In the grand tapestry of life on Earth, the myriad ways in which animals have adapted to their environments are nothing short of astonishing. From the icy expanses of the poles to the arid stretches of deserts, and the crushing depths of the oceans to the towering heights of mountain ranges, animals demonstrate an incredible array of adaptations that enable them to thrive in extreme environments. This blog delves into the fascinating world of animal adaptations, exploring how various creatures have evolved to not only survive but also flourish in some of the planet’s most inhospitable areas.
Animals have developed remarkable strategies for coping with extreme conditions. Take, for instance, the polar bears and penguins whose thick fur and blubber provide essential insulation against freezing temperatures, or desert creatures that have mastered water conservation techniques to endure scorching heat. In the profound darkness of the deep sea, some species wield bioluminescence and camouflage as tools for survival, while others exhibit extraordinary pressure and temperature tolerance.
Moreover, high altitudes present their own set of challenges, yet mountain creatures boast features like efficient oxygen usage and specialized limbs that allow them to navigate rugged terrains. Each adaptation is a testament to nature’s ingenuity, showcasing a remarkable blend of biology, behavior, and environment.
As we journey through these adaptations, we’ll also touch upon broader themes, such as the animals list that naturally categorize these incredible beings based on their habitats and behaviors. Whether you’re intrigued by the nocturnal habits of certain creatures or the structural marvels of vertebrates, this exploration promises to enrich your appreciation of the animal kingdom’s resilience and innovation. Join us as we reflect on how these adaptations not only highlight the diversity of life but also underscore the profound beauty and complexity of nature.
Introduction to Animal Adaptations
The animal kingdom is a vast and intricate tapestry of life, showcasing an array of creatures that have evolved in remarkable ways to thrive in diverse environments. From the blistering deserts to the icy poles, animals exhibit extraordinary adaptations that enable them to survive and flourish in conditions that would be inhospitable to many. Understanding these adaptations not only illuminates the beauty and complexity of nature but also underscores the resilience and ingenuity of life on Earth.
Definition and Importance of Adaptations
Adaptations are the unique characteristics or behaviors that have evolved in animals over time to increase their chances of survival and reproduction in specific environments. These can be physical, such as a polar bear’s thick fur and layer of blubber for insulation, or behavioral, like the migratory patterns of birds to escape harsh climates. Adaptations can also be physiological, such as a camel’s ability to conserve water in the desert.
The importance of these adaptations cannot be overstated. They are the result of millions of years of evolution and natural selection, where only the traits that best suit an environment are passed down through generations. This process ensures that species are well-equipped to handle challenges posed by their habitats, whether it be finding food, avoiding predators, or coping with extreme temperatures.
Adaptations also highlight the interconnectedness of ecosystems. The success of a species often depends on its ability to adapt to its environment, which in turn affects other species and the ecosystem as a whole. For example, the adaptation of herbivores to efficiently digest plant material influences the plant species composition and the predators that rely on these herbivores for food.
Overview of Extreme Environments
The Earth is home to a variety of extreme environments, each posing unique challenges to the animals that inhabit them. These environments are characterized by conditions that are at the limits of what most organisms can endure, such as extreme temperatures, high pressures, or limited resources.
In the Arctic and Antarctic regions, temperatures can plummet far below freezing, and animals must contend with long periods of darkness. Here, creatures like the Arctic fox and emperor penguin have developed adaptations such as insulating body coverings and social behaviors that help conserve heat.
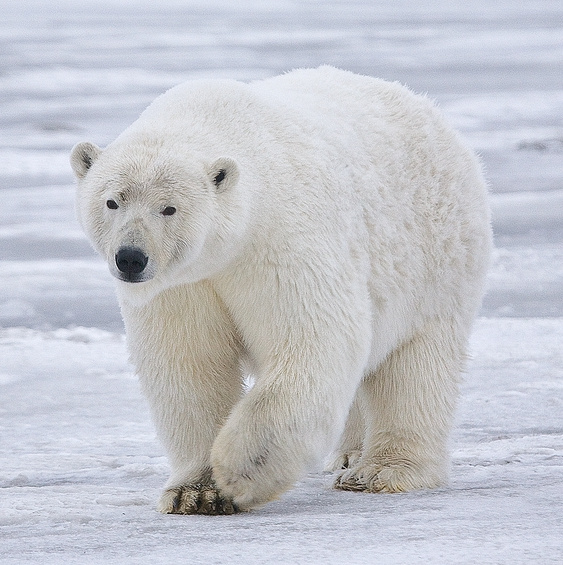

A polar bears thick fur and blubber are critical adaptations for Arctic survival
Conversely, deserts are known for their scorching heat and scarcity of water. Animals such as camels and fennec foxes have evolved strategies for water conservation and behavioral adaptations like nocturnal activity to avoid the heat of the day.
