India, a land of unparalleled biodiversity, is home to some of the most majestic and endangered animals on our planet. From the iconic Bengal tiger prowling through dense forests to the rare Indian rhinoceros grazing in grasslands, these creatures are not only symbols of natural beauty but are also vital to the health of ecosystems. However, the rapid pace of industrialization, coupled with habitat destruction, poaching, and the insidious effects of climate change, is pushing many of these species perilously close to extinction. The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) has flagged numerous Indian species as endangered or critically endangered, highlighting the urgent need for conservation efforts.
In this blog, we will delve into the rich tapestry of India’s flora and fauna, exploring the major threats that endanger these species and the intricate web of ecosystems that depend on their survival. We’ll examine the challenges faced by the Bengal tiger, Asian elephant, and Indian rhinoceros, among others, and celebrate the successes of conservation initiatives that are making a difference. More importantly, we’ll discuss how every individual can contribute to the preservation of these irreplaceable treasures.
This is not just a call to action but a shared responsibility. The survival of these endangered animals in India is crucial not only for ecological balance but also for the legacy we leave for future generations. Join us as we explore the urgent need for conservation and discover how we can all play a part in safeguarding these magnificent creatures.
Understanding the Biodiversity of India
Richness of India’s Flora and Fauna
India is a treasure trove of biodiversity, often celebrated for its rich tapestry of ecosystems ranging from lush tropical rainforests to arid deserts. This incredible diversity is not just a testament to the country’s varied climates and landscapes but also a crucial pillar for the global ecological balance. With over 45,000 species of plants and 91,000 species of animals, India stands as a beacon of biological wealth. It is home to several biodiversity hotspots like the Western Ghats and the Eastern Himalayas, each harboring unique species not found anywhere else on Earth.
The flora of India is as diverse as it is abundant. From the towering conifers of the Himalayan forests to the sprawling mangroves of the Sundarbans, India’s plant life supports countless animal species, providing food and shelter. The expansive grasslands and deciduous forests are vital habitats for many of the country’s iconic wildlife, including the endangered animals in India like the Bengal tiger and the Indian rhinoceros.
On the faunal front, India is equally impressive. It is one of the few countries in the world where both lions and tigers coexist. The subcontinent’s diverse ecosystems support a wide array of mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and insects. Species such as the Asiatic lion, the snow leopard, and the Indian elephant not only captivate wildlife enthusiasts but also play critical roles in their respective ecosystems.
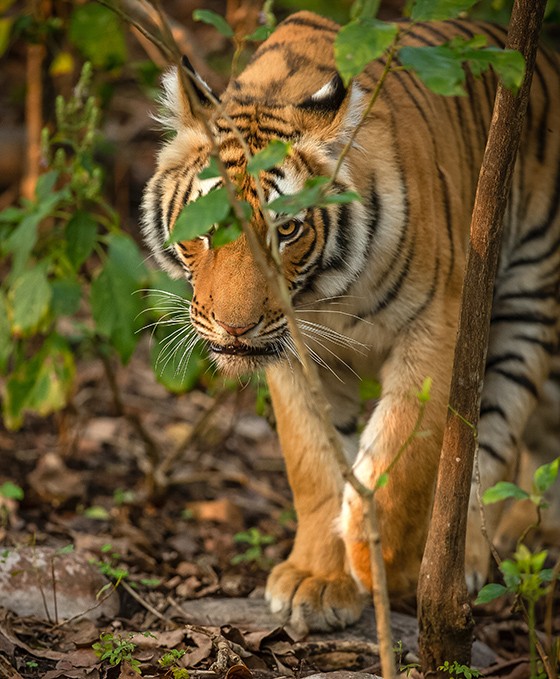

A glimpse of Indias diverse wildlife in a thriving forest ecosystem
Importance of Biodiversity for Ecosystems
The importance of biodiversity in India extends beyond mere statistics and lists of species. It is the very fabric that holds ecosystems together, ensuring their resilience and functionality. Each species, whether plant or animal, plays a specific role in its ecosystem, contributing to the intricate balance of nature.
