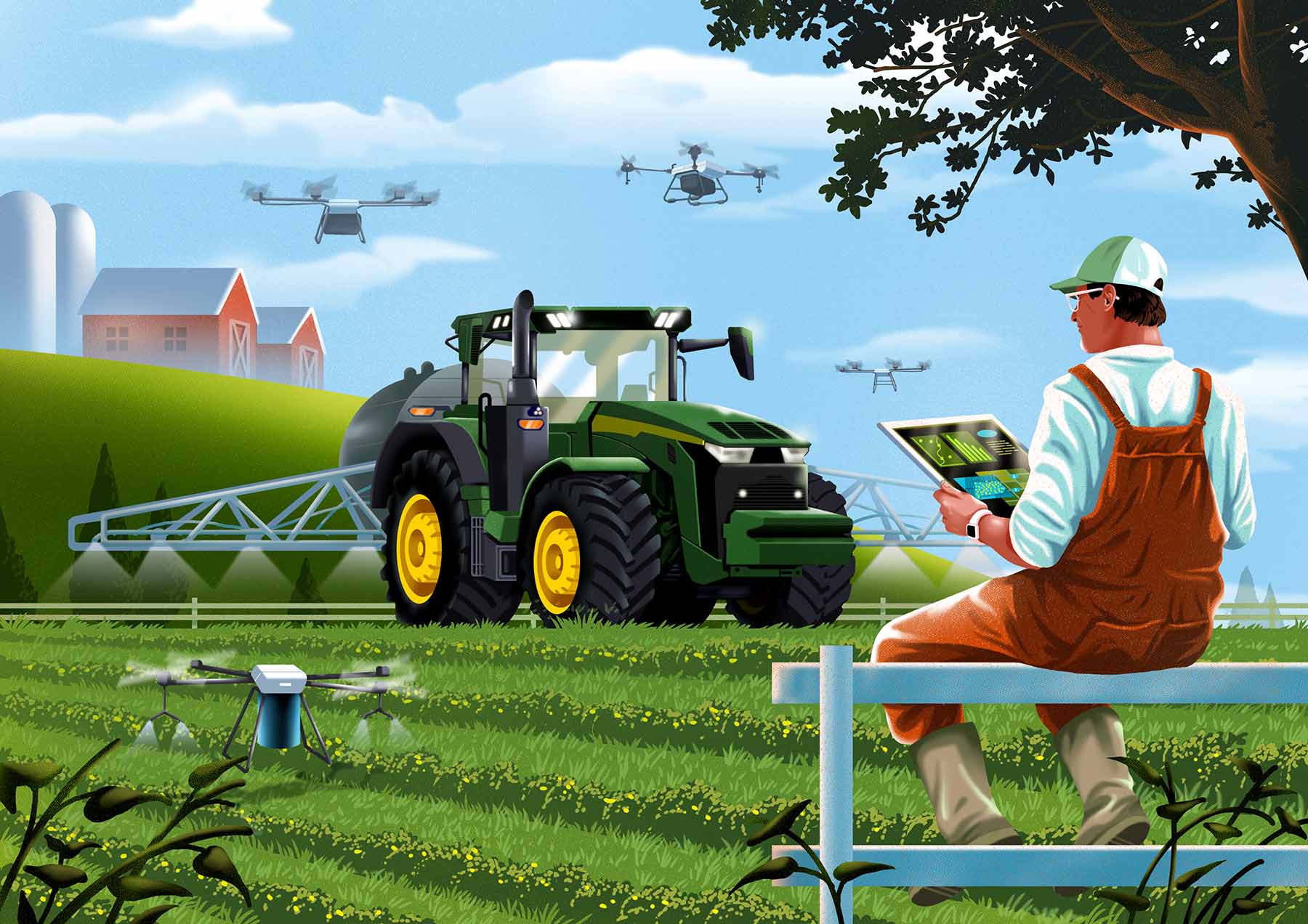

Modern farming technology utilizing drones and tractors
Importance of Farm Animals in Agriculture
Farm animals are an integral part of agriculture, providing essential resources and services that are crucial for human survival. They are not just producers of meat, milk, eggs, and wool; they also play a vital role in the sustainability and economic viability of farms around the world.
The presence of farm animals on agricultural lands contributes significantly to the nutrient cycle. Animals help to recycle nutrients through their manure, which enriches the soil and promotes healthy crop growth. This symbiotic relationship between plants and animals is fundamental to sustainable farming practices.