In the deep sea, life exists under immense pressure and in complete darkness. Creatures such as the anglerfish use bioluminescence to attract prey, while others have developed unique physiological adaptations to withstand the crushing pressures of the deep ocean.
High altitude environments, such as mountain ranges, present challenges of low oxygen levels and harsh weather. Animals like the snow leopard and the Andean condor have developed specialized lungs and efficient oxygen usage to thrive at high altitudes.
In summary, the animals list that thrive in these extreme environments demonstrate the remarkable adaptability of life. Their adaptations are not only fascinating but also critical for their survival, showcasing the resilience of nature in the face of daunting challenges. Understanding these adaptations enriches our appreciation of biodiversity and the intricate balance of ecosystems on our planet.
Arctic and Antarctic Adaptations
The Arctic and Antarctic regions are some of the most inhospitable places on Earth, with temperatures plunging to extreme lows and vast stretches of ice dominating the landscape. Yet, these regions teem with life, all thanks to the incredible adaptations of the animals that call them home. From the thick fur of polar bears to the unique behavioral strategies of penguins, these adaptations showcase nature’s resilience and ingenuity.
Thick Fur and Blubber in Polar Animals
In the icy realms of the Arctic and Antarctic, maintaining body heat is crucial for survival. One of the most striking adaptations to combat the cold is the development of thick fur and blubber in polar animals. These features serve as essential insulators, keeping animals warm even in sub-zero temperatures.
Polar bears, for instance, have a two-layered fur system: a dense underfur covered by guard hairs. This combination traps heat close to the body and is highly effective in insulating against the cold. Beyond fur, polar bears also have a thick layer of blubber under their skin, which serves as both an energy reserve during periods of scarce food and an additional layer of insulation.
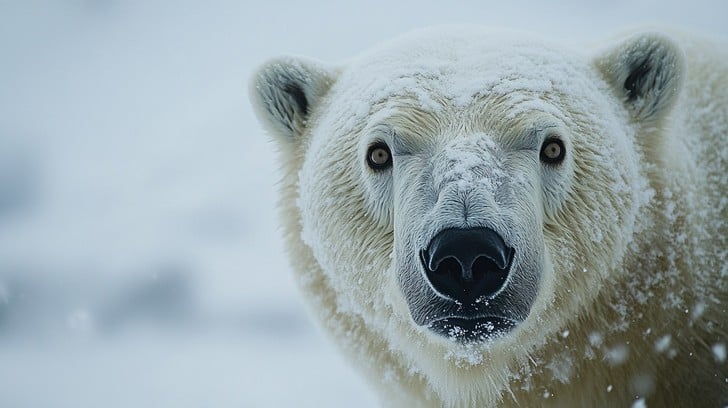

A polar bear with its thick fur in the snowy Arctic environment
Similarly, seals and whales rely heavily on blubber. For these marine mammals, the blubber not only keeps them warm but also aids in buoyancy, allowing them to navigate the icy waters with ease. The blubber can be several inches thick, providing substantial protection against the frigid ocean temperatures.
In the Antarctic, penguins have adapted through a combination of dense feathers and a thick layer of fat. Emperor penguins, the largest of the species, huddle together in large groups to conserve warmth, a behavioral adaptation that complements their physical traits.
Behavioral Strategies for Cold Survival
Beyond physical adaptations, many polar animals have developed behavioral strategies to survive the harsh conditions of their environments. These behaviors are often as critical to their survival as their physical traits.
One of the most notable behaviors is migration. Many bird species, such as the Arctic tern, undertake long migrations to escape the extreme cold. They travel thousands of miles to warmer climates during the winter months, returning to the Arctic only when temperatures rise.
Hibernation is another strategy employed by several Arctic animals, including the Arctic ground squirrel. These animals enter a state of reduced metabolic activity, allowing them to conserve energy during the coldest months when food is scarce. During hibernation, their body temperature drops significantly, and their heart rate slows, minimizing energy expenditure.
In the Antarctic, penguins have developed unique social behaviors to withstand the cold. Emperor penguins, for instance, form tightly packed huddles, taking turns to move from the outside to the center of the group, ensuring that all members share the warmth and protection from the wind.
