In the world of animal breeding, myths and misconceptions often cloud the reality, leading to misguided practices that can have serious repercussions. From the natural beauty of domesticated pets to the robust utility of livestock, breeding has been an integral part of human history. Yet, as time has passed, so have the myths that accompany this practice, sometimes causing more harm than good. Have you ever heard the saying that purebred animals are always superior? Or perhaps that breeding is just a simple, profitable venture? These beliefs, although widespread, often overlook the complexities and ethical dimensions involved. For instance, the notion that female animals need to experience motherhood to be healthy is not only outdated but potentially harmful.
In this blog, we will delve into the science and ethics behind animal breeding, debunking common myths and exploring the genetic principles at play. You’ll discover how selective breeding shapes the animals we see today and the ethical considerations that must be taken into account to ensure animal welfare. We’ll also discuss the impact of these myths on animal populations, including issues like overpopulation and the threat to genetic diversity.
As we journey through this topic, you’ll learn how to make informed decisions, whether you’re considering adopting a pet or exploring reputable breeders. The goal is to move towards responsible breeding practices that prioritize the health and well-being of animals over aesthetic or financial gain. Join us as we uncover the truths behind these myths and work towards a more ethical approach to animal breeding.
Understanding Common Animal Breeding Myths
When it comes to animal breeding, there are plenty of myths and misconceptions that have stood the test of time. These myths often stem from outdated beliefs or a lack of understanding about the complexities involved in breeding animals. By debunking these myths, we can promote healthier practices and ensure the well-being of animals.
Myth: Purebred Animals Are Always Superior
One of the most pervasive myths in animal breeding is the belief that purebred animals are inherently superior to mixed breeds. This idea has been popularized by shows, advertisements, and a general preference for pedigree animals. However, the reality is far more complex.
Genetic Diversity and Health: Purebred animals are often the product of selective breeding, which can lead to a limited gene pool. This lack of genetic diversity increases the risk of hereditary diseases and health issues. For example, purebred dogs are more prone to conditions like hip dysplasia, heart diseases, and certain types of cancers compared to their mixed-breed counterparts.
Temperament and Behavior: While purebred animals may exhibit specific traits that are desirable, such as size or coat type, they don’t necessarily have superior temperaments. Mixed breeds can be just as friendly, intelligent, and trainable. In fact, the blending of different genetic backgrounds can lead to more balanced behavior and adaptability.
Aesthetic vs. Practicality: The allure of a purebred often lies in their appearance, but this focus on aesthetics can overshadow practical considerations. For instance, breeding for a certain look can result in structural issues, such as breathing problems in flat-faced dog breeds or skin conditions in certain cat breeds.

Myth: Breeding is a Simple Process
Another common misconception is that breeding animals is a straightforward task that anyone can undertake. This myth downplays the complexity and responsibility involved in ethical breeding practices.
Knowledge and Expertise: Successful breeding requires a deep understanding of genetics, animal behavior, and health care. Breeders must be knowledgeable about the specific needs and potential health issues of the breeds they work with. This includes understanding genetic markers and being able to make informed decisions to avoid passing on undesirable traits.
Financial and Emotional Investment: Breeding is not just a financial endeavor; it’s an emotional commitment. Responsible breeders invest in veterinary care, proper nutrition, and safe living environments for their animals. They must be prepared for unexpected costs, such as emergency surgeries or treatments for health complications.
Ethical Responsibility: Breeding animals comes with ethical responsibilities. This includes ensuring the animals are treated humanely and that breeding practices do not contribute to overpopulation. Breeders must also be committed to finding suitable homes for the animals they produce, rather than viewing them as mere commodities.
By understanding and debunking these myths, we can promote a more realistic and ethical approach to animal breeding. It is crucial to prioritize the health and well-being of animals over outdated beliefs and misconceptions.
The Science Behind Animal Breeding
Animal breeding is an intricate field that combines both art and science. While many may perceive it as merely pairing animals, the reality is far more complex. The science of animal breeding delves into genetic principles and the role of selective breeding, both of which are pivotal in understanding how to responsibly and ethically breed animals.
Genetic Principles in Breeding
At the heart of animal breeding lies the understanding of genetics. Genetics is the study of genes, genetic variation, and heredity in organisms, and it plays a critical role in determining an animal’s traits. When it comes to breeding, genetics helps breeders predict which traits will be passed down to the offspring.
The fundamental principles of genetics revolve around the ideas of dominant and recessive genes. In any given pair of genes, the dominant gene will typically mask the presence of the recessive gene. For example, if a dominant gene codes for a certain fur color, that color will likely appear in the offspring if it is present. However, when two recessive genes pair up, they can express traits that might otherwise remain hidden.
Understanding genetic principles allows breeders to make informed decisions about pairing animals in ways that enhance desired traits while minimizing the risk of genetic disorders. This is particularly crucial in combating issues stemming from inbreeding, which can increase the likelihood of genetic anomalies and health problems. Inbred populations often suffer from reduced genetic diversity, which can lead to a host of health issues.
Moreover, genetic diversity is a cornerstone of healthy breeding practices. Diverse gene pools provide resilience against diseases and environmental changes, ensuring that animal populations remain robust and adaptable.

