In the swirling dance of life on Earth, animals going extinct cast a sobering shadow over our planet’s future. As we stand at the precipice of a new era, the loss of species is not just a distant echo from the past but an urgent call to action today. This blog delves into the heart of extinction, unraveling the complexities behind why certain animals recently extinct and others teeter on the brink. From the haunting tale of the Bramble Cay Melomys to the critically endangered Vaquita, we explore the threads of human activity and environmental change that drive species towards oblivion.
The reality is stark: animals close to extinction may vanish forever if we do not act swiftly. With the clock ticking towards 2025, species like the Javan Rhino and Amur Leopard face dire prospects. Yet, there is hope. Conservation efforts, both large and small, are making waves across the globe, offering a lifeline to those species clinging to existence. This blog not only highlights the dire situation but also empowers you with knowledge on how to make a difference.
As we reflect on the broader implications of species loss, it becomes clear that the stakes are not just ecological but existential. The tapestry of life is rich and intricate, and each lost species is a thread removed from the vibrant fabric of biodiversity that sustains us all. Join us as we navigate these critical issues, armed with information and a shared responsibility to protect the natural world for future generations. Together, we can transform this crisis into an opportunity for profound change, safeguarding the incredible diversity of life that remains.
Understanding Extinction
Defining Extinction and Its Types
Extinction is a term that evokes a sense of irreversible loss, marking the end of a species’ existence on our planet. In biological terms, extinction occurs when there are no living members of a particular species left in the wild or captivity. The concept is straightforward, yet its implications are profound, signaling not just the loss of individual animals, but the disappearance of entire ecological roles and genetic lineages.
There are several types of extinction, each with its own context and implications:
- Globally Extinct: This is the absolute end of a species, with no individuals remaining alive anywhere on Earth. The Dodo (Raphus cucullatus), a flightless bird from Mauritius, is a classic example of a species that is globally extinct.
- Extinct in the Wild: In this scenario, a species no longer exists in its natural habitat but survives in captivity or controlled environments. For instance, the Scimitar-horned Oryx is extinct in the wild but has been successfully bred in captivity, with reintroduction efforts underway.
- Functionally Extinct: This occurs when the numbers of a species have dwindled to the point where they can no longer play a significant role in their ecosystem or reproduce enough to maintain a viable population. The Yangtze River Dolphin is often cited as functionally extinct due to its critically low numbers.
Understanding these distinctions is crucial as we explore the current challenges faced by animals going extinct and the efforts required to prevent further losses.
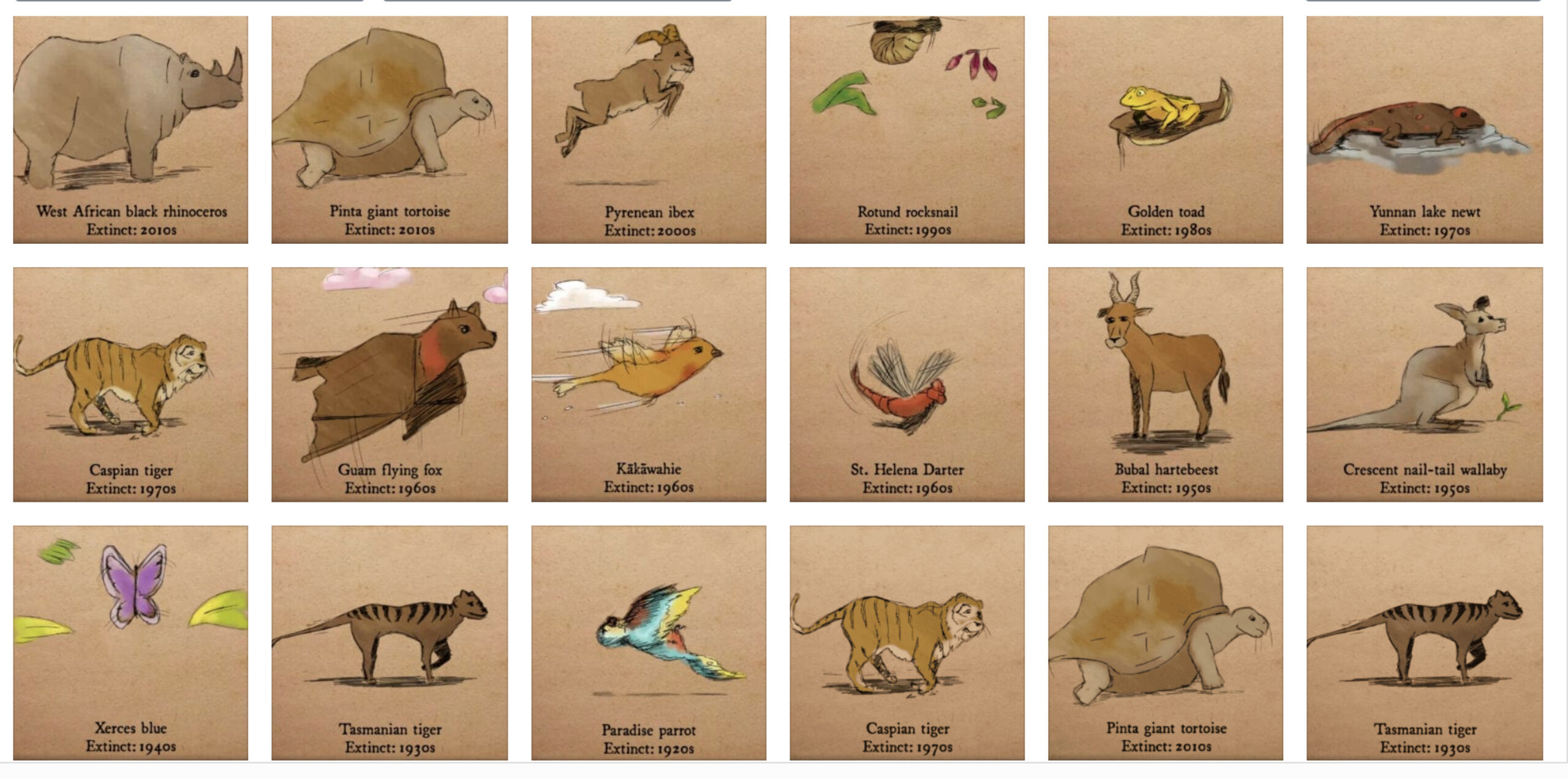

Images of various extinct animal species
Historical Context of Animal Extinctions
To comprehend the gravity of modern extinction events, one must look back at the historical context of animal extinctions. Earth has witnessed five major mass extinction events, each reshaping the diversity of life. The most famous of these is the Cretaceous-Paleogene extinction event, which led to the demise of the dinosaurs around 66 million years ago. These mass extinctions were primarily driven by natural phenomena such as volcanic eruptions, meteor impacts, and drastic climate changes.