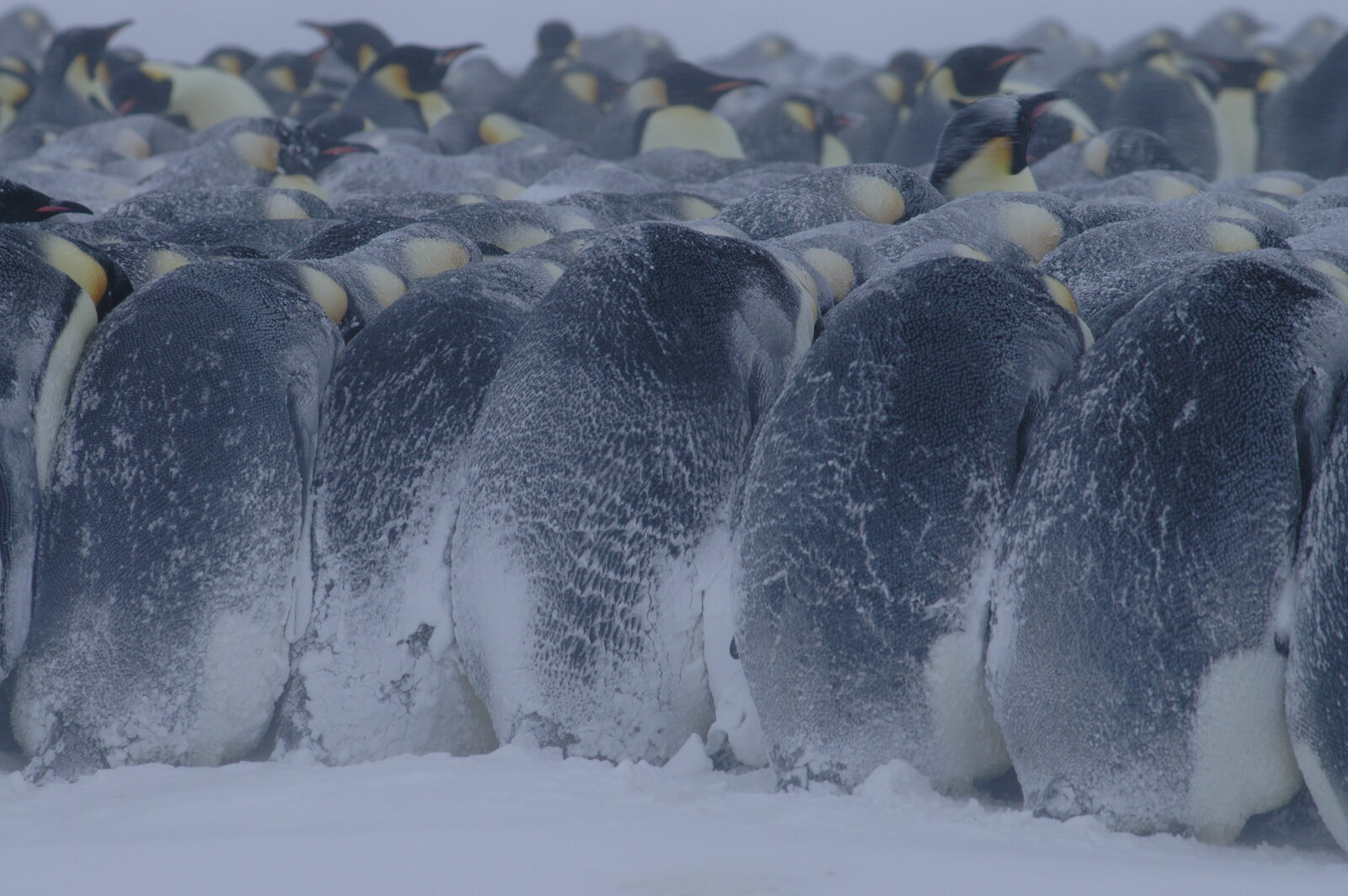

Emperor penguins huddling together to keep warm in Antarctica
Additionally, some animals exhibit seasonal changes in behavior. For example, the Arctic fox changes its hunting habits based on the season, relying on stored food caches during the winter when prey is scarce.
These physical and behavioral adaptations demonstrate the remarkable ability of animals to thrive in some of the planet’s most extreme environments. The diversity of strategies employed by Arctic and Antarctic animals is a testament to the power of evolution and the intricate balance of ecosystems in these regions. The animals list found in these icy habitats is a source of endless fascination and inspiration, highlighting nature’s incredible capacity for adaptation and survival.
Desert Adaptations
Water Conservation Techniques in Desert Animals
Deserts, with their scorching days and freezing nights, present a unique set of challenges for any creature trying to call this environment home. The key to survival here is effective water conservation. Animals have evolved remarkable adaptations that allow them to thrive in such arid conditions where water is a scarce commodity.
One of the most fascinating examples of water conservation can be found in the camel, often dubbed the “ship of the desert.” Camels can survive for weeks without water, thanks to their ability to withstand dehydration. They have specialized kidneys and intestines that enable them to absorb every possible drop of water from their food and urine. When they do have access to water, camels can drink up to 40 gallons in one go to replenish their reserves.
Similarly, the kangaroo rat is another desert dweller that has mastered water conservation. This small rodent, native to the deserts of North America, rarely drinks water. Instead, it obtains moisture from the seeds it consumes. The kangaroo rat’s kidneys are highly efficient, producing urine that is more concentrated than seawater, minimizing water loss.
