In the vast tapestry of life on Earth, kinds of animals play a starring role, weaving together ecosystems and enriching our planet with their endless variety. From the tiniest insect flitting through a sunlit meadow to the majestic whales gliding through the deep, each creature contributes to a complex web of biodiversity that sustains us all. Understanding this array of life is not just an academic exercise; it’s an invitation to marvel at the wonders of evolution and adaptation. As we delve into this blog, we’ll explore how scientists meticulously classify these creatures, uncovering the characteristics that bind them into major groups such as mammals, birds, reptiles, and more.
Imagine standing in a forest, the air filled with birdsong and the rustle of unseen life. This everyday magic is a testament to the importance of biodiversity, a vital force that ensures the health of our ecosystems. Yet, as fascinating as these creatures are, they face unprecedented threats from human activity and environmental changes. Our journey through the animal kingdom will not only highlight their incredible adaptations and survival strategies but also underscore the urgent need for conservation efforts. Whether you’re an avid animal lover or a curious reader, this exploration promises to deepen your appreciation for the remarkable diversity of life that calls Earth home. So, let’s embark on this adventure into the heart of nature’s wonder, celebrating the myriad kinds of animals that share our world and the delicate balance that sustains them.
Introduction to Animal Diversity
The natural world is a breathtaking tapestry of life, woven together with infinite colors, shapes, and sizes. From the tiniest microorganisms to the majestic blue whales, the diversity of life on Earth is both awe-inspiring and crucial to our planet’s health and stability. This diversity, or biodiversity, is a testament to the adaptability and ingenuity of life, showcasing how different species have evolved and thrived in a multitude of environments. In this section, we will delve into the importance of biodiversity and explore how scientists classify the myriad kinds of animals that share our planet.
The Importance of Biodiversity
Biodiversity is not merely a measure of the number of species on Earth; it is the foundation of ecosystem health and resilience. Each species, no matter how small or seemingly insignificant, plays a unique role in maintaining the balance of nature. For example, bees and other pollinators are crucial for the reproduction of many flowering plants, which in turn provide food and habitat for other animals. The loss of such a species could lead to a cascading effect, disrupting entire ecosystems.
Moreover, biodiversity has direct and tangible benefits for humans. It contributes to ecosystem services such as clean air and water, fertile soil for agriculture, and even the discovery of new medicines. Areas rich in biodiversity also tend to be more resilient to environmental changes and extreme weather events, acting as buffers against climate change.
Yet, biodiversity is under threat. Habitat destruction, pollution, climate change, and overexploitation are just a few of the challenges facing the natural world today. It is crucial for us to understand and appreciate the value of biodiversity to ensure its preservation for future generations.

A vibrant ecosystem teeming with biodiversity
How Scientists Classify Animals
The task of classifying the vast array of life on Earth is no small feat. Scientists use a system called taxonomy to categorize kinds of animals based on shared characteristics and evolutionary relationships. This system helps scientists communicate about species, understand their evolutionary history, and develop conservation strategies.
The classification hierarchy starts broadly with domains and narrows down through kingdoms, phyla, classes, orders, families, genera, and finally, species. For instance, humans belong to the domain Eukarya, kingdom Animalia, phylum Chordata, class Mammalia, order Primates, family Hominidae, genus Homo, and species Homo sapiens.
At the core of animal classification is the concept of shared characteristics. For example, mammals are characterized by their ability to nurse their young with milk, while birds are distinguished by their feathers and ability to fly. Reptiles and amphibians, often grouped together, are known for their cold-blooded nature and unique adaptations to land and water environments.
By understanding these classifications, we gain insights into the evolutionary adaptations that have enabled different species to survive and thrive. This knowledge is essential for protecting endangered species and preserving the delicate balance of ecosystems.