Moreover, farm animals offer labor and companionship. Historically, animals like horses and oxen have been used for plowing fields and transporting goods, tasks that were once too labor-intensive for humans alone. While machinery has largely replaced animal labor in many parts of the world, the traditional role of animals in farming is still prevalent in developing regions.
The economic impact of farm animals cannot be underestimated. They provide livelihoods for millions of people globally, from small-scale farmers to large agricultural businesses. The 8 forms of farm animals commonly found on farms—cattle, chickens, pigs, sheep, goats, horses, ducks, and turkeys—each contribute uniquely to agricultural life. For instance, cattle are a primary source of milk and meat, while sheep provide wool and meat.
Beyond their economic contributions, farm animals also enrich human lives in more subtle ways. They are often part of educational and therapeutic programs, helping children and adults alike to learn about animal care and develop empathy for living creatures. Kids farm animals programs, for example, engage children with activities like farm visits and petting zoos, fostering a connection with nature and agriculture.
In conclusion, as we continue to explore the future of farm animals in modern farming, it is essential to recognize their enduring importance in agriculture. They are not only key to food production and economic stability but also to the cultural and environmental fabric of our world. As farming practices continue to evolve, the relationship between humans and farm animals will remain a cornerstone of agricultural innovation and sustainability.
Technological Advancements in Livestock Management
The world of modern farming is undergoing a transformative shift, largely driven by technological advancements that are reshaping how we manage livestock. These innovations are not just about increasing productivity but also about enhancing animal welfare, ensuring sustainability, and improving efficiency in farm operations. Two key areas of technological progress in this field are Automation and Robotics and Precision Livestock Farming.
Automation and Robotics
In the realm of agriculture, automation and robotics are revolutionizing traditional practices. These technologies are designed to automate routine tasks, reduce labor costs, and increase precision in farm operations. On a modern farm, robots can now perform tasks such as milking, feeding, and cleaning with remarkable efficiency.
Milking Robots are perhaps the most well-known application of robotics in livestock management. These robots can milk cows with minimal human intervention, ensuring that each cow is milked at the optimal time and frequency. The use of milking robots not only boosts productivity but also improves udder health by minimizing the risk of infection through consistent and gentle handling.
Another significant application is the automated feeding systems. These systems precisely measure and deliver feed to animals based on their individual nutritional needs, which can vary by age, size, and health status. Automation in feeding ensures that each animal receives the right amount of nutrients, improving their overall health and productivity.
Robotic systems are also used in barn cleaning and manure management, which are essential for maintaining hygienic living conditions for farm animals. By automating these tasks, farms can significantly reduce labor costs and enhance the cleanliness of animal housing, contributing to better animal welfare.
Precision Livestock Farming
Precision Livestock Farming (PLF) represents a paradigm shift in how farm animals are managed. This approach uses technology to monitor and manage the health, welfare, and productivity of livestock with unprecedented accuracy. The goal of PLF is to optimize production, improve animal welfare, and reduce environmental impact.
One of the key tools in PLF is sensor technology. Sensors placed on animals can track various parameters such as body temperature, movement, and behavior. These sensors collect data in real-time, allowing farmers to monitor the health status of each animal closely. For instance, a sudden change in an animal’s activity level could indicate illness, prompting early intervention and treatment.
Data analytics play a central role in PLF by processing the vast amounts of data collected from sensors. Advanced algorithms analyze this data to provide insights into animal health, growth rates, and even predict potential health issues before they become serious. This proactive approach to livestock management helps in reducing mortality rates and increasing overall farm productivity.
Moreover, PLF includes the use of drones for monitoring livestock on large farms. Drones equipped with cameras and sensors can cover vast areas quickly, providing farmers with detailed images and data. This technology is particularly useful for monitoring free-range animals, ensuring they are healthy and accounted for.
In conclusion, the integration of automation, robotics, and precision technology in livestock management is transforming the agricultural landscape. These innovations not only enhance the efficiency and productivity of farm operations but also emphasize the importance of animal welfare and environmental sustainability. As technology continues to evolve, the future of farm animals in agriculture looks promising, with a focus on creating a more sustainable and humane farming industry.
Sustainable Practices and Animal Welfare
In the evolving world of modern farming, sustainable practices and animal welfare have become increasingly significant. As consumers grow more conscious of how their food is produced, farmers are adopting innovative methods to ensure ethical treatment of farm animals while maintaining ecological balance. Let’s delve into two critical areas: organic and free-range farming, and ethical treatment and welfare standards.