Another marvel of desert adaptation is the thorny devil, a lizard found in Australia’s deserts. Its skin is covered with grooves that channel dew and rain directly to its mouth. This unique adaptation allows the thorny devil to collect and drink water from the slightest moisture in the environment.
These examples illustrate the ingenuity of nature, where each species’ survival hinges on its ability to adapt to the harsh realities of the desert. These animals form a crucial part of the animals list that showcases nature’s resilience and resourcefulness in extreme habitats.
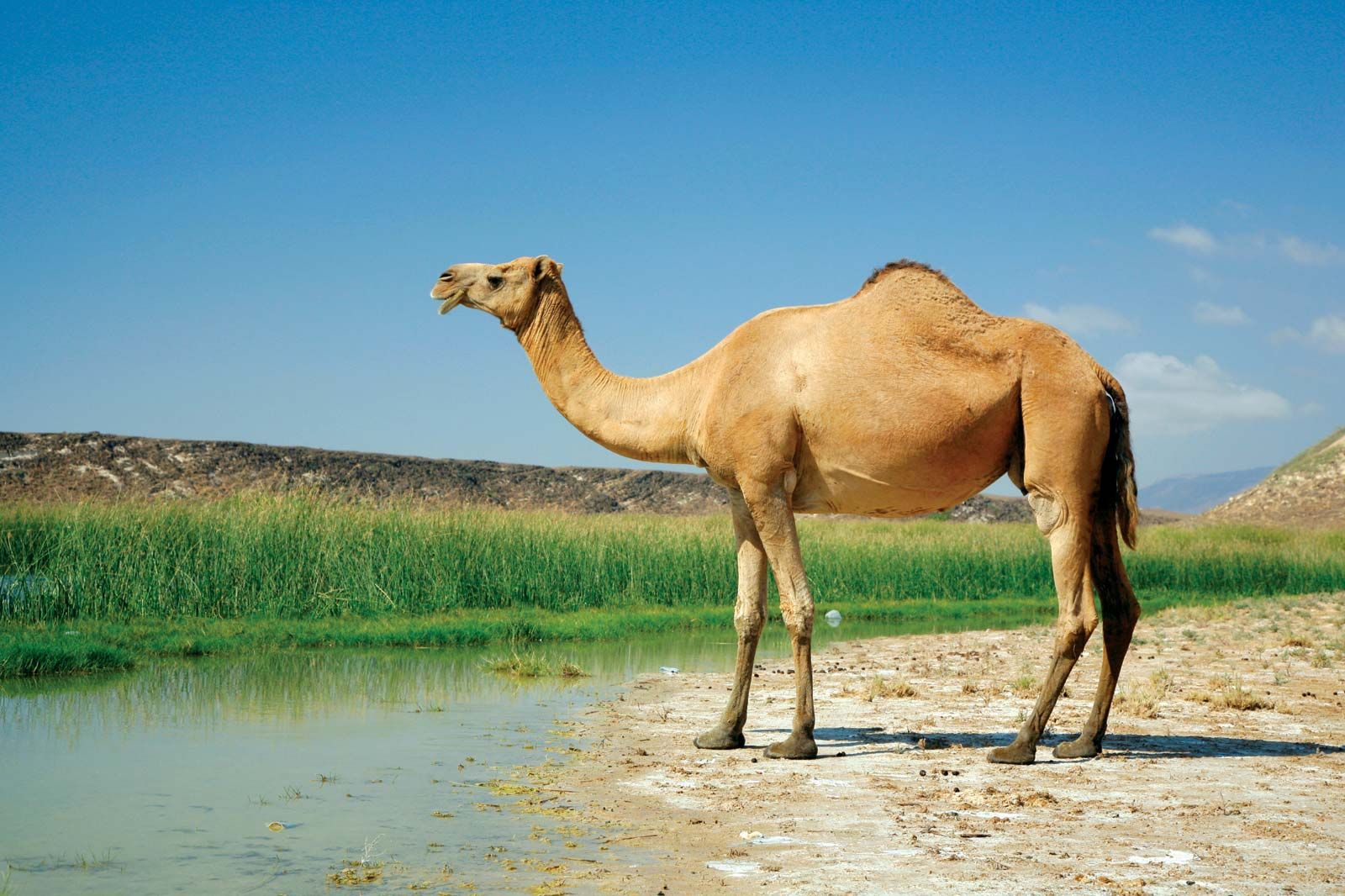

A camel the quintessential desert survivor conserving water efficiently
Nocturnal and Burrowing Behaviors
The desert’s extreme temperatures mean that many animals have adopted nocturnal lifestyles to avoid the blistering heat of the day. This shift not only helps them regulate their body temperature but also reduces water loss through evaporation.