Biodiversity ensures ecosystem services that are vital to human survival. These include the purification of air and water, pollination of crops, and regulation of climate. The dense forests of India act as carbon sinks, reducing the impact of climate change by absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. Mangroves protect coastlines from erosion and extreme weather events, while pollinators like bees and butterflies are essential for the production of fruits and vegetables, directly impacting food security.
Moreover, biodiversity is a reservoir of genetic information that can be pivotal in medical and scientific advancements. Many plants native to India have medicinal properties and have been used in traditional medicine for centuries. This genetic diversity is also a buffer against pests and diseases, ensuring agricultural sustainability.
The cultural significance of biodiversity cannot be overlooked either. Many Indian communities have deep-rooted connections to their natural surroundings, with flora and fauna featuring prominently in religious and cultural practices. These connections foster a sense of stewardship and conservation among local populations.
However, the richness of India’s biodiversity is under severe threat. Habitat destruction, climate change, and human encroachment are pushing many species towards extinction. The endangered animals in India, such as the Bengal tiger and the Indian rhinoceros, are symbolic of the urgent need for conservation efforts to preserve this irreplaceable natural heritage.
A thriving Indian forest ecosystem demonstrating biodiversity
Major Threats to Wildlife in India
India, with its breathtaking landscapes and diverse ecosystems, is home to an array of endangered animals that are integral to the planet’s biological heritage. However, these species face significant threats that jeopardize their survival. Understanding these threats is the first step towards effective conservation.
Habitat Destruction and Fragmentation
One of the most pressing concerns for wildlife in India is habitat destruction and fragmentation. Rapid urbanization, agricultural expansion, and industrial development have led to massive deforestation. The once vast and continuous habitats are now becoming isolated patches, making it difficult for animals to find food, mate, and migrate. This isolation not only reduces genetic diversity but also increases the chances of inbreeding, which can lead to weaker offspring.
For instance, the Bengal Tiger, an iconic symbol of India’s wildlife, requires large territories to hunt and roam. As forests are cleared for human settlements and agriculture, these majestic creatures find themselves confined to smaller areas, leading to increased human-tiger conflicts. Similarly, the Asian Elephant, known for its long migratory routes, is now restricted by roads, railways, and fences, leading to frequent and often fatal encounters with humans.
Poaching and Illegal Wildlife Trade
Poaching and illegal wildlife trade are among the most lucrative illicit activities worldwide, second only to drug trafficking. In India, this threat has led to a sharp decline in the populations of several species. The demand for animal parts, such as tiger bones, rhino horns, and elephant tusks, drives this illegal trade, with devastating effects on wildlife.
The Indian Rhinoceros, once widespread across the northern plains, has been hunted relentlessly for its horn, believed to have medicinal properties in some cultures. Similarly, the Asian Elephants are targeted for their ivory, despite international bans. The situation is exacerbated by the fact that these animals are often killed indiscriminately, with entire herds sometimes wiped out in a single poaching incident.