Organic and Free-Range Farming
Organic and free-range farming have gained momentum as preferred methods for raising farm animals. These practices not only prioritize the health and well-being of animals but also promote ecological sustainability.
Organic Farming:
Organic farming emphasizes the use of natural processes and materials. In the context of farm animals, this means providing organic feed, free from synthetic additives or genetically modified organisms (GMOs). Organic practices also limit the use of antibiotics and hormones, focusing instead on natural remedies and preventive measures to maintain animal health.
One of the hallmarks of organic farming is the emphasis on natural living conditions. Farm animals are allowed to roam freely, engage in natural behaviors, and have access to pasture. This not only improves their quality of life but also leads to healthier products for consumers. For instance, organic eggs and milk are often cited for their superior taste and nutritional value.
Free-Range Farming:
Free-range farming complements organic methods by prioritizing the freedom and mobility of farm animals. In free-range systems, animals such as chickens, cows, and pigs are given ample space to move around and express natural behaviors. This stands in stark contrast to conventional farming, where animals are often confined to small spaces.
Free-range farming is particularly popular in poultry production. Chickens raised in this manner are allowed to forage, resulting in eggs that are richer in omega-3 fatty acids and vitamins. Similarly, free-range pork and beef are recognized for their better flavor and texture.
Both organic and free-range farming practices are aligned with consumer demands for transparency and quality. They reflect a growing awareness that the welfare of farm animals is intrinsically linked to the health of the planet and the people who inhabit it.
Ethical Treatment and Welfare Standards
The ethical treatment of farm animals is a cornerstone of sustainable agriculture. As society becomes more attuned to animal rights, there is a concerted push towards establishing and enforcing welfare standards that ensure humane treatment throughout an animal’s life.
Welfare Standards:
Animal welfare standards are guidelines and regulations designed to protect farm animals from abuse and neglect. These standards cover various aspects, including housing, nutrition, health care, and handling. Key organizations like the World Organisation for Animal Health (OIE) and the Farm Animal Welfare Council (FAWC) play pivotal roles in shaping these standards.
One widely recognized framework is the “Five Freedoms,” which outlines fundamental rights for animals: freedom from hunger and thirst, discomfort, pain, injury, or disease, freedom to express normal behavior, and freedom from fear and distress. These freedoms serve as a baseline for assessing animal welfare across different farming systems.
Ethical Treatment Practices:
Ethical treatment extends beyond meeting minimum standards; it involves a commitment to continually improving the living conditions of farm animals. This can include providing enrichment activities, ensuring social interactions, and minimizing stressful situations.
For example, in dairy farming, ethical practices might involve using gentle milking techniques and ensuring cows have comfortable bedding. Poultry farms may implement rotational grazing to provide fresh pastures and reduce the risk of disease.
Moreover, transparency in farming operations is crucial for maintaining consumer trust. Many farms now offer tours and educational programs to showcase their commitment to ethical practices, allowing the public to witness firsthand the care provided to farm animals.

Cows enjoying a comfortable and ethical farming environment
In conclusion, sustainable practices and animal welfare are not just trends but essential components of the future of agriculture. By embracing organic and free-range farming, and upholding high ethical standards, the farming industry can ensure the well-being of farm animals while meeting the demands of a conscientious consumer base. This holistic approach not only benefits the animals but also contributes to a healthier planet and community.
Innovations in Animal Nutrition and Health
The field of animal nutrition and health is undergoing a remarkable transformation with innovations that are setting new standards in the way we care for farm animals. These advancements not only improve the health and productivity of these animals but also enhance the sustainability and efficiency of modern farming practices. Let’s delve into how innovations in feed technology and veterinary science are reshaping the world of farm animals.
Advances in Feed Technology
In the realm of animal agriculture, feed technology plays a crucial role in ensuring that farm animals receive the necessary nutrients for optimal growth and productivity. The development of advanced feed formulations is one of the most significant innovations in this area. By utilizing cutting-edge technology, feed manufacturers can now create highly specialized feeds that cater to the unique dietary needs of different types of farm animals.
One of the key advancements in feed technology is the use of precision feeding systems. These systems leverage data analytics and machine learning to tailor feed compositions to the specific requirements of individual animals. This approach not only maximizes nutritional intake but also minimizes waste, leading to more sustainable farming practices.
Moreover, the incorporation of probiotics and prebiotics into animal feeds is gaining popularity. These supplements support the gut health of farm animals, thereby enhancing their immune systems and overall well-being. This is particularly beneficial for animals such as cows and pigs, which are prone to digestive issues.