However, the current extinction crisis, often dubbed the “Sixth Extinction,” is largely attributed to human activities. Throughout history, as humans spread across the globe, numerous species have been driven to extinction due to overhunting, habitat destruction, and introduced species. The Passenger Pigeon (Ectopistes migratorius), once numbering in the billions in North America, was hunted to extinction by the early 20th century. Similarly, the Great Auk (Pinguinus impennis), a flightless bird, was driven to extinction by excessive hunting for its feathers and meat.
More recently, the list of animals recently extinct continues to grow, with species like the Western Black Rhinoceros and the Bramble Cay Melomys disappearing within our lifetime. These examples highlight the urgent need to address the factors driving animals close to extinction today, as we stand on the brink of losing even more species.
As we delve deeper into the factors driving species toward extinction, it is imperative to remember the lessons from history. The current rate of extinction is unprecedented, and without significant intervention, we risk losing not just individual species, but the rich tapestry of life that sustains the planet’s ecosystems.
Factors Driving Species Toward Extinction
Understanding the forces pushing species toward the brink of extinction is crucial in combating this crisis. The extinction of species is not just a natural phenomenon; it is increasingly exacerbated by human actions and environmental changes. In this section, we will delve into the main factors driving species toward extinction, including habitat loss, climate change, and human activities such as overhunting and pollution.
Habitat Loss and Environmental Changes
One of the most significant drivers of species extinction is habitat loss. As human populations expand, natural habitats are destroyed to make way for agriculture, urban development, and industrial activities. This loss not only reduces the living space available for wildlife but also fragments ecosystems, making it difficult for species to survive and reproduce. For example, the Amazon rainforest, often referred to as the “lungs of the Earth,” is being rapidly deforested. This destruction poses a severe threat to countless species that rely on the forest for their survival.
Furthermore, environmental changes such as desertification, pollution, and waterway modifications disrupt the delicate balance of ecosystems. Wetlands, which are crucial for numerous bird and amphibian species, are being drained for agricultural use, leading to a decline in biodiversity. The resulting environmental changes not only threaten individual species but also the intricate ecosystems that support them.
Climate Change Impact
Climate change is another critical factor driving species toward extinction. Rising global temperatures, shifting weather patterns, and increased frequency of extreme weather events have profound effects on the natural world. Many species are unable to adapt quickly enough to these rapid changes, leading to population declines and, eventually, extinction.
For example, polar bears are one of the most well-known victims of climate change. As Arctic ice melts due to rising temperatures, polar bears lose their hunting grounds and face starvation. Similarly, coral reefs, which are home to a quarter of all marine species, are experiencing mass bleaching events due to warming ocean temperatures. These changes not only impact the species directly affected but also the entire food chains and ecosystems they are part of.