The Role of Selective Breeding
Selective breeding, or artificial selection, is a process where breeders choose specific animals to reproduce based on desirable traits. This practice has been used for centuries to enhance characteristics such as size, temperament, or productivity in animals, whether for companionship, work, or food production.
The role of selective breeding is significant as it allows breeders to cultivate specific traits over generations. For example, in the realm of livestock, selective breeding has been used to produce cows with higher milk yields or chickens that lay more eggs. In pets, it might be used to cultivate a particular coat color or temperament.
However, selective breeding comes with its own set of ethical considerations. While it can lead to improvements in certain traits, it can also inadvertently prioritize aesthetics or productivity over the animal’s overall well-being. For instance, breeding dogs for flat faces can lead to respiratory issues, a common problem in breeds like pugs and bulldogs.
Moreover, selective breeding must be balanced with considerations of genetic health and diversity. Breeding for extreme traits can lead to unintended consequences, such as reduced fertility or increased susceptibility to diseases. Responsible breeders focus on maintaining a balance between achieving desirable traits and preserving genetic diversity to ensure the health and longevity of the breed.
In conclusion, both genetic principles and selective breeding play crucial roles in the science of animal breeding. They provide the foundation for making informed, ethical, and responsible breeding decisions that prioritize the health and well-being of animals. By understanding and applying these principles, breeders can contribute to the sustainability and diversity of animal populations, ensuring that future generations are healthy and vibrant.
Incorporating a scientific approach to breeding not only helps debunk common myths surrounding the practice but also emphasizes the importance of informed decision-making in the realm of animals breeding.
Ethical Considerations in Animal Breeding
In the world of animal breeding, ethical considerations are paramount. These concerns not only focus on the welfare of the animals involved but also delve into the broader implications of breeding practices on animal populations and genetic diversity. Ethical breeding practices are essential to ensure the health and well-being of animals and to maintain ecological balance.
Animal Welfare Concerns
One of the primary ethical issues in animal breeding is the welfare of the animals. Animal welfare concerns revolve around the physical and mental well-being of animals, which can be compromised by poor breeding practices. For instance, overbreeding and inbreeding can result in serious health issues, ranging from genetic disorders to weakened immune systems. Animals subjected to continuous breeding cycles often suffer from exhaustion, shortened lifespans, and increased risks of complications during pregnancies.
Moreover, the conditions in which breeding animals are kept can greatly affect their welfare. Ethical breeders must provide adequate space, nutrition, and veterinary care for their animals. However, not all breeders adhere to these standards. In some cases, animals are kept in cramped, unsanitary conditions, leading to stress, disease, and even death. Ensuring animal welfare in breeding practices is not just a moral obligation but a critical component of responsible breeding.

Breeding for Specific Traits and Its Implications
Breeding animals for specific traits, such as color, size, or temperament, is a common practice. However, this approach can have significant ethical implications. Selective breeding for aesthetic traits often comes at the cost of the animal’s health. For example, certain dog breeds have been selectively bred for flat faces, leading to respiratory problems and other health issues. This focus on physical appearance can overshadow the importance of genetic diversity and overall health.
The implications of breeding for specific traits extend beyond individual animals. It can lead to a narrowing of the gene pool, which increases the risk of genetic disorders. This lack of genetic diversity can make populations more susceptible to diseases and reduce their ability to adapt to environmental changes. Furthermore, prioritizing certain traits can perpetuate harmful stereotypes and unrealistic standards for animals, leading to increased abandonment and neglect when animals fail to meet these expectations.
Ethical breeding requires a balance between achieving desired traits and maintaining the health and well-being of the animal. Breeders must prioritize the long-term health and genetic diversity of species over short-term aesthetic goals. This approach not only benefits individual animals but also contributes to the sustainability and resilience of animal populations as a whole.
In conclusion, addressing ethical considerations in animal breeding is crucial for the welfare of animals and the preservation of biodiversity. Breeders, pet owners, and the public must work together to ensure that animals are bred responsibly and ethically, prioritizing their health, well-being, and genetic diversity over superficial traits.
The Impact of Breeding Myths on Animal Populations
The world of animal breeding is often shrouded in myths and misconceptions that can have profound impacts on animal populations. These myths, if left unchecked, can lead to significant issues such as overpopulation and the loss of genetic diversity. Understanding these impacts is crucial for promoting responsible breeding practices and ensuring the health and sustainability of animal populations.
Overpopulation and Its Consequences
One of the most pressing issues arising from misconceptions in animal breeding is overpopulation. Many people still believe the myth that animals should reproduce at least once before being spayed or neutered, which contributes to a growing number of unwanted animals. This belief exacerbates the problem, leading to shelters being overwhelmed and countless animals being euthanized due to lack of homes.
The consequences of overpopulation are severe. Shelters across the globe face the daunting task of caring for millions of homeless animals each year. Unfortunately, the resources available are often insufficient to provide for all these animals, leading to overcrowding, disease, and high euthanasia rates. These outcomes are not only tragic for the animals involved but also place a considerable strain on animal welfare organizations and communities.
Moreover, overpopulation can lead to an increase in stray animals, which can create public health concerns. Stray animals may spread diseases, cause traffic accidents, and even become aggressive in their struggle to survive. These issues highlight the importance of dispelling breeding myths and promoting responsible pet ownership, including spaying and neutering.