Enzyme technology is another breakthrough in feed innovation. By adding enzymes to animal feeds, farmers can improve the digestibility of feed ingredients, allowing animals to extract more energy and nutrients from their food. This not only boosts growth rates but also reduces the environmental footprint of farming by decreasing methane emissions from ruminants like cattle.
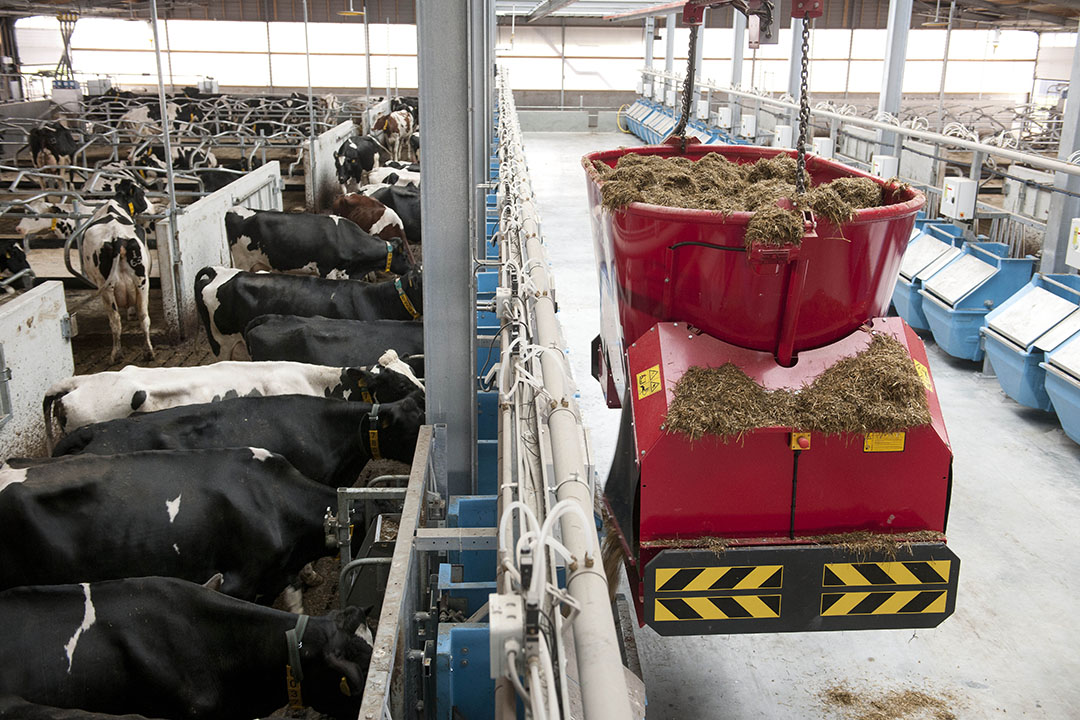

Advanced feed technology systems in modern livestock farming
Veterinary Science and Disease Prevention
In conjunction with advances in feed technology, veterinary science is making significant strides in disease prevention and health management for farm animals. The focus is shifting from traditional treatment methods to preventive healthcare, which is more cost-effective and sustainable.
One of the most promising developments in this field is the use of vaccination programs tailored to specific farm conditions. By understanding the unique disease risks of different environments, veterinarians can design vaccination schedules that effectively protect animals from common illnesses. This proactive approach not only reduces the reliance on antibiotics but also helps combat the growing issue of antibiotic resistance.
Biotechnology is also playing a pivotal role in advancing animal health. Techniques such as genetic engineering are being used to develop disease-resistant breeds of farm animals. For example, certain genetic modifications can make pigs resistant to PRRS (Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome), a disease that has significant economic impacts on pig farming.
Furthermore, the integration of health monitoring technologies is revolutionizing farm animal care. Wearable sensors and smart devices can track vital signs and behavior patterns, alerting farmers to potential health issues before they become serious. This real-time data allows for timely interventions, reducing the incidence of disease outbreaks and improving overall herd health.