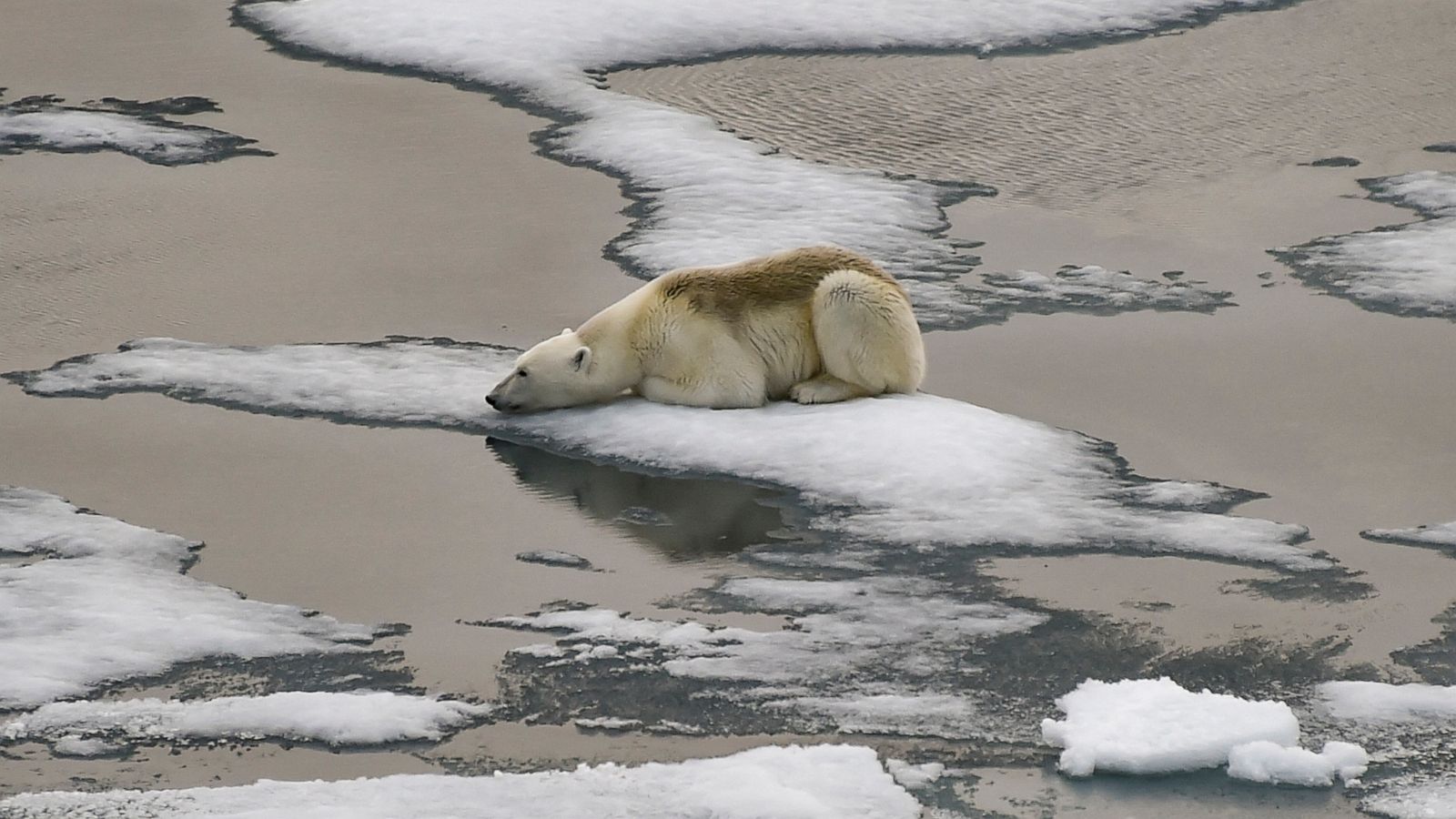

Polar bear on melting Arctic ice
Human Activities: Overhunting and Pollution
Human activities have a profound impact on species extinction, particularly through overhunting and pollution. Overhunting and poaching have driven many species to the brink. Iconic animals like the African elephant and rhinoceros are hunted for their tusks and horns, despite international bans and conservation efforts. The illegal wildlife trade continues to flourish, posing a significant threat to species already at risk.

Elephant poached for tusks in African savannah
Pollution is another human activity contributing to the extinction crisis. Oceans and waterways are polluted with plastics, chemicals, and oil spills, endangering marine life. Birds and marine animals often ingest plastics, mistaking them for food, leading to injury or death. The introduction of pollutants into ecosystems can also disrupt reproductive processes, leading to population declines.
Moreover, air pollution and the release of greenhouse gases contribute to climate change, further exacerbating the issues faced by species already struggling to adapt. As the world becomes more industrialized, it is crucial to address these human activities to protect biodiversity.
In summary, the factors driving species toward extinction are complex and interconnected. From habitat loss and climate change to human activities like overhunting and pollution, each element plays a role in pushing species closer to extinction. Understanding these factors is the first step in developing effective conservation strategies to protect animals going extinct and preserve the rich tapestry of life on Earth.
Recently Extinct and Critically Endangered Species
Notable Recently Extinct Animals
The list of animals that have disappeared forever is a heartbreaking reminder of the fragility of life on Earth. Each species lost is a story untold, and each extinction a call for urgent action. Among the animals recently extinct, the Pinta Island Tortoise, known for the iconic “Lonesome George,” stands out. George’s death in 2012 marked the end of his species, a poignant symbol of isolation and loss.