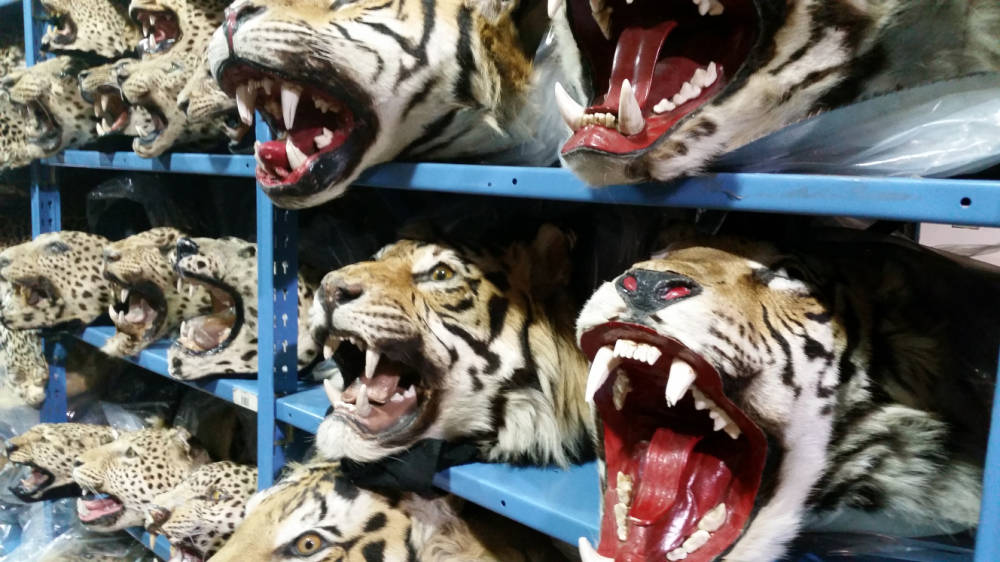

Confiscated illegal wildlife products in India
Impact of Climate Change
Climate change poses a significant, albeit often underestimated, threat to India’s wildlife. The shifting climate alters habitats, disrupts food availability, and increases the frequency of extreme weather events. For instance, the Snow Leopard, which inhabits the high altitudes of the Himalayas, faces habitat loss due to warming temperatures that push the tree line upward.
Moreover, the changing monsoon patterns affect the water availability in rivers and wetlands, crucial for species like the Ganges River Dolphin. Increased temperatures and altered rainfall patterns can lead to droughts or floods, both of which have dire consequences for wildlife.
In conclusion, the major threats to endangered animals in India are interconnected, each exacerbating the other. Habitat destruction leads to increased human-wildlife conflict, poaching reduces already dwindling populations, and climate change adds unpredictability to their survival. Addressing these threats requires a multi-faceted approach, involving policy changes, community engagement, and global cooperation to ensure that India’s rich biodiversity is preserved for future generations.
Iconic Endangered Species in India
India’s rich tapestry of wildlife is woven with species that are not only integral to the ecosystem but also hold immense cultural and historical significance. Among these, certain species stand out due to their iconic status and the unique challenges they face in the wild. This section delves into the plight of the Bengal Tiger, the Asian Elephant, and the Indian Rhinoceros, highlighting their struggles and the conservation efforts underway to ensure their survival.
Bengal Tiger: The Struggle for Survival
The Bengal Tiger is perhaps the most emblematic of all endangered animals in India. As a symbol of strength and beauty, the Bengal tiger roams the dense forests and marshy grasslands of the Indian subcontinent. Despite its majestic presence, this magnificent predator is listed as endangered due to a myriad of threats that jeopardize its existence.
Habitat loss remains the primary threat to Bengal tigers. As human populations expand, forests are cleared for agriculture, settlements, and infrastructure projects, leading to a devastating fragmentation of the tiger’s natural habitat. This not only reduces their living space but also isolates populations, making it difficult for tigers to find mates and maintain genetic diversity.
Poaching is another significant threat. Tigers are hunted for their pelts and body parts, which are highly valued in illegal wildlife trade markets. Despite stringent laws and increased patrolling, poaching continues to threaten their numbers.
Conservation efforts such as Project Tiger, launched in 1973, have made considerable strides in stabilizing and even increasing tiger populations in certain reserves. However, the battle is far from over, and continuous efforts are required to ensure the survival of this iconic species.