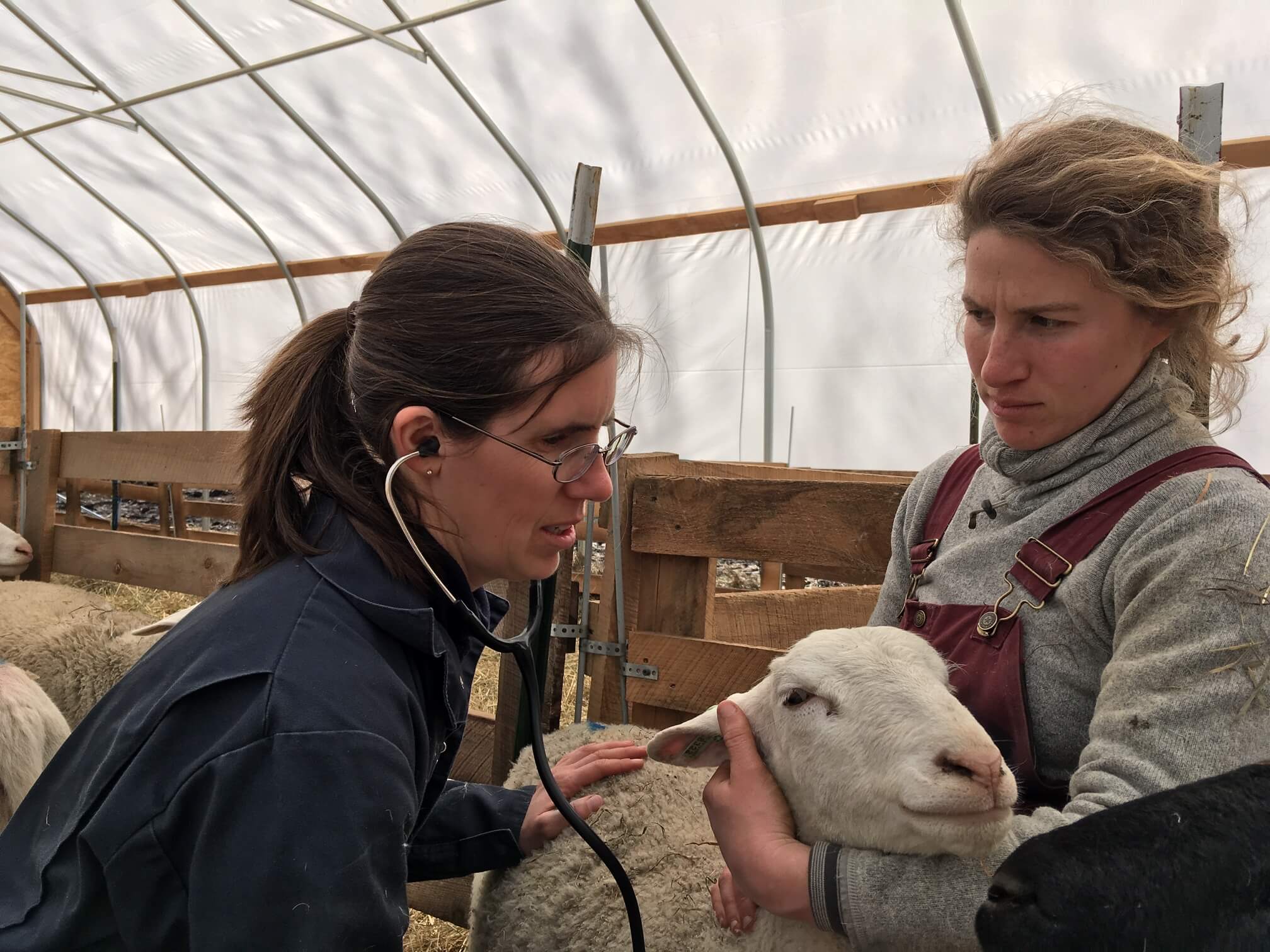

Hightech veterinary care and disease prevention in farm animals
In conclusion, the innovations in animal nutrition and health are pivotal to the evolution of modern farming. By enhancing feed technology and advancing veterinary science, we are not only improving the quality of life for farm animals but also paving the way for more sustainable and efficient agricultural practices. As we continue to explore these innovations, the future of farm animals looks promising, with healthier livestock and more productive farms on the horizon.
The Role of Biotechnology in Animal Breeding
In the rapidly advancing world of agriculture, the integration of biotechnology in animal breeding has become a cornerstone of modern farming practices. This approach not only enhances productivity but also addresses critical issues like sustainability, animal welfare, and food security. Biotechnology in animal breeding involves the application of scientific techniques to improve and manipulate the genetics of farm animals, ensuring they meet the ever-growing demands of the agricultural sector.