The Threat to Genetic Diversity
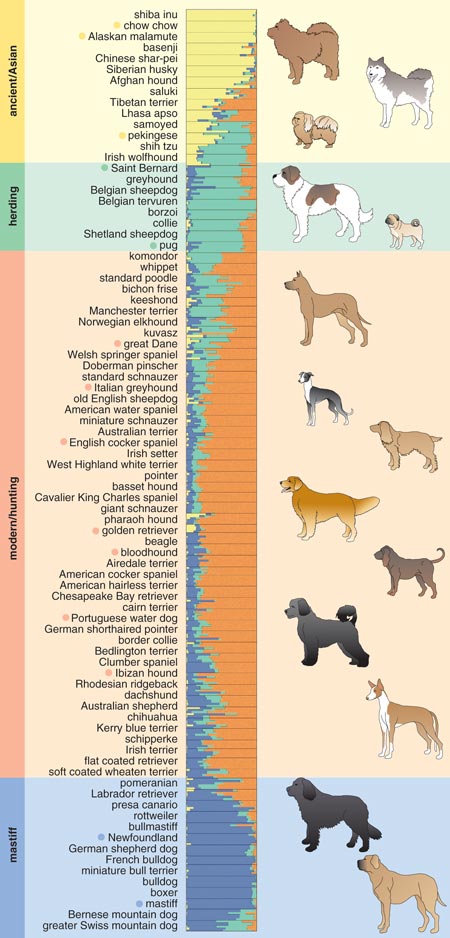
Another critical impact of breeding myths is the threat to genetic diversity. A common misconception is that purebred animals are inherently superior, leading to a preference for breeding within a limited gene pool. This practice, known as inbreeding, can significantly reduce genetic diversity and increase the risk of genetic disorders.
Genetic diversity is vital for the health and resilience of animal populations. It allows species to adapt to changing environments and resist diseases. When breeding practices favor a narrow genetic pool, the resulting lack of diversity can lead to a host of problems. Animals may suffer from inherited conditions, weaker immune systems, and reduced fertility.
Inbreeding not only affects the health of individual animals but also poses a threat to entire breeds. For instance, certain dog breeds are known to suffer from specific genetic disorders due to centuries of inbreeding. Breeding for specific traits, such as a particular coat color or size, often exacerbates these issues, as the gene pool is further limited to achieve these desired characteristics.
The myth that breeding is a simple process neglects the complexity and importance of maintaining genetic diversity. Responsible breeders understand the importance of introducing new bloodlines and carefully selecting breeding pairs to ensure the long-term health and viability of animal populations.