The fennec fox, with its large ears and small body, is a prime example. Its nocturnal habits help it avoid the sun, while its large ears dissipate heat, keeping it cool during the night. The fennec fox also possesses thick fur that insulates it from the cold desert nights.
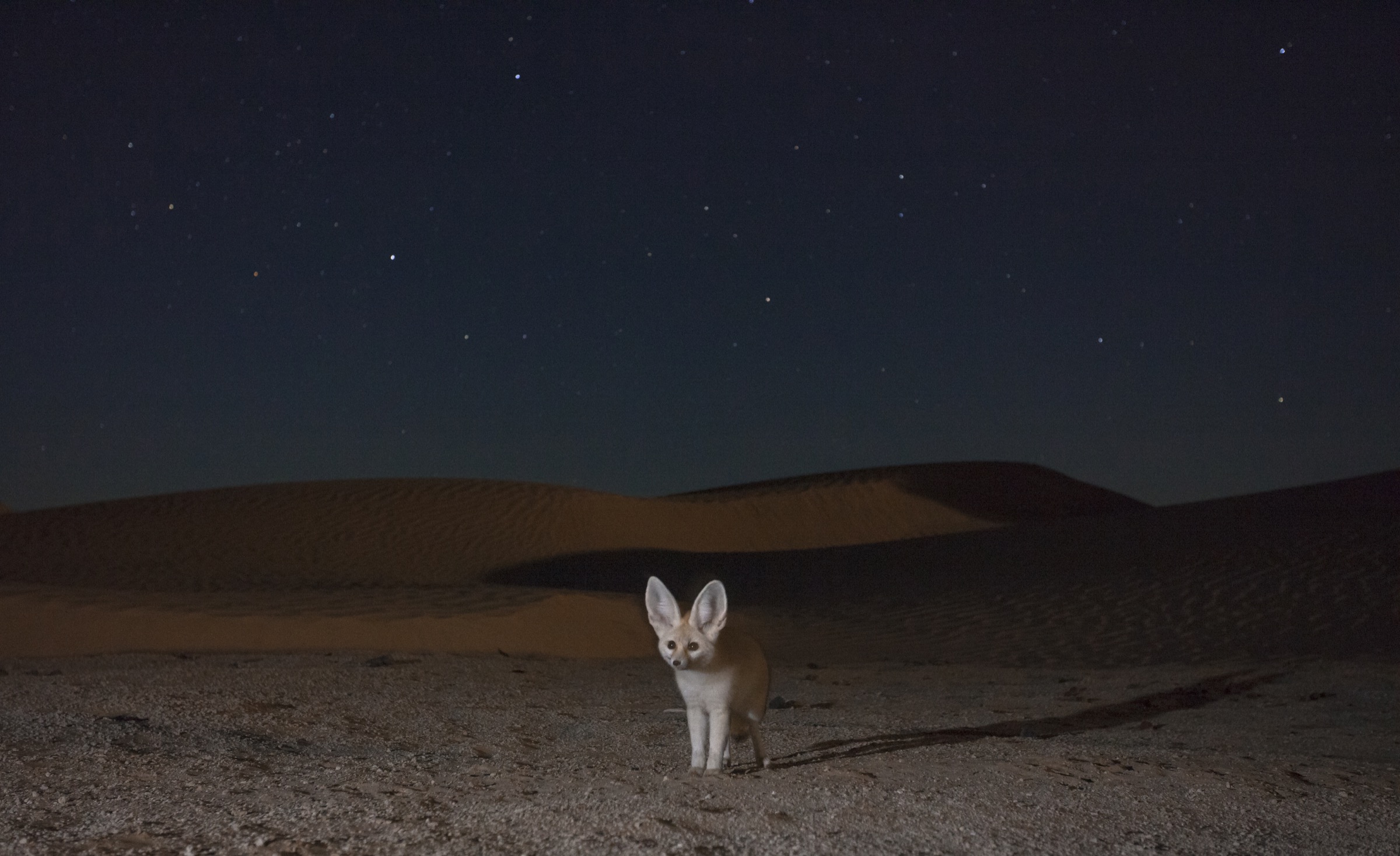

A fennec fox utilizing its nocturnal habits to stay cool
In contrast, burrowing is another effective strategy used by desert animals to escape the heat. The desert tortoise spends the majority of its life underground in burrows, which provide a stable microclimate and protection from predators. These burrows maintain a relatively constant temperature, offering a respite from the desert’s temperature swings.
The meerkat is another burrowing expert, living in large colonies with complex networks of tunnels. These social animals not only escape the heat by retreating into their burrows during the day but also use them as a safe haven from predators.
By adopting these behaviors, desert animals effectively manage the harsh environmental challenges they face daily. The adaptations of these creatures are not only fascinating but also a testament to the incredible versatility of life. As we explore the animals list, we gain deeper insights into how life persists in some of the most unforgiving places on Earth.