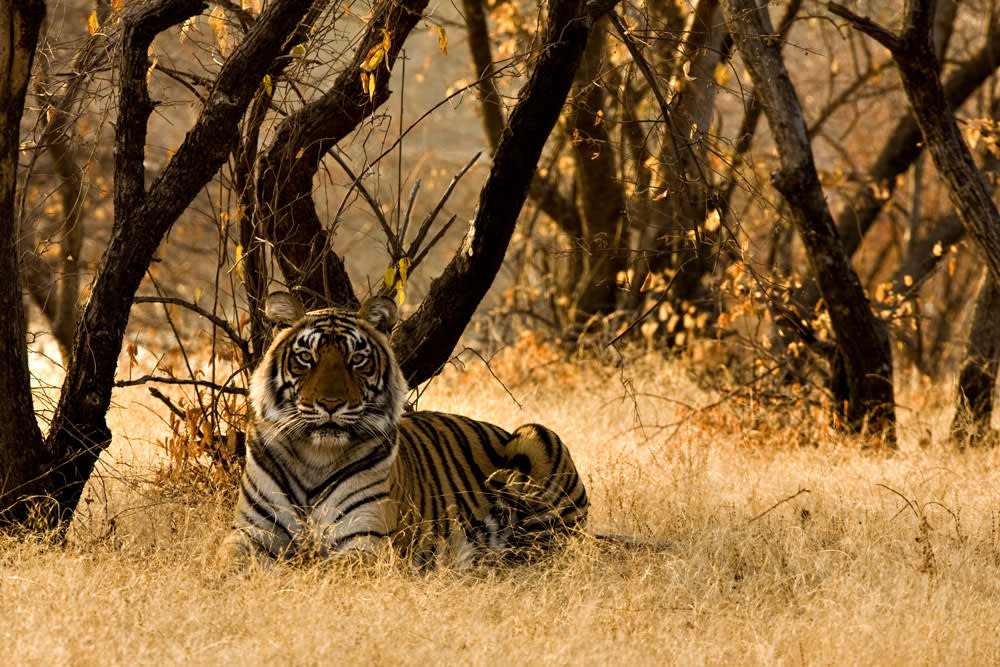

A majestic Bengal tiger prowling through its natural habitat in India
Asian Elephant: Challenges and Conservation Efforts
The Asian Elephant is another keystone species that faces significant threats. Revered in Indian culture and religion, elephants play a crucial role in maintaining forest ecosystems and biodiversity. Yet, they are classified as endangered due to habitat destruction, human-elephant conflict, and poaching.
With the expansion of agricultural lands, elephants have lost vast tracts of their natural habitat, forcing them into smaller areas where they come into conflict with human populations. These conflicts often result in tragic consequences, with both human and elephant casualties.
In addition to habitat loss, poaching for ivory continues to pose a threat to Asian elephants, despite international bans on the ivory trade. Conservationists are working tirelessly to mitigate these threats through various initiatives, such as creating elephant corridors that connect fragmented habitats, thus allowing elephants to migrate safely.
Community-based conservation programs have also been initiated to reduce human-elephant conflict, providing local communities with education and resources to coexist peacefully with these gentle giants.
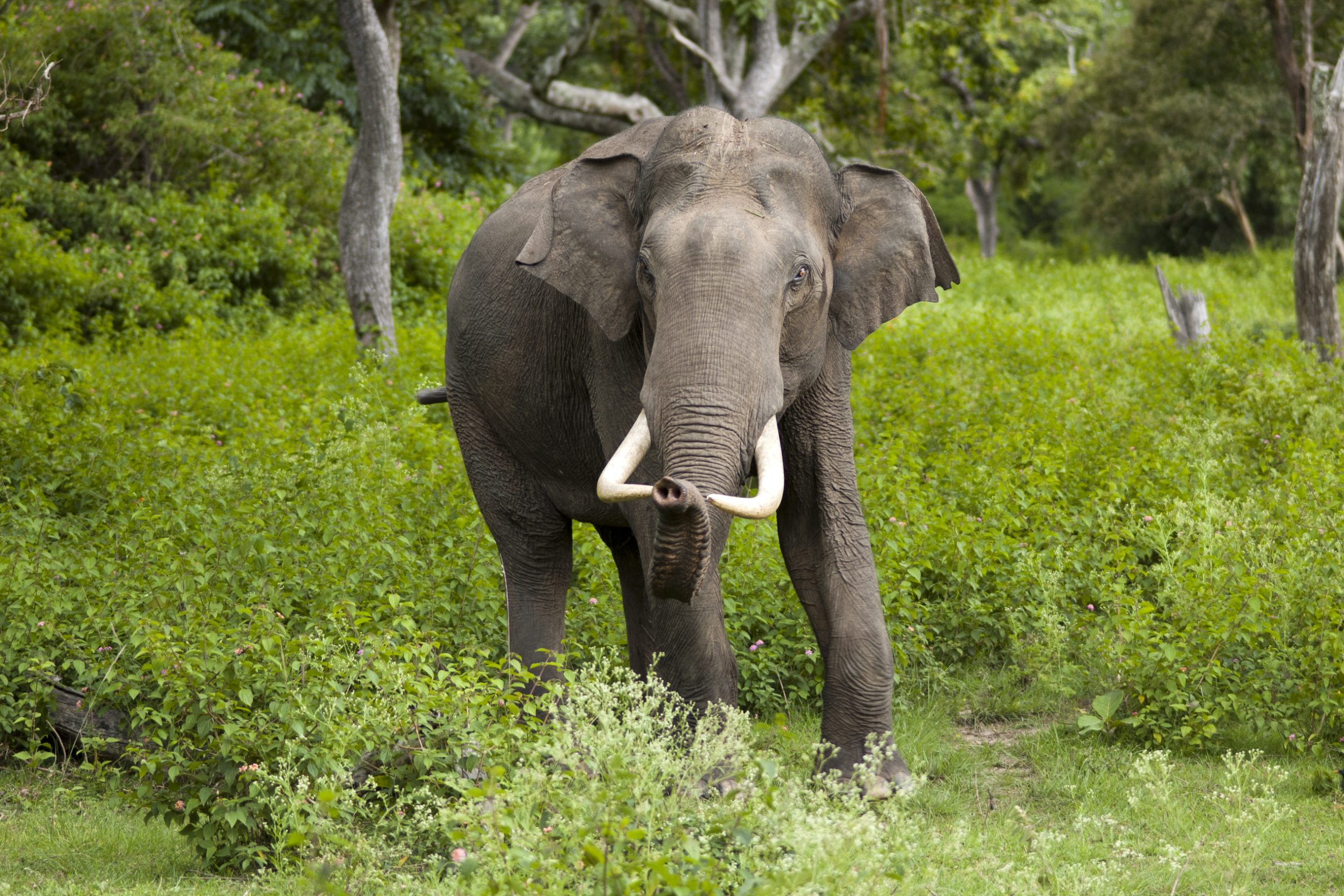

An Asian elephant gracefully walking through a wildlife sanctuary in India
Indian Rhinoceros: Protecting the Rare Giants
The Indian Rhinoceros, also known as the greater one-horned rhinoceros, is a creature of formidable presence and unique appearance. Once widespread across the northern Indian subcontinent, today, these rhinoceroses are primarily found in protected areas in India and Nepal.
The primary threat to the Indian rhinoceros is poaching for its horn, which is erroneously believed to have medicinal properties and is highly coveted in illegal markets. Additionally, habitat loss due to agricultural expansion and human encroachment poses significant challenges to their survival.