Scientists engaged in the classification of animal species
In summary, appreciating the importance of biodiversity and understanding how scientists classify the myriad kinds of animals is essential for fostering a deeper connection to the natural world. This knowledge not only enriches our understanding of life on Earth but also empowers us to take meaningful action towards its preservation. As we continue to explore the diversity of animal life, we are reminded of our responsibility to protect the intricate web of life that sustains us all.
Major Animal Groups
Mammals: Characteristics and Examples
Mammals are a fascinating and diverse group of animals that share several defining characteristics. These warm-blooded creatures are known for having hair or fur, giving birth to live young (with a few exceptions like the monotremes, which lay eggs), and nurturing their offspring with milk produced by the mammary glands. This unique trait of milk production is what gives this group its name.
Mammals can be found in virtually every habitat on Earth, from the icy expanses of the Arctic to the arid deserts of Africa. Humans, elephants, lions, and whales are just a few examples of the incredible diversity within this group. Each species has adapted to its environment in remarkable ways. For instance, whales have evolved to live in the ocean, with streamlined bodies and the ability to hold their breath for extended periods, while bats have developed the ability to fly, making them the only mammals capable of true flight.
The adaptability of mammals is a testament to their evolutionary success. The variety of life strategies observed among mammals, such as the solitary nature of the elusive snow leopard or the complex social structures of elephant herds, highlights the incredible versatility of this group.

A diverse group of mammals in their natural habitats
Birds: Unique Features and Adaptations
Birds are another captivating group within the kinds of animals that inhabit our planet. These warm-blooded creatures are characterized by their feathers, which not only provide insulation but also enable flight. While not all birds can fly, such as penguins and ostriches, those that do have developed a wide range of adaptations to help them soar through the skies.
Birds are known for their keen vision, which is essential for hunting and navigation. For example, eagles are famed for their extraordinary eyesight, allowing them to spot prey from great distances. Additionally, the beak shapes and sizes of birds have evolved to suit their dietary needs, from the powerful talons and hooked beaks of raptors to the long, slender bills of hummingbirds designed for sipping nectar.
Their ability to inhabit diverse environments, from the frigid tundras to tropical rainforests, speaks volumes about their adaptability. Birds play crucial roles in ecosystems, such as pollination, seed dispersal, and pest control, underscoring their importance to biodiversity.

A variety of bird species showcasing their unique adaptations
Reptiles and Amphibians: Cold-blooded Wonders
Reptiles and amphibians are often grouped together due to their cold-blooded nature, meaning their body temperature is regulated by external conditions. However, these two groups have distinct characteristics and life histories.
Reptiles, such as snakes, lizards, turtles, and crocodiles, are covered in scales that help prevent water loss, making them well-suited for life in dry environments. Most reptiles lay eggs, although some, like certain species of snakes, give birth to live young. Reptiles are known for their diverse range of habitats, from deserts to swamps, and they have adapted unique survival strategies, such as the ability to go without food for extended periods.
Amphibians, including frogs, toads, and salamanders, are unique in that they typically have a dual life, spending part of their life cycle in water and part on land. They have permeable skin, which allows them to breathe through it, making them highly sensitive to environmental changes and pollution. Amphibians are often considered ecological indicators due to their sensitivity to habitat changes.
Both reptiles and amphibians are essential components of their ecosystems, playing roles in controlling insect populations and serving as food for other animals. Despite their often misunderstood nature, these cold-blooded wonders contribute significantly to the world’s biodiversity.
Through understanding these major groups, the kinds of animals that populate our planet reveal the astonishing diversity and complexity of life on Earth. Each group, with its unique traits and adaptations, illustrates the intricate tapestry of ecosystems and the importance of conserving biodiversity for future generations.
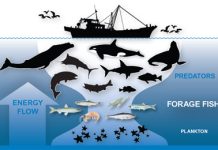
Aquatic Life
Fish: The Diverse World Underwater
The underwater realm is home to a staggering variety of kinds of animals, with fish being one of the most diverse groups. Fish are cold-blooded creatures that live in water and breathe through gills, a feature that distinguishes them from other aquatic animals. Their diversity is evident in their size, shape, and habitat preferences, ranging from the tiny goby fish to the massive whale shark.
Fish have adapted to nearly every aquatic environment on Earth, from the tepid waters of tropical coral reefs to the icy depths of the Arctic Ocean. Each species possesses unique adaptations that allow it to thrive in its specific habitat. For example, the anglerfish uses a bioluminescent lure to attract prey in the dark depths of the ocean, while the clownfish forms symbiotic relationships with sea anemones for protection.