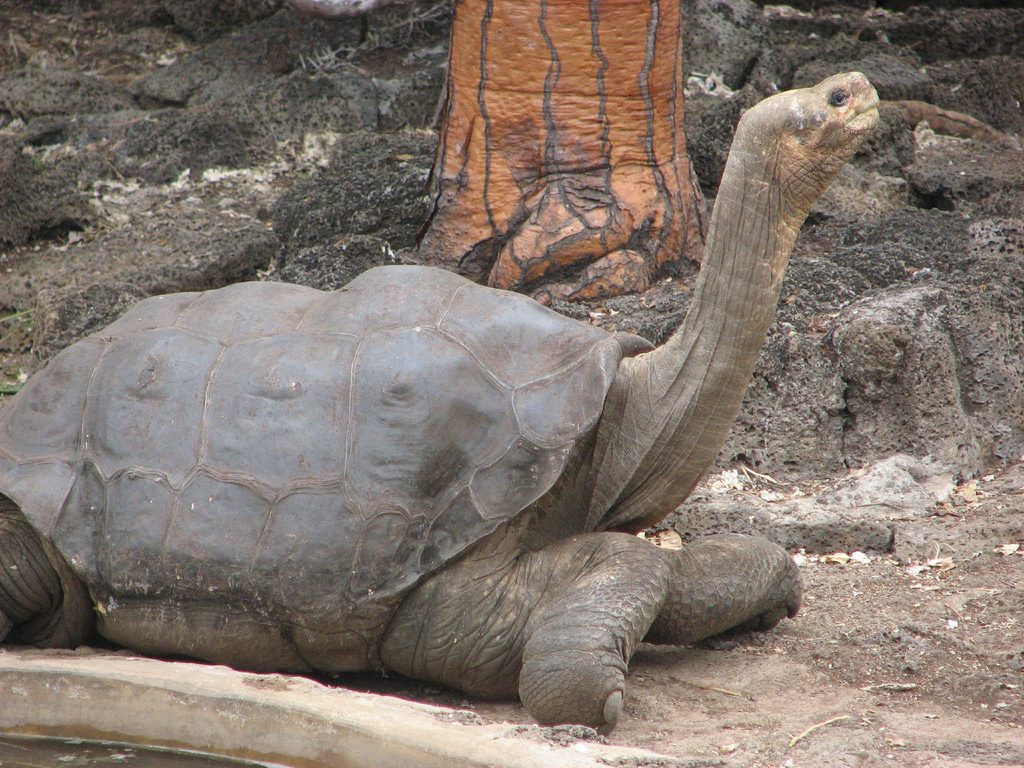

Lonesome George the last of the Pinta Island Tortoises
Another tragic loss is the Bramble Cay Melomys, which became the first mammal to go extinct due to climate change in 2016. This small rodent’s habitat was swallowed by rising sea levels, leaving no refuge for survival. The story of the Spix’s Macaw, once declared extinct in the wild in 2000, offers a glimmer of hope as conservation efforts have seen its reintroduction in small numbers. Yet, the monumental task of restoring a viable population remains daunting.
The Western Black Rhinoceros was declared extinct in 2011, a victim of rampant poaching driven by the illegal wildlife trade. Its loss is not just the disappearance of a species but a vivid illustration of the consequences of human greed. Similarly, the Baiji or Yangtze River Dolphin, declared functionally extinct in 2006, suffers from human-induced threats such as habitat destruction and pollution.
These animals recently extinct remind us of the impermanence of species and the urgent need for conservation actions.
Critically Endangered Species on the Brink
As we reflect on the animals that have been lost, it is crucial to focus on those teetering on the edge of extinction. The term “critically endangered” is a stark warning, signifying that a species faces an extremely high risk of extinction in the wild. Among the animals close to extinction, the Vaquita, a small porpoise found in the Gulf of California, is one of the most dire cases. With fewer than 10 individuals left, the Vaquita’s plight is a testament to the destructive impact of illegal fishing practices.
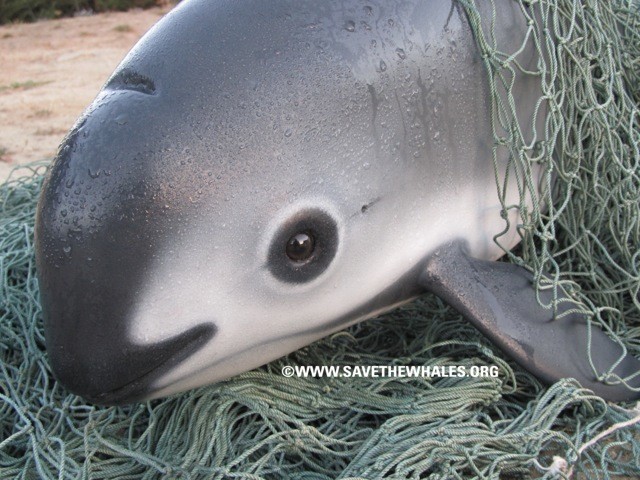

Vaquita the critically endangered porpoise
The Kakapo, a flightless parrot native to New Zealand, has about 250 individuals remaining. Conservation efforts have focused on intensive management of their populations, offering a beacon of hope for their survival. Meanwhile, the Yangtze Giant Softshell Turtle, with only 3–4 known individuals, highlights the critical need for habitat protection and breeding programs.