Deep Sea Adaptations
The deep sea is one of Earth’s most mysterious and extreme environments, characterized by darkness, freezing temperatures, and immense pressure. Despite these harsh conditions, a myriad of fascinating creatures have evolved unique adaptations to thrive in this underexplored realm. Let’s delve into the ways these creatures adapt, focusing on bioluminescence, camouflage, and pressure and temperature tolerance.
Bioluminescence and Camouflage
In the deep sea, where sunlight does not penetrate, bioluminescence becomes an invaluable adaptation. This phenomenon is the production and emission of light by living organisms, a trait that many deep-sea creatures utilize for various purposes, including communication, predation, and evasion from predators.
Bioluminescent creatures like the anglerfish use this adaptation to lure prey. The anglerfish’s bioluminescent lure, a fleshy growth on its head, attracts smaller fish close enough to be devoured. This clever use of light is a perfect example of nature’s ingenuity in the deep sea.
Camouflage is another critical adaptation that deep-sea creatures employ. Many animals have evolved to blend seamlessly into their dark surroundings. The giant squid, for instance, has the ability to change the color of its skin to match the dark depths, making it nearly invisible to predators. Additionally, some species, like the glass squid, are nearly transparent, reducing their visibility in the dim waters.
This combination of bioluminescence and camouflage not only aids in survival but also illustrates the diverse strategies creatures employ in the deep sea. By developing these adaptations, animals can effectively navigate the challenges of their environment while maintaining a place in the deep-sea animals list.
Pressure and Temperature Tolerance
The deep sea is characterized by crushing pressures and frigid temperatures, conditions that would be lethal to most surface-dwelling organisms. However, deep-sea animals have evolved remarkable adaptations to withstand these extremes.
The pressure in the deep sea can reach over 1,000 times that of the surface, yet creatures like the deep-sea octopus and viperfish live comfortably in these conditions. These animals have adapted by developing flexible, gelatinous bodies that can withstand immense pressure without collapsing. Their cellular structures have also evolved to maintain function under high pressure, allowing these organisms to thrive where others cannot.
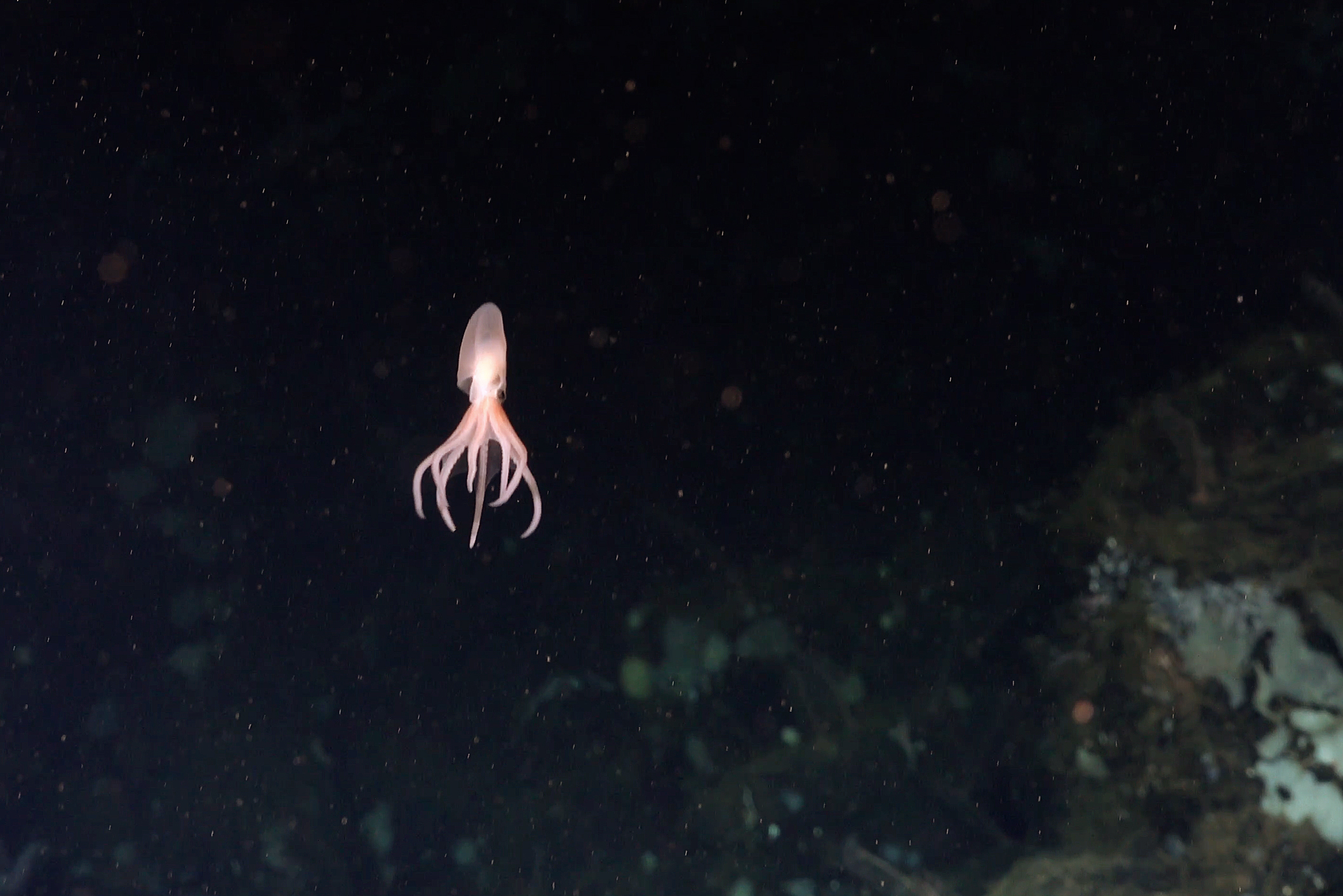

A deepsea octopus a master of surviving highpressure environments
Temperature tolerance is another critical adaptation. The deep sea is a cold environment, with temperatures hovering just above freezing. Deep-sea creatures have evolved specialized proteins and enzymes that remain functional at low temperatures. For instance, the icefish, found in Antarctic waters, possess antifreeze proteins in their blood, preventing it from freezing in icy waters.