A vibrant coral reef teeming with diverse species of fish
Beyond their ecological roles, fish are vital to human societies as a primary food source and a cornerstone of many economies. The fishing industry supports millions of jobs worldwide, and fish farming or aquaculture is a rapidly growing sector that aims to meet the increasing demand for seafood sustainably. However, overfishing, pollution, and climate change pose significant threats to fish populations, underscoring the need for effective conservation strategies to ensure their survival.
Marine Mammals: From Dolphins to Whales
Marine mammals are a fascinating group within the aquatic life category, admired for their intelligence, complex social structures, and remarkable adaptations to life in water. Unlike fish, marine mammals are warm-blooded and breathe air, often seen surfacing to inhale oxygen. This group includes a variety of species, such as dolphins, whales, seals, and manatees.
Dolphins are renowned for their playful behavior and advanced communication skills. They use a sophisticated system of clicks and whistles to communicate with each other, which is crucial for hunting and social interaction. Whales, on the other hand, represent some of the largest creatures on Earth. The blue whale, for instance, can weigh up to 200 tons and is known for its mesmerizing songs that can travel long distances underwater.

A pod of dolphins gracefully swimming in the ocean
Marine mammals play essential roles in their ecosystems, from regulating prey populations to contributing to nutrient cycling through their waste. Despite their importance, many marine mammals face threats from human activities, including habitat destruction, entanglement in fishing gear, and the impacts of climate change. Conservation efforts, such as the establishment of marine protected areas and international agreements like the Marine Mammal Protection Act, aim to safeguard these incredible creatures and their habitats.
In conclusion, the aquatic life category of the kinds of animals encompasses a remarkable array of species, each with unique adaptations and ecological roles. Understanding and protecting these creatures is crucial for maintaining the health and diversity of our planet’s oceans.
Invertebrates: The Overlooked Majority
Invertebrates, despite being the most numerous group in the animal kingdom, often go unnoticed in the grand tapestry of biodiversity. These creatures lack a backbone, a characteristic that sets them apart from vertebrates like mammals, birds, and reptiles. Yet, they play a crucial role in our ecosystems, contributing to everything from pollination and decomposition to serving as indicators of environmental health. In this section, we delve into the fascinating world of invertebrates, focusing on two key groups: insects and mollusks along with crustaceans.
Insects: The Most Numerous Group
Insects are undoubtedly the most diverse and numerous group among the kinds of animals. They are ubiquitous, found in nearly every habitat on Earth, from the frozen landscapes of Antarctica to the arid deserts. This incredible adaptability is largely due to their small size, versatile diet, and the ability to reproduce rapidly.
Insects are characterized by having three main body parts—the head, thorax, and abdomen—and typically six legs. Their success is also attributed to their ability to fly, a trait that allows them to escape predators, find food, and explore new habitats. Bees, for example, are not only essential pollinators but also a critical component of agricultural ecosystems. Without them, many of the fruits and vegetables we enjoy would be scarce.
Some insects, like ants, demonstrate remarkable social structures. Ant colonies operate with a level of organization that rivals human societies, with distinct roles such as workers, soldiers, and queens. This social behavior has fascinated scientists for decades and offers insights into the evolution of cooperation.