The Axolotl, an amphibian known for its unique regenerative abilities, is now extremely rare in the wild, suffering from habitat loss and pollution. The Cross River Gorilla, with fewer than 300 left, is threatened by hunting and habitat encroachment, emphasizing the urgent need for protective measures.
These species are not just names on a list; they are integral parts of ecosystems and cultural heritage. Their potential loss is a reminder of the broader implications of extinction, which impacts biodiversity and ecosystem health. As we look toward the future, the fate of these animals is uncertain. Without immediate and effective conservation efforts, these animals going extinct may soon join the ranks of those we mourn today.
To prevent the looming threat of extinction, it is imperative to support conservation initiatives and raise awareness about the plight of these species. Whether through supporting wildlife organizations, refraining from purchasing illegal wildlife products, or educating others, every action counts. By working together, we can alter the course for these animals going extinct and ensure they remain part of our world’s rich biodiversity.
Predictions: Animals at Risk of Extinction by 2025
High-Risk Species with Urgent Needs
In the rapidly changing landscape of our planet, several species teeter on the brink of extinction, facing imminent threats that could lead to their disappearance by 2025. These animals going extinct are not just statistics; they are a poignant reminder of the fragility of life on Earth and the urgent need for conservation efforts.
One of the most critically endangered species is the Javan Rhino, with fewer than 80 individuals left in the wild. Found only in the Ujung Kulon National Park in Indonesia, these rhinos face threats from habitat loss due to agricultural encroachment and the ever-looming danger of natural disasters like tsunamis and volcanic eruptions. Immediate conservation actions, such as habitat protection and anti-poaching measures, are crucial to prevent their extinction.
Similarly, the Sumatran Elephant is under dire threat, with its population dwindling to under 2,000. Habitat destruction, primarily due to palm oil plantations, has severely fragmented their living space, leading to increased human-elephant conflicts and making them vulnerable to poaching. Without swift and decisive action to protect their habitats and reduce conflicts, these magnificent creatures may soon be added to the list of animals recently extinct.
Another species facing an uncertain future is the Amur Leopard, with less than 120 individuals remaining. These leopards are found in the temperate forests of the Russian Far East and China. They suffer from habitat loss, prey depletion, and poaching. Conservationists are working tirelessly to establish protected areas and corridors to facilitate their movement and ensure their survival.
The Irrawaddy Dolphin, found in coastal and freshwater regions across South and Southeast Asia, is declining rapidly due to habitat degradation, pollution, and entanglement in fishing gear. As their numbers dwindle, targeted conservation strategies, including establishing protected areas and sustainable fishing practices, are essential to prevent their extinction.
Lastly, the Spoon-billed Sandpiper, with fewer than 700 individuals left, faces a precarious existence. Habitat loss along their migratory route, particularly in their breeding grounds in Russia and wintering areas in Southeast Asia, poses a significant threat. Conservationists are implementing habitat restoration projects and international cooperation to save this unique species from extinction.
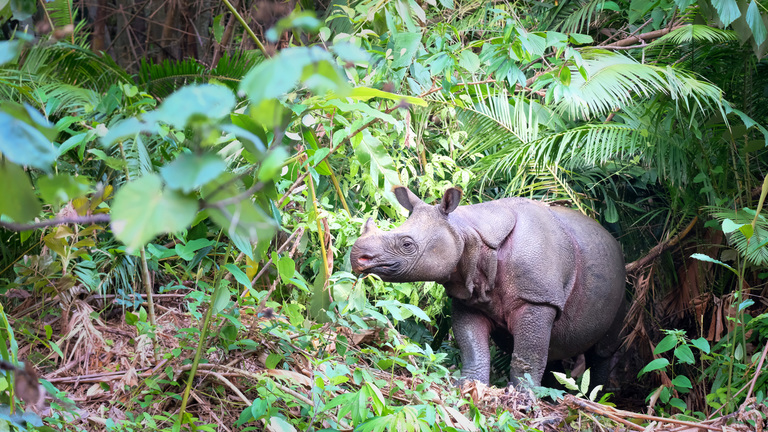

Critically endangered Javan Rhino in its natural habitat
Regional Analysis of At-Risk Species
The factors driving species toward extinction are often region-specific, dictated by unique environmental and human-induced pressures. Understanding these regional dynamics is vital for crafting effective conservation strategies.