Successful conservation efforts have been implemented, particularly in Kaziranga National Park, where strict protection measures and anti-poaching initiatives have led to a gradual increase in their population. Translocation projects are also underway to expand their range and reduce the risk of disease and natural disasters impacting a concentrated population.
Despite these efforts, the Indian rhinoceros remains vulnerable, and continued international cooperation and stringent enforcement of anti-poaching laws are crucial to ensuring its continued existence.

An Indian rhinoceros grazing peacefully in Kaziranga National Park
The survival of these iconic species is a testament to the broader struggle of endangered animals in India. Their stories highlight the urgent need for continued conservation efforts and the collaborative role of governments, NGOs, and individuals in preserving India’s rich biodiversity for future generations.
Conservation Efforts and Success Stories
The conservation of endangered animals in India is not just a national concern; it is a global responsibility. With its rich biodiversity, India has seen significant efforts and successes in protecting its endangered species. These efforts are a combination of government initiatives, legal frameworks, and the crucial involvement of NGOs and local communities.
Government Initiatives and Legal Frameworks
The Indian government has been at the forefront of wildlife conservation, implementing several key initiatives and legal frameworks to protect its endangered species. One of the most notable efforts is Project Tiger, launched in 1973. This project aimed to create a safe haven for the Bengal tiger, whose numbers were rapidly declining due to poaching and habitat loss. Over the years, Project Tiger has expanded to include 50 tiger reserves across the country, leading to a gradual increase in the tiger population.