These adaptations demonstrate the incredible resilience of deep-sea animals, showcasing their ability to endure and prosper in some of the most hostile environments on Earth. By studying these adaptations, we gain insight into the vast and varied animals list that populate our planet, highlighting the remarkable capabilities of life to persist in even the most extreme conditions.
Adaptations in High Altitude Environments
High altitude environments present unique challenges to animal life due to their thin atmosphere and cold temperatures. The creatures that thrive in these regions have developed remarkable adaptations that allow them to survive and flourish. Let’s delve into the fascinating world of these adaptations.
Efficient Oxygen Usage in Mountain Creatures
At high altitudes, the oxygen levels are significantly lower than at sea level, which presents a major challenge for most life forms that depend on a constant supply of oxygen for cellular functions. However, mountain creatures have evolved various adaptations to overcome this scarcity.
One of the most fascinating examples is the Bar-headed Goose, known for its incredible migratory journey over the Himalayas. This bird has a higher density of capillaries in its muscles, allowing for more efficient oxygen delivery. Additionally, its hemoglobin has a higher affinity for oxygen, enabling it to capture and utilize oxygen more effectively even in the thin air of high altitudes.
Similarly, mammals such as the Yak have evolved larger lungs and a greater capacity for oxygen uptake. These adaptations allow them to breathe more efficiently, maximizing the amount of oxygen absorbed with each breath. Furthermore, the Tibetan Antelope, or Chiru, has a high concentration of red blood cells, which enhances its ability to transport oxygen throughout its body, sustaining its high-altitude endurance.

Barheaded Goose soaring over the Himalayas
Specialized Limbs and Body Structures
In addition to efficient oxygen usage, animals in high altitudes have developed specialized limbs and body structures to navigate the rugged and often icy terrain. These adaptations not only aid in locomotion but also help in thermoregulation and survival.
The Snow Leopard, with its thick fur and long, bushy tail, is perfectly adapted to the cold, mountainous environments of Central Asia. Its large paws act like snowshoes, distributing weight more evenly and preventing it from sinking into the snow. This adaptation is crucial for stealthily stalking prey on snowy slopes.
Mountain goats, such as the Alpine Ibex, exhibit extraordinary climbing abilities, thanks to their specialized hooves. These hooves have a hard outer rim for gripping rocky surfaces and a soft, concave underside that provides traction. This unique hoof structure allows them to scale steep, rocky cliffs with incredible agility and precision, escaping predators and reaching vegetation inaccessible to other herbivores.
Moreover, animals like the Andean Condor have large wingspans that enable them to soar effortlessly at high altitudes, conserving energy while searching for food across vast mountain ranges.