Genetic Engineering and Selective Breeding
Genetic engineering and selective breeding are two pivotal techniques in the realm of animal biotechnology. While selective breeding has been practiced for centuries, allowing farmers to choose animals with desirable traits for reproduction, genetic engineering brings a modern twist to this age-old practice.
Selective breeding involves pairing animals with favorable characteristics, such as higher milk production in cows or leaner meat in pigs, to produce offspring that inherit these traits. This method has been instrumental in developing the diverse array of farm animals we rely on today. However, selective breeding is a slow process, often requiring several generations to achieve desired outcomes.
In contrast, genetic engineering offers a more direct approach. This technique involves altering the DNA of an organism to introduce new traits or enhance existing ones. For example, scientists can modify the genes of chickens to improve their resistance to diseases or increase their growth rates. Genetic engineering can significantly reduce the time required to achieve specific breeding goals, making it a powerful tool in modern agriculture.
The potential of genetic engineering also extends to addressing environmental concerns. For instance, researchers are working on developing cattle that produce less methane, a potent greenhouse gas, thereby reducing the environmental impact of livestock farming.
Despite its promising prospects, genetic engineering in animal breeding raises ethical questions and regulatory challenges. Concerns about animal welfare, ecological balance, and food safety must be carefully considered. Nevertheless, with responsible application and strict guidelines, genetic engineering holds the potential to revolutionize the way farm animals are bred, ensuring they can meet the needs of a growing global population.
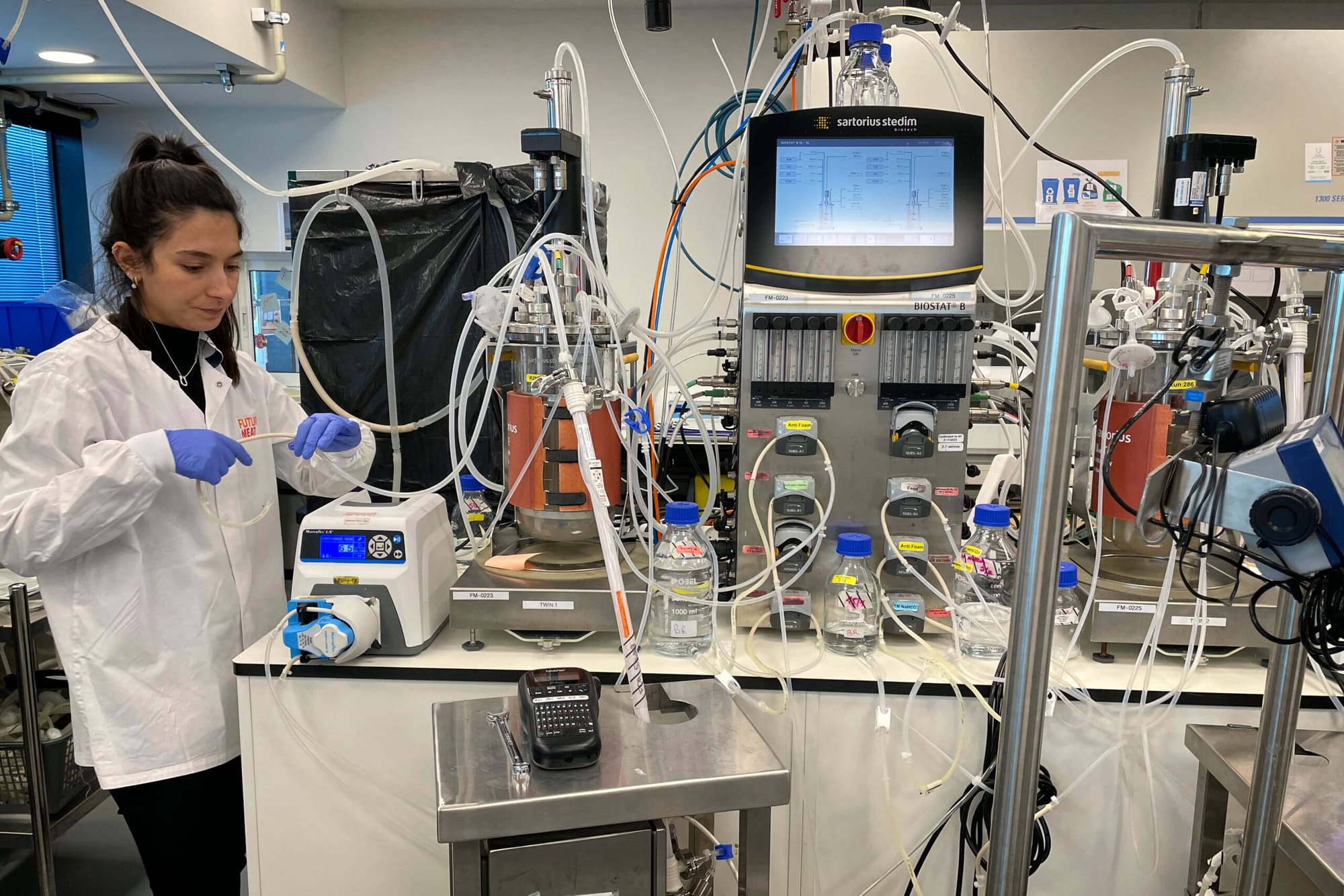

Scientists working on genetic engineering of farm animals in a laboratory
Cloning and Future Prospects
Cloning represents another frontier in the application of biotechnology to animal breeding. Unlike genetic engineering, which modifies genes, cloning involves creating a genetically identical copy of an animal. This technique has sparked significant interest and debate since the famous cloning of Dolly the sheep in 1996.