Southeast Asia is a hotspot for biodiversity and, unfortunately, for endangered species as well. The region is home to the Sumatran Elephant and Javan Rhino, both facing threats from deforestation and habitat fragmentation. In addition, the Irrawaddy Dolphin inhabits the coastal areas here, where pollution and fishing practices exacerbate their decline. Conservation efforts in Southeast Asia focus on habitat preservation, anti-poaching initiatives, and sustainable development to balance human needs with wildlife protection.
In the Russian Far East, the Amur Leopard is a symbol of the region’s rich biodiversity. However, illegal logging and infrastructure development threaten their habitat. Conservationists are working with local governments to establish protected areas and enforce anti-poaching laws to safeguard these leopards and other wildlife.
The Arctic and Sub-Arctic regions face unique challenges due to climate change, impacting species like the Spoon-billed Sandpiper. Melting ice and changing weather patterns disrupt their migratory routes and breeding grounds. International collaboration is essential in these regions to address climate change and protect critical habitats.
In Africa, the Cross River Gorilla is another species at risk, with fewer than 300 individuals left. Habitat destruction and hunting pose significant threats to their survival. Conservation efforts focus on community engagement and law enforcement to protect these gorillas and their habitats.
Globally, the threat of animals going extinct is a pressing concern that transcends borders and requires a united effort. By understanding the regional contexts and the unique challenges faced by these high-risk species, we can tailor conservation strategies to address the specific threats and work toward a sustainable future for all Earth’s inhabitants.
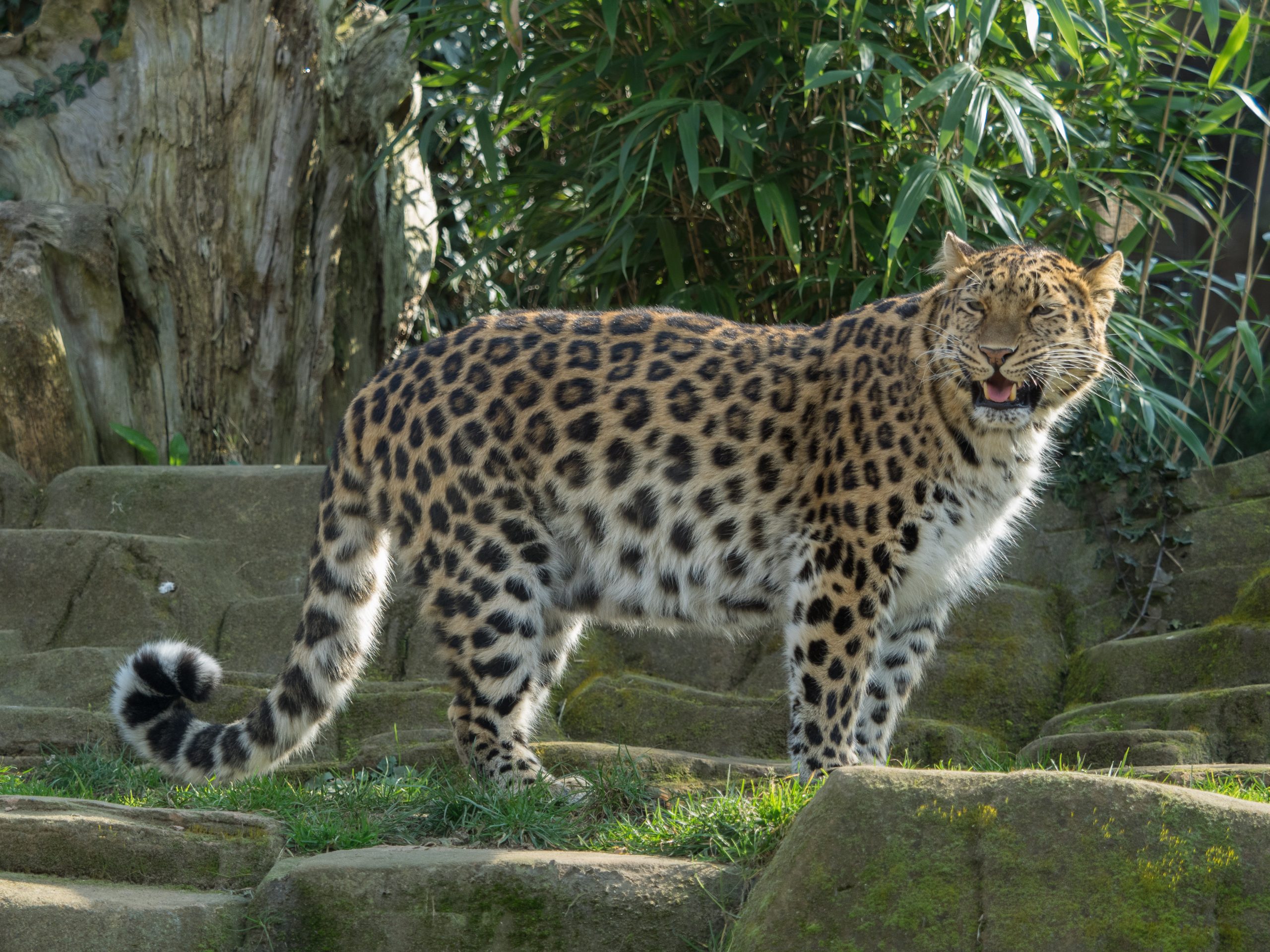

Amur Leopard in its natural habitat in the Russian Far East
In conclusion, the plight of these high-risk species highlights the need for urgent and sustained conservation efforts. By raising awareness and taking decisive action, we can prevent these animals from joining the list of animals recently extinct and ensure that future generations inherit a world rich in biodiversity.