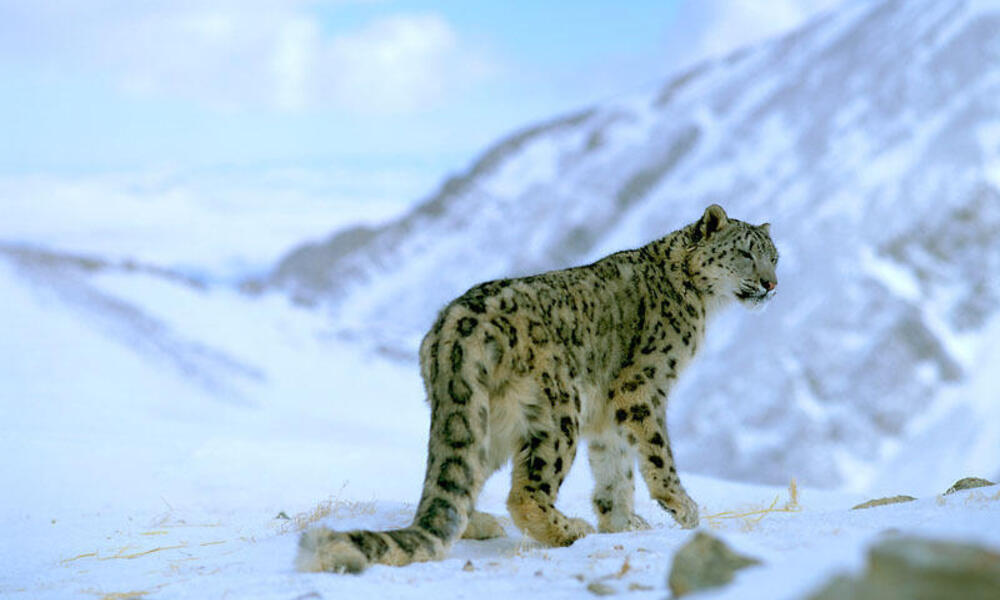

Snow Leopard navigating the snowy terrain
Through these incredible adaptations, animals have not only survived but have thrived in some of the most inhospitable environments on Earth. These adaptations are a testament to the ingenuity of nature and the relentless drive of life to persist against all odds. This exploration of the animals list in high-altitude environments serves as a reminder of the diverse strategies life employs to conquer challenges, inspiring curiosity and admiration for the natural world.
Reflecting on Nature’s Ingenuity
Nature has always been a masterful architect, and nowhere is this more evident than in the incredible adaptations animals have developed to thrive in some of the most extreme environments on Earth. These adaptations are not mere survival tactics; they are exquisite examples of nature’s ingenuity, showcasing the complex interplay between organisms and their habitats.
The Marvel of Evolutionary Design
The process of adaptation is a testament to the power of evolutionary design. Over countless generations, animals have honed their abilities, resulting in specialized traits that enable them to survive and flourish where others could not. From the thick fur and blubber of polar bears that insulate them against the biting cold of the Arctic, to the water-conserving abilities of desert creatures, each adaptation is a solution to a unique environmental challenge.
Consider how the nocturnal animals list includes creatures like the owl and the bat, which have evolved heightened senses to navigate and hunt in the darkness. This evolution reflects a broader pattern of adaptation across the animal kingdom, where changes in behavior, physiology, and anatomy enable species to exploit new niches and reduce competition.
Ingenious Survival Strategies
One of the most astonishing aspects of animal adaptations is the variety of survival strategies they employ. In desert environments, where water is scarce, animals have developed remarkable techniques for conserving moisture. For instance, the kangaroo rat can survive without drinking water, obtaining all the moisture it needs from the seeds it consumes. This level of adaptation is a prime example of the animals list showcasing nature’s ingenuity.
In the deep sea, animals face the dual challenges of high pressure and low light. Creatures like the anglerfish have evolved bioluminescent lures to attract prey in the pitch-black depths, while their bodies are adapted to withstand crushing pressures that would incapacitate land-dwelling organisms. These adaptations highlight the incredible versatility of life, thriving against all odds in environments that seem inhospitable.
Lessons from the Natural World
Reflecting on these adaptations offers valuable lessons for humanity. The intricate solutions found in nature can inspire technological and scientific innovation. By studying the vertebrate animals list, for instance, we can gain insights into biomechanics, leading to advancements in robotics and prosthetics. The efficiency of certain animal adaptations also inspires sustainable practices, such as the development of water-saving technologies modeled after desert plants and animals.
Moreover, these adaptations remind us of the delicate balance within ecosystems. Each adaptation is a response to specific environmental pressures, underscoring the interconnectedness of life and the importance of preserving habitats. As we face global environmental challenges, understanding and learning from these natural strategies becomes increasingly crucial.
The Endless Wonders of Adaptation
In conclusion, the study of animal adaptations is not just an exploration of survival; it is a journey into the marvels of nature’s creativity and resourcefulness. Each adaptation tells a story of resilience and innovation, enriching our understanding of the natural world. As we continue to uncover the secrets behind these fascinating traits, we gain not only knowledge but also an appreciation for the intricate tapestry of life on Earth.
Join us at WildWhiskers, where we celebrate these incredible stories and delve deeper into the wonders of the animal kingdom. With “Tiny Tails, Big Stories!”, we invite you to explore, learn, and share your passion for the diverse and magical lives of animals around us.