In agriculture, cloning can be used to replicate animals with superior traits, ensuring a consistent and high-quality stock of farm animals. For example, a cow with exceptional milk production or disease resistance can be cloned to produce more animals with these advantageous characteristics. This can lead to increased efficiency and productivity on farms.
Cloning also offers the possibility of preserving endangered livestock breeds or reintroducing extinct varieties, thus maintaining biodiversity within agriculture. It could serve as a safety net for genetic resources, allowing farmers to safeguard valuable traits that might otherwise be lost.
However, the practice of cloning is not without its challenges. Ethical concerns about the welfare of cloned animals, the potential loss of genetic diversity, and societal acceptance are significant hurdles that need to be addressed. Additionally, the high cost and technical complexity of cloning currently limit its widespread adoption in farming.
Looking to the future, advancements in biotechnology and a better understanding of genetic science could make cloning a more viable option for farmers. As the technology matures, it might become a critical tool in addressing food security and sustainability challenges, providing a reliable source of high-quality farm animals.

Cloning process of farm animals in a scientific environment
In summary, biotechnology, through genetic engineering and cloning, plays a crucial role in modern animal breeding. While it offers remarkable opportunities to enhance productivity and sustainability in agriculture, it must be pursued with caution and ethical consideration. As we continue to innovate and refine these technologies, the future of farm animals in agriculture looks promising, poised to meet the demands of a growing global population while ensuring the welfare of the animals themselves.
Concluding Thoughts on the Future of Farm Animals in Agriculture
As we stand on the cusp of a new era in agriculture, the future of farm animals is intertwined with technological advancement, ethical considerations, and sustainable practices. The role of farm animals continues to evolve, reflecting broader changes in society, technology, and environmental awareness.
Embracing Technological Innovations
The future of farm animals in modern farming will undoubtedly be shaped by technological innovations. Automation and robotics have already begun to revolutionize livestock management, ensuring that farm animals are cared for with precision and efficiency. From robotic milking machines to automated feeding systems, these technologies promise to reduce the labor-intensive demands on farmers while enhancing the welfare of animals. Precision livestock farming uses data and analytics to monitor the health and productivity of animals in real-time, allowing for quick interventions and personalized care. This not only boosts farm productivity but also ensures that animals live healthier and more comfortable lives.