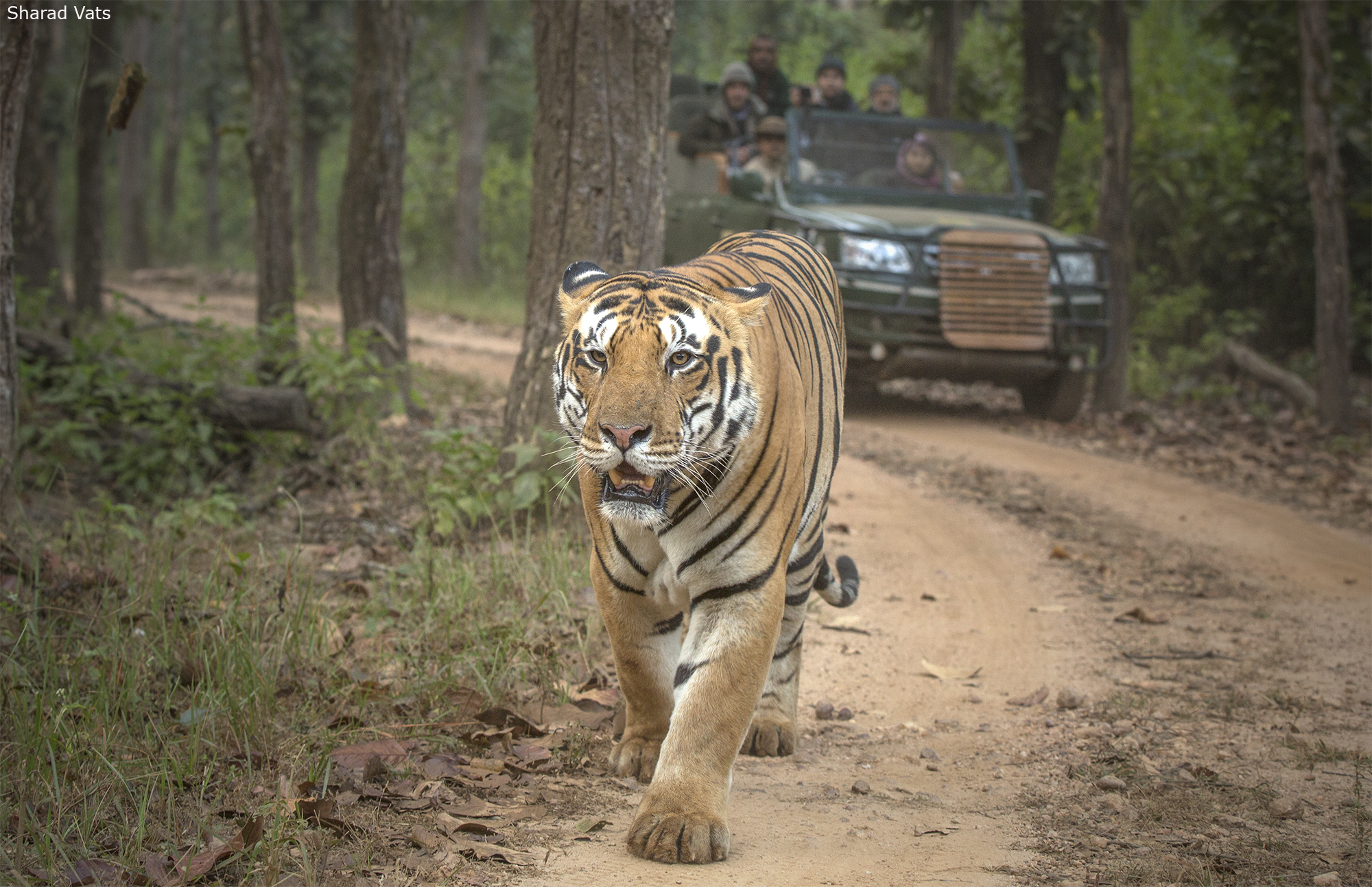

A majestic Bengal tiger in its natural habitat
Another significant legal framework is the Wildlife Protection Act of 1972, which provides a comprehensive legal structure for the protection of endangered species and their habitats. This act prohibits hunting and provides for the establishment of wildlife sanctuaries and national parks, which serve as critical refuges for endangered animals in India.