A bee pollinating a flower crucial for ecosystem health
Mollusks and Crustaceans: Ocean and Land Dwellers
Mollusks and crustaceans represent another important segment of invertebrates, often found in both marine and terrestrial environments. Mollusks, which include snails, slugs, and octopuses, are known for their soft bodies, often protected by a hard shell. The diversity within this group is astounding. Octopuses, for example, are renowned for their intelligence, capable of solving complex problems and displaying behaviors often associated with higher vertebrates.
Crustaceans such as crabs, lobsters, and shrimp, primarily inhabit aquatic environments. These creatures are not only vital to the marine food chain but also hold significant economic value as a staple in global seafood industries. The structure of crustaceans, with their hard exoskeletons and jointed limbs, enables them to thrive in diverse environments, from the depths of the ocean to bustling coastal zones.
Interestingly, some mollusks and crustaceans have adapted to life on land. Terrestrial snails and slugs are common in gardens, playing important roles in decomposing organic matter and enriching soil fertility. Their adaptability showcases the incredible versatility and resilience of invertebrates.

An octopus demonstrating its intelligence and adaptability in a coral reef
In conclusion, invertebrates like insects, mollusks, and crustaceans are more than just the overlooked majority; they are essential players in the complex kinds of animals that sustain life on Earth. Understanding their roles and contributions helps us appreciate the intricate balance of our ecosystems and the importance of conserving these remarkable creatures.
Conservation Efforts and Challenges
Threats to Animal Biodiversity
The biodiversity of our planet is a marvel of nature, yet it faces numerous threats that jeopardize the existence of countless species. Understanding these threats is crucial to devising effective conservation strategies. One of the most significant challenges to animal biodiversity is habitat loss, primarily driven by human activities such as deforestation, urbanization, and agriculture. As natural habitats shrink, many animals are forced into smaller areas, leading to increased competition for resources and a heightened risk of extinction.
Climate change is another major threat, altering habitats and ecosystems at an unprecedented rate. Rising temperatures, changing precipitation patterns, and extreme weather events affect the delicate balance of ecosystems, disrupting the lives of many species. For instance, polar bears are struggling as sea ice melts, while coral reefs suffer from bleaching due to warmer ocean temperatures.
Pollution is yet another critical threat, with chemicals, plastics, and waste contaminating air, water, and soil. Marine life is particularly vulnerable, with plastics causing fatalities in various species due to ingestion or entanglement. Additionally, chemical pollutants can disrupt reproductive and developmental processes in animals, leading to population declines.
Overexploitation through activities such as overfishing, hunting, and poaching significantly reduces animal populations. Many species, like rhinoceroses and elephants, are hunted for their horns and tusks, driving them dangerously close to extinction. Furthermore, the illegal wildlife trade exacerbates the situation, threatening the survival of numerous animals.
Invasive species also pose a significant threat by outcompeting native species for resources, altering habitats, and introducing new diseases. These threats highlight the urgent need for comprehensive conservation efforts to protect the kinds of animals that enrich our planet.

Deforestation leading to loss of animal habitats
Global and Local Conservation Initiatives
In response to these pressing challenges, a variety of global and local conservation initiatives have been implemented to safeguard animal biodiversity. Internationally, treaties such as the Convention on Biological Diversity and the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species (CITES) play crucial roles in fostering cooperation among nations to protect wildlife and regulate trade.
Conservation organizations like the World Wildlife Fund (WWF) and the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) work tirelessly to raise awareness, fund research, and implement conservation projects globally. These efforts include establishing protected areas, restoring habitats, and supporting sustainable practices to reduce human-wildlife conflicts.
On a local level, community-driven initiatives are equally vital. Local conservation groups often focus on specific ecosystems or species, employing strategies that align with the cultural and economic contexts of their regions. For example, community-managed reserves in the Amazon have proven effective in reducing deforestation while providing livelihoods for local populations.
Education and awareness campaigns are also instrumental in fostering a conservation ethic. By engaging communities and educating the public about the importance of biodiversity, these initiatives encourage sustainable practices and empower individuals to contribute to conservation efforts.
Furthermore, technological advancements have bolstered conservation efforts. Remote sensing, satellite imagery, and GPS tracking provide invaluable data for monitoring wildlife populations and assessing the health of ecosystems. These tools enable more targeted and efficient conservation strategies, maximizing the impact of limited resources.
In conclusion, while the threats to animal biodiversity are daunting, concerted global and local efforts offer hope for the future. By valuing and protecting the diverse kinds of animals that inhabit our planet, we not only preserve the natural world but also ensure a sustainable future for generations to come.