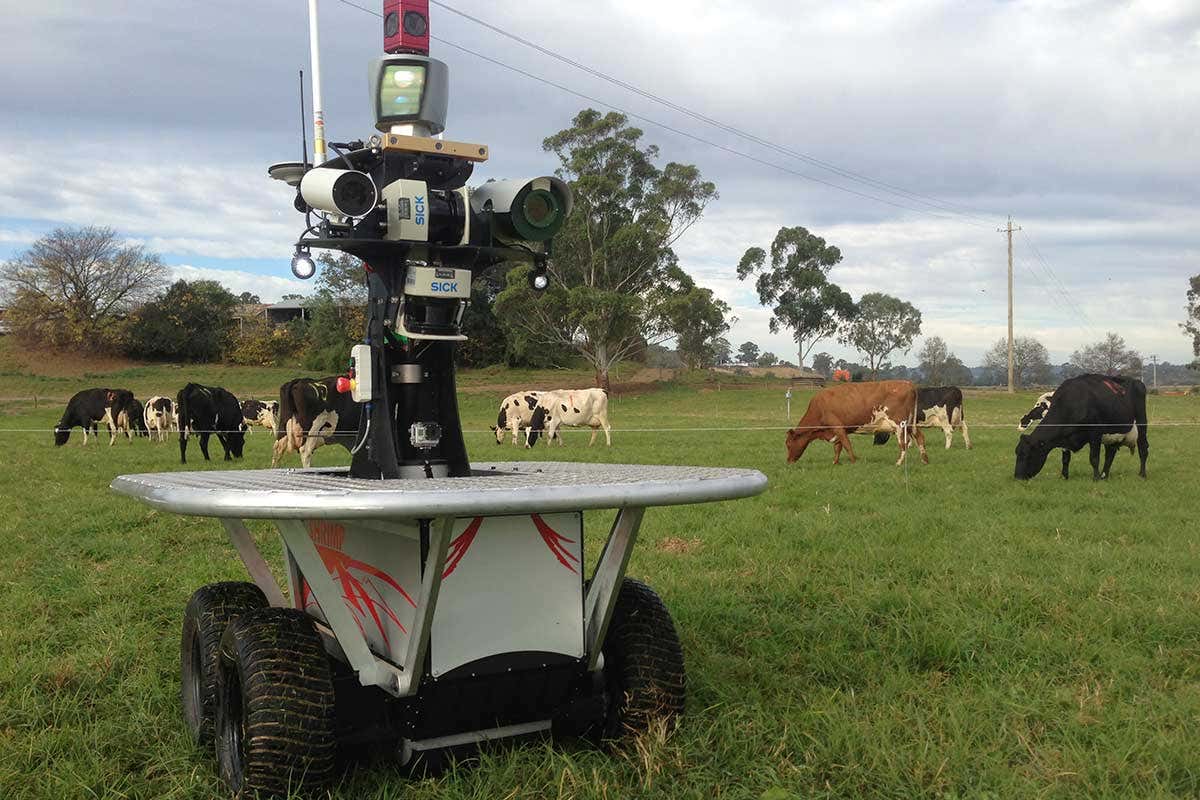

A futuristic farm with robotic systems managing livestock
Commitment to Sustainability and Ethics
With a growing global emphasis on sustainability, the future of farm animals must align with eco-friendly and ethical standards. The move towards organic and free-range farming is a testament to this shift, as consumers increasingly demand transparency and humane treatment of animals. These practices not only promise better quality products but also a reduced environmental footprint. Ethical treatment and welfare standards are becoming central to farming policies worldwide, ensuring that the welfare of animals is prioritized alongside productivity goals. As more farmers adopt these practices, the positive impact on the environment and animal well-being is likely to become more pronounced.
Advancements in Animal Health and Nutrition
Another critical area shaping the future of farm animals is in animal nutrition and health. Advances in feed technology and veterinary science are pivotal in promoting the health and productivity of animals. Innovations such as tailored feed formulations and enhanced disease prevention methods ensure that farm animals receive optimal nutrition and care. This not only improves the quality of agricultural products but also enhances animal welfare by reducing illness and increasing longevity.

A veterinarian carefully examining livestock health on a modern farm
The Role of Biotechnology
Biotechnology is set to play a transformative role in the future of farm animals. Through genetic engineering and selective breeding, farmers can enhance desirable traits in animals, such as disease resistance and productivity. While cloning and other biotechnological advancements present exciting possibilities, they also raise ethical questions that society must address. As these technologies advance, the balance between innovation and ethics will be crucial in determining their adoption and impact on agriculture.
A Vision for the Future
In conclusion, the future of farm animals in agriculture is one of promise and responsibility. As technological, ethical, and sustainable practices continue to evolve, farmers and consumers alike must adapt to the changing landscape. By embracing these advancements, we can ensure that farm animals remain an integral part of our agricultural systems, contributing to food security, economic stability, and environmental sustainability.
The journey towards this future is not without challenges, but with a commitment to innovation and ethical stewardship, we can create a world where farm animals thrive alongside humans, contributing to a healthier planet and a more sustainable agricultural industry.

Farm animals happily grazing in a sustainable and green pasture
WildWhiskers is a dedicated news platform for animal lovers around the world. From heartwarming stories about pets to the wild journeys of animals in nature, we bring you fun, thoughtful, and adorable content every day. With the slogan “Tiny Tails, Big Stories!”, WildWhiskers is more than just a news site — it’s a community for animal enthusiasts, a place to discover, learn, and share your love for the animal kingdom. Join WildWhiskers and open your heart to the small but magical lives of animals around us!