Conservation Efforts and How to Help
In the face of rapid increases in the number of animals going extinct, it is imperative to focus on conservation efforts that can make a tangible difference. The plight of our planet’s biodiversity is dire, but various organizations and individual actions offer hope and pathways to mitigate these losses.
Organizations and Initiatives Making a Difference
Numerous organizations around the world are dedicated to the conservation of endangered species and the protection of biodiversity. These entities play a crucial role in research, habitat preservation, policy advocacy, and education. Here are some of the key organizations making a significant impact:
- World Wildlife Fund (WWF): As one of the largest conservation organizations globally, WWF works on a variety of fronts including protecting natural habitats, promoting sustainable practices, and advocating for strong policies to curb climate change and pollution. Their efforts have helped numerous species and ecosystems recover and thrive.
- International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN): Known for its comprehensive Red List of Threatened Species, the IUCN plays an essential role in assessing the conservation status of plant and animal species. Their work helps prioritize conservation actions and mobilize resources to protect species that are on the brink of extinction.
- Wildlife Conservation Society (WCS): With a focus on saving wildlife and wild places, WCS conducts field research and conservation projects in over 60 countries. Their initiatives range from protecting forest elephants in Africa to conserving the Amazon rainforest.
- The Nature Conservancy (TNC): TNC works to conserve the lands and waters on which all life depends. They employ a collaborative approach, working with local communities, governments, and businesses to develop conservation solutions that are sustainable and scalable.
- Conservation International: This organization emphasizes the importance of nature in human well-being. They use science, policy, and partnerships to protect the critical benefits that nature provides to humanity, including biodiversity and climate regulation.
These organizations, along with countless local and regional initiatives, are vital in the fight to prevent more animals from going extinct. They provide opportunities for individuals to get involved, whether through donations, volunteer work, or advocacy.
Individual Actions to Support Conservation
While organizations lead large-scale efforts, individuals also have a powerful role to play in conservation. Here are some ways you can contribute to the protection of endangered species:
- Educate Yourself and Others: Understanding the causes and consequences of extinction is the first step toward making a difference. Share your knowledge with others to raise awareness and inspire action within your community.
- Support Sustainable Products: Choose sustainably sourced products that do not harm wildlife habitats. For example, opt for sustainably harvested seafood, certified palm oil, and products with minimal packaging to reduce pollution.
- Reduce, Reuse, Recycle: Minimize your ecological footprint by reducing waste and recycling whenever possible. This helps decrease pollution and the demand for raw materials, protecting natural habitats.
- Volunteer for Conservation Projects: Many organizations offer opportunities for individuals to volunteer in habitat restoration projects, wildlife monitoring, and community education programs. Engaging in such activities can make a direct impact on local ecosystems.
- Advocate for Policy Change: Support policies and leaders that prioritize environmental conservation. Your voice can influence legislation and policies that protect endangered species and their habitats.
- Avoid Illegal Wildlife Products: Do not purchase products made from threatened or endangered species. This includes ivory, certain exotic pets, and souvenirs made from animal parts.
By taking these actions, individuals can significantly contribute to the conservation of species at risk of extinction. Each step, no matter how small, plays a part in the larger effort to prevent more animals from going extinct.
In summary, while the challenge of preventing animals going extinct is daunting, both organizations and individuals have the power to enact meaningful change. Through concerted efforts, we can protect the rich biodiversity of our planet for future generations to enjoy and learn from.
Reflecting on the Importance of Biodiversity
The Broader Implications of Species Loss
The decline of biodiversity through species extinction is not just a loss of beautiful creatures that once roamed the earth; it signifies much deeper environmental and ecological issues. When we discuss animals going extinct, we are touching upon a cascade of effects that ripple through ecosystems and have profound consequences for the planet.