Local community engaged in conservation efforts in the Amazon
Celebrating the Wonders of Animal Life
Animal life is a tapestry woven with an infinite variety of threads, each representing different kinds of animals that inhabit our planet. The celebration of this diversity extends beyond mere admiration — it invites us to delve into the intricate details of their existence, explore their unique adaptations, and cherish their roles in the ecosystem. This celebration also embodies a commitment to preserving these wonders for future generations.
The Marvel of Adaptations
One of the most captivating aspects of animal life is the myriad adaptations they have evolved to survive in diverse environments. From the chameleon with its color-changing ability to blend into surroundings, to the arctic fox with its thick fur that provides insulation in freezing climates, these adaptations are a testament to nature’s ingenuity.

The arctic fox a master of adaptation in cold climates
Adaptations are not just physical. Behavioral adaptations, such as the intricate dance of the bowerbird to attract a mate or the migratory patterns of the Monarch butterfly, reveal the complex strategies animals use to thrive. These adaptations are not only fascinating but also crucial for survival, showcasing the remarkable ways in which life has evolved to meet the challenges of different habitats.
The Symphony of Ecosystems
Every species, no matter how small, plays a significant role in its ecosystem. Consider the bees, whose pollination activities are essential for the reproduction of many plants, or the vultures, which prevent the spread of disease by consuming carrion. These roles highlight the interconnectedness of life and the importance of each species in maintaining ecological balance.
The celebration of animal life is incomplete without acknowledging the intricate webs of life that bind them. Coral reefs, for instance, are bustling underwater cities that provide habitat and nourishment for a multitude of marine species. These ecosystems are not only vital for the species that inhabit them but also for human communities that rely on them for food and protection against storms.

A vibrant coral reef teeming with marine life
Cultural Connections and Inspirations
Animals have been a source of inspiration and reverence throughout human history. They appear in myths, art, and literature, symbolizing various attributes such as strength, wisdom, and freedom. The eagle, for instance, is often associated with power and freedom, while the elephant is revered for its wisdom and memory.
Beyond symbolism, animals influence our daily lives, shaping cultures and economies. The domestication of animals has been pivotal in human development, providing companionship, labor, and resources. Pets, like dogs and cats, enrich our lives with their companionship, reminding us of the simple joys of life and the importance of empathy and care.
The Role of Humans in Celebrating Animal Life
As we celebrate the diversity of animal life, we must also recognize our responsibility to protect it. Conservation efforts, driven by both local communities and global initiatives, aim to preserve these natural wonders. From establishing protected areas like national parks to supporting sustainable practices, these efforts are crucial in safeguarding biodiversity.
Education plays a vital role in conservation. By learning about different kinds of animals, their habitats, and the threats they face, we become informed advocates for their protection. Initiatives such as wildlife documentaries and educational programs help raise awareness and inspire action.
Embracing a Future of Coexistence
The ultimate celebration of animal life is the commitment to coexistence. This involves respecting and preserving the natural habitats of animals, reducing human-induced threats, and fostering environments where wildlife can thrive alongside human development.
In conclusion, the wonders of animal life are a testament to the richness of our planet. By celebrating these wonders, we not only appreciate the beauty and diversity of life but also commit to being stewards of the Earth. As we continue to discover, learn, and share our love for the animal kingdom, we pave the way for a future where all species can flourish.

A thriving ecosystem showcasing the diversity of wildlife
WildWhiskers is a dedicated news platform for animal lovers around the world. From heartwarming stories about pets to the wild journeys of animals in nature, we bring you fun, thoughtful, and adorable content every day. With the slogan “Tiny Tails, Big Stories!”, WildWhiskers is more than just a news site — it’s a community for animal enthusiasts, a place to discover, learn, and share your love for the animal kingdom. Join WildWhiskers and open your heart to the small but magical lives of animals around us!