Moreover, the National Wildlife Action Plan outlines strategic actions for the conservation of wildlife and their habitats. This plan emphasizes the integration of conservation with local community development, ensuring that conservation efforts are sustainable and benefit local populations.
Role of NGOs and Community Involvement
While government initiatives lay the foundation for wildlife conservation, the role of Non-Governmental Organizations (NGOs) and community involvement cannot be overstated. NGOs like the Wildlife Trust of India and the World Wildlife Fund have been pivotal in implementing grassroots conservation programs. These organizations work closely with local communities to promote awareness, education, and sustainable practices that benefit both wildlife and people.
Community-driven conservation is a critical component of protecting endangered animals in India. In many regions, local communities have taken the lead in conservation efforts, recognizing the intrinsic link between their livelihoods and the health of ecosystems. For example, in the Gir Forest, home to the Asiatic lion, local communities have been actively involved in conservation activities, leading to a steady increase in the lion population.

Local community members participating in conservation efforts
Eco-tourism initiatives have also played a significant role in involving communities in conservation. By promoting eco-tourism, communities benefit economically, which in turn incentivizes them to protect local wildlife. This approach has been especially successful in areas like the Kaziranga National Park, known for its population of the Indian rhinoceros.
In conclusion, the combined efforts of the government, NGOs, and local communities have resulted in numerous conservation success stories across India. These efforts demonstrate that with coordinated action and commitment, it is possible to secure a future for endangered animals in India, ensuring that these majestic creatures continue to thrive for generations to come.
How Individuals Can Contribute to Conservation
The survival of endangered animals in India is not just the responsibility of the government or conservation organizations. It is a collective duty that each individual can participate in, ensuring these majestic creatures continue to thrive in their natural habitats. Here’s how every citizen can play a pivotal role in this mission:
Raising Awareness and Education
One of the most impactful ways individuals can contribute to conservation efforts is by raising awareness about the plight of endangered animals in India. Education plays a crucial role in altering perceptions and inspiring action. By educating ourselves and others, we can foster a deeper understanding and appreciation for wildlife and the ecosystems they inhabit.
- Community Engagement: Hosting or participating in local workshops, seminars, or discussion groups can be effective in spreading awareness. These platforms can serve as educational hubs where individuals learn about the challenges faced by endangered species and the importance of biodiversity.
- Utilizing Social Media: In today’s digital age, social media is a powerful tool. Platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter can be used to share information, stories, and updates about endangered animals in India. By creating compelling content, individuals can engage a broader audience and encourage them to take action.
- Educational Programs: Schools and universities can incorporate wildlife conservation topics into their curricula. Field trips to national parks and wildlife sanctuaries can provide students with firsthand experience, fostering a lifelong appreciation for nature.
Students engaged in a wildlife conservation workshop
Supporting Sustainable Practices
Supporting and adopting sustainable practices is another vital way individuals can contribute to the conservation of endangered animals in India. Sustainable living not only benefits the environment but also aids in reducing the human footprint on wildlife habitats.
- Eco-Friendly Lifestyle: Adopting an eco-friendly lifestyle by reducing waste, recycling, and opting for sustainable products can significantly lessen environmental impact. Choosing products that do not harm wildlife or contribute to habitat destruction is an important step toward supporting conservation.
- Responsible Tourism: When visiting wildlife reserves and national parks, it is crucial to practice responsible tourism. Following park guidelines, respecting wildlife, and avoiding littering can help preserve these areas for future generations. Supporting local eco-tourism initiatives also provides economic benefits to communities and promotes conservation efforts.
- Supporting Wildlife NGOs: Financially supporting or volunteering with wildlife NGOs and conservation groups enables these organizations to continue their vital work. These groups often rely on public support to fund research, on-the-ground conservation projects, and educational campaigns.