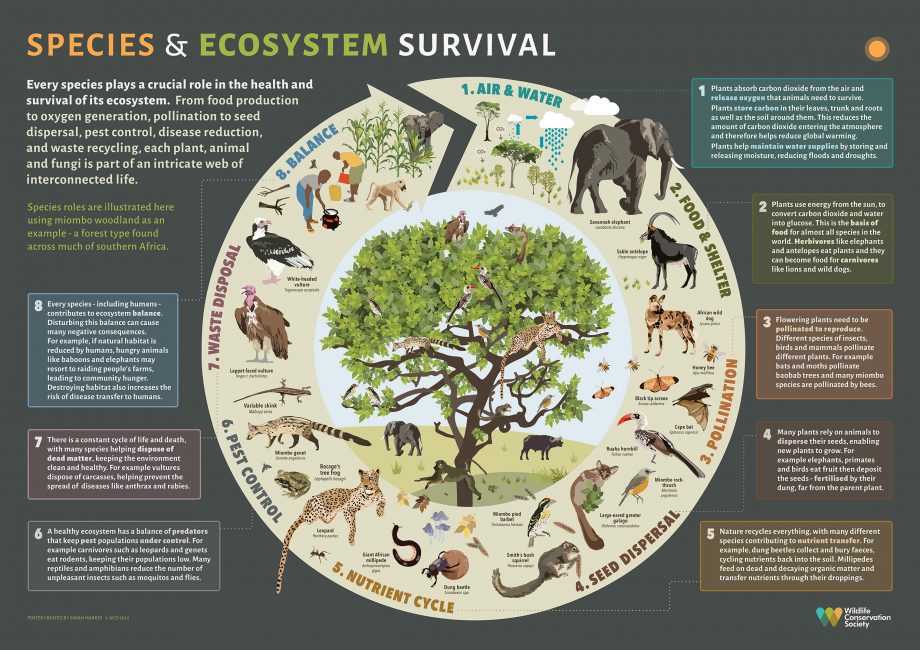
Ecosystem Stability and Functionality: Every species, from the tiniest insect to the largest mammal, plays a specific role in its ecosystem. The extinction of a single species can disrupt food chains, leading to overpopulation of some species and the decline of others, ultimately affecting ecosystem balance and functionality. For instance, the extinction of predators like the dodo bird led to the overabundance of certain plants, hindering the growth of others and altering the landscape fundamentally.
Economic Impact: Biodiversity is crucial for industries such as agriculture, pharmaceuticals, and tourism. The loss of plant species could mean the loss of potential medicinal resources. Similarly, animals that are part of a region’s appeal for tourists can impact local economies if they disappear. The economic consequences of losing biodiversity are vast and often underestimated.
Cultural and Aesthetic Loss: Many cultures hold certain animals in high regard, integrating them into their traditions and folklore. The extinction of these animals can lead to a loss of cultural heritage and identity. Additionally, the beauty and wonder of these creatures inspire art, literature, and innovation, enriching human experience and creativity.
Resilience to Environmental Changes: Biodiverse ecosystems are more resilient to changes such as climate change and natural disasters. They can adapt to shifts and recover more readily from perturbations. When species are lost, ecosystems become more vulnerable and less capable of handling environmental stressors.
In light of these broader implications, the urgency to act against the tide of extinction becomes ever more pressing. The loss of biodiversity is a silent crisis that demands immediate attention, requiring a concerted effort from all sectors of society to prevent further species from joining the list of animals recently extinct.
A vibrant ecosystem showcasing biodiversity
A Call to Action for Future Generations
As we face the reality of species loss, it becomes imperative to look towards the future and inspire action among the next generations. The fight against extinction is not just the responsibility of conservationists, but of every individual who shares this planet. Here’s how we can collectively contribute to this cause:
Education and Awareness: Educating young people about the importance of biodiversity and the impact of species loss is crucial. Schools and communities can integrate environmental education into their curricula, highlighting the stories of animals going extinct and those already extinct in the wild. Awareness fosters empathy and understanding, laying the foundation for proactive conservation efforts.
Supporting Conservation Initiatives: Encourage future generations to support initiatives that aim to protect endangered species and their habitats. Whether it’s through volunteering, fundraising, or advocating for policy changes, young people can play a significant role in conservation. Highlight organizations that are making strides in this area and inspire involvement.
Promoting Sustainable Practices: Instilling sustainable habits in daily life can significantly impact conservation efforts. Teaching young individuals the importance of reducing waste, conserving water, and supporting sustainable products can lead to a more environmentally conscious society.
Advocating for Policy Change: Engage future generations in political discourse, empowering them to advocate for policies that prioritize environmental protection and species conservation. Political engagement is a powerful tool for effecting change on a larger scale.
Fostering a Connection with Nature: Encourage young people to spend time in nature, fostering a personal connection with the environment. This connection can inspire a lifelong commitment to protecting the natural world and preventing more species from becoming animals close to extinction.
Our actions today will shape the world of tomorrow. By prioritizing biodiversity and taking actionable steps, we can ensure that future generations inherit a planet rich in life and beauty. Let us be the torchbearers of change, lighting the way towards a future where no species faces the threat of extinction.

Children engaging in environmental education
As we reflect on these points, it becomes evident that the stakes are high, but so too is the potential for positive change. Together, we can create a future where biodiversity thrives and the stories of animals going extinct become a thing of the past.
WildWhiskers is a dedicated news platform for animal lovers around the world. From heartwarming stories about pets to the wild journeys of animals in nature, we bring you fun, thoughtful, and adorable content every day. With the slogan “Tiny Tails, Big Stories!”, WildWhiskers is more than just a news site — it’s a community for animal enthusiasts, a place to discover, learn, and share your love for the animal kingdom. Join WildWhiskers and open your heart to the small but magical lives of animals around us!