In conclusion, the myths surrounding animal breeding have significant implications for animal populations. By addressing overpopulation and preserving genetic diversity, we can work towards more sustainable and ethical breeding practices. It is essential to educate the public about these issues to ensure a brighter future for all animals.
How to Make Informed Decisions About Animal Breeding
In the world of animal breeding, making informed decisions is crucial for both prospective pet owners and breeders themselves. Understanding the intricacies involved can lead to healthier animals and more ethical practices. Here, we delve into the key considerations that should guide anyone interested in this field.
Researching Reputable Breeders
When considering getting a pet from a breeder, it’s essential to conduct thorough research to find a reputable one. A good breeder prioritizes the health and well-being of their animals over profit. They are knowledgeable about the breeds they work with and can provide detailed information on the animals’ lineage, health history, and temperament.
Key Characteristics of Reputable Breeders:
-
Transparency: Reputable breeders welcome questions and are open about their breeding practices. They allow potential buyers to visit their facilities and meet the animals in person.
-
Health Testing: They perform genetic testing and health screenings to ensure that their animals are free from hereditary diseases. This practice is crucial in maintaining the health and longevity of the breed.
-
Lifetime Support and Return Policy: They offer support to new owners and are willing to take back animals if circumstances change. This demonstrates a long-term commitment to the animals’ welfare.
-
Limited Litters: Good breeders focus on quality over quantity, often having only a few litters each year to ensure that they can provide adequate care and attention to each animal.
By choosing a reputable breeder, you contribute to ethical animal breeding practices, ensuring that the animals are treated with respect and care throughout their lives.
The Importance of Adoption and Rescue
While breeding animals responsibly is important, adoption and rescue provide a crucial alternative that addresses the growing issue of animal overpopulation. Every year, millions of animals end up in shelters, and many of them are euthanized due to a lack of available homes.
Benefits of Adoption and Rescue:
-
Saving Lives: By adopting, you directly save an animal’s life and free up space in shelters for other animals in need.
-
Cost-Effective: Adoption fees are often significantly lower than purchasing from breeders, and many shelters include vaccinations, microchipping, and spaying or neutering in the adoption fee.
-
Variety of Choices: Shelters house a wide variety of animals, including purebreds and mixed breeds, allowing prospective pet owners to find the perfect match for their lifestyle.
-
Support from Shelter Staff: Shelter employees are usually familiar with the animals’ personalities and can help match them with the right families.
Adopting a pet not only provides a loving home to an animal in need but also helps combat the negative consequences of irresponsible animal breeding practices. It is a compassionate choice that benefits both the animals and society.

In conclusion, whether choosing to adopt or buy from a breeder, making informed decisions about animal breeding is essential. It ensures the health and happiness of the animals and promotes ethical standards in the breeding community. By researching reputable breeders and considering adoption, you contribute positively to animal welfare and help create a more responsible future in animal care.
Conclusion: Moving Towards Responsible Animal Breeding Practices
As we navigate the complex world of animal breeding, it becomes increasingly clear that understanding and debunking myths are crucial steps towards more ethical and responsible practices. These myths, if left unchecked, can perpetuate harm not only to individual animals but also to entire populations, affecting their health, welfare, and genetic diversity. The journey towards responsible breeding is not just about correcting misconceptions; it’s about fostering a deeper respect and understanding for the animals we share our lives with.
Responsible animal breeding begins with education and awareness. By acknowledging the science behind breeding and the ethical implications of our choices, we can make informed decisions that prioritize animal welfare over aesthetics or profit. For instance, the myth that “purebred animals are always superior” often leads to inbreeding and a narrow genetic pool, which can result in serious health issues. Understanding that genetic diversity is a cornerstone of healthy populations is essential for anyone involved in breeding practices.
Moreover, ethical breeding takes into account the holistic needs of animals. It considers not just their physical health but their psychological well-being too. Animals are sentient beings, capable of experiencing a range of emotions. Ensuring they live in environments that cater to their needs and give them opportunities for enrichment is vital. Breeding should never be a process that prioritizes financial gain over the well-being of the animals involved.

One of the most significant shifts we can make is moving away from the idea that breeding is a simple or easy undertaking. It requires a deep understanding of genetics, a commitment to ethical standards, and a dedication to the animals’ best interests. This includes giving animals adequate rest between pregnancies and ensuring that breeding programs do not overburden them physically or emotionally.
Furthermore, the role of adoption and rescue cannot be understated in the broader conversation about animal breeding. By choosing to adopt or rescue animals, we alleviate the pressures of overpopulation and provide homes to animals in need. This act of compassion not only helps individual animals but also supports a more sustainable approach to managing animal populations.
Finally, it is essential to support and engage with reputable breeders who prioritize the health and welfare of animals. These breeders are often transparent about their practices, knowledgeable about the breeds, and committed to maintaining high standards of care. They understand that breeding is a responsibility that extends beyond the immediate litter to the long-term health and sustainability of the breed.
In conclusion, moving towards responsible animal breeding practices is a multifaceted journey that requires cooperation, compassion, and commitment from all stakeholders involved. By challenging myths, prioritizing welfare, and making informed choices, we can ensure that the practice of breeding animals contributes positively to their lives and the ecosystems they inhabit.
At WildWhiskers, we are committed to bringing you insightful and responsible content that enriches your understanding of the animal kingdom. Join us in our mission to promote ethical practices and celebrate the beauty and diversity of animals in all their forms.
WildWhiskers is a dedicated news platform for animal lovers around the world. From heartwarming stories about pets to the wild journeys of animals in nature, we bring you fun, thoughtful, and adorable content every day. With the slogan “Tiny Tails, Big Stories!”, WildWhiskers is more than just a news site — it’s a community for animal enthusiasts, a place to discover, learn, and share your love for the animal kingdom. Join WildWhiskers and open your heart to the small but magical lives of animals around us!