By engaging in these activities, individuals can make a profound difference in the fight to save endangered animals in India. Every small action contributes to the larger goal of preserving biodiversity and ensuring the survival of these incredible species. Let us harness the power of knowledge and sustainable living to secure a future where wildlife and humans coexist harmoniously.
The Path Forward for India’s Wildlife Conservation
The road ahead for India’s wildlife conservation is both challenging and promising. As one of the most biodiverse nations on Earth, India holds the key to not only its own ecological future but also the global environmental landscape. Preserving the country’s wildlife is a multifaceted effort that requires strategic actions, policy reforms, and active community involvement.
Implementing Robust Conservation Policies
To safeguard the future of endangered animals in India, it is crucial to enforce and strengthen existing conservation policies. The Wildlife Protection Act of 1972 has laid the groundwork for protecting endangered species, but its implementation needs to be more rigorous. Enhancing legal frameworks and introducing stricter penalties for poaching and illegal wildlife trade can serve as deterrents against these crimes. Additionally, integrating wildlife corridors into urban planning can help mitigate habitat fragmentation and ensure safe passage for migratory species.
Wildlife corridor providing safe passage for animals
Leveraging Technology in Conservation Efforts
Technology can play a pivotal role in wildlife conservation. From using drones for monitoring poaching activities to deploying AI for tracking animal populations, tech innovations offer new avenues for protecting endangered species. Satellite imaging can help conservationists monitor habitat changes, while GPS collars on animals like tigers and elephants can provide valuable data on their movements and behaviors.
Promoting Community-Based Conservation
Empowering local communities to take charge of conservation efforts can lead to sustainable outcomes. By involving indigenous populations and local stakeholders in decision-making processes, conservation initiatives can become more inclusive and effective. Community-based ecotourism, for instance, not only raises awareness but also provides economic incentives for locals to protect their natural heritage. Such grassroot movements can be a powerful force in the fight to save endangered animals in India.

Local community involved in wildlife conservation efforts
Expanding Educational Programs
Education is a cornerstone of long-term conservation success. By incorporating wildlife conservation topics into school curricula and organizing awareness campaigns, future generations can be equipped with the knowledge and passion to protect their environment. Educational programs that focus on the importance of biodiversity and the threats faced by various species can instill a sense of responsibility and stewardship in young citizens.
Strengthening International Cooperation
Wildlife conservation is a global concern, and international cooperation is vital. India can benefit from and contribute to global conservation efforts through knowledge exchange, collaborative research, and joint initiatives. By partnering with international organizations, India can access resources, expertise, and funding necessary for comprehensive conservation strategies.
Encouraging Sustainable Development
Balancing economic growth with ecological preservation is essential for the future of India’s wildlife. Developing sustainable practices in agriculture, forestry, and tourism can minimize environmental impact. Encouraging industries to adopt green technologies and reduce carbon footprints can help mitigate the effects of climate change on wildlife habitats.

Sustainable farming practices in India
The Role of Citizens in Conservation
Every individual can contribute to wildlife conservation by adopting sustainable lifestyles, supporting conservation organizations, and advocating for policy changes. Simple actions like reducing plastic use, supporting eco-friendly products, and participating in local conservation activities can collectively make a significant impact.
Conclusion
The path forward for India’s wildlife conservation is a shared journey that requires determination, innovation, and cooperation. By building on existing efforts and exploring new avenues, India can secure a future where its rich biodiversity thrives alongside human development. The survival of endangered animals in India is not just an environmental issue but a testament to our commitment to preserving the natural world for future generations.
WildWhiskers is a dedicated news platform for animal lovers around the world. From heartwarming stories about pets to the wild journeys of animals in nature, we bring you fun, thoughtful, and adorable content every day. With the slogan “Tiny Tails, Big Stories!”, WildWhiskers is more than just a news site — it’s a community for animal enthusiasts, a place to discover, learn, and share your love for the animal kingdom. Join WildWhiskers and open your heart to the small but magical lives of animals around us!