In the enchanting world of nature, the young ones of animals embark on a journey of discovery and survival, a journey that is as fascinating as it is complex. From the very first moments of life, these young creatures are thrust into an environment where every step, every leap, and every playful interaction serves as a critical lesson. Imagine a baby elephant tentatively learning to maneuver its trunk, or a lion cub energetically chasing after its siblings in a mock hunt—their actions are not just adorable; they are vital rehearsals for the challenges that lie ahead.
As we delve into the world of young animals, we’ll explore how instinctual behaviors and parental guidance play pivotal roles in their initial exploration of surroundings. Through the lens of play, we’ll uncover how these young adventurers develop essential survival skills, honing their instincts while navigating the diverse habitats they call home. Whether it’s the dense forests, sweeping deserts, or the vast oceans, each environment offers a unique set of challenges and opportunities for these creatures.
Yet, the path of exploration is fraught with peril. Predators lurk, and environmental changes pose constant threats. Despite these dangers, the resilience and adaptability of these young animals shine through, as they gain independence and develop complex behaviors that ensure their survival. This blog will take you on a journey to witness the remarkable transformation of these young ones as they grow and thrive in their natural habitats. By understanding their world, we gain a deeper appreciation for the delicate balance of nature and the wondrous journey of growth and discovery that every young animal undertakes. Join us as we uncover the secrets of how these incredible creatures explore and adapt to their ever-changing world.
The First Steps: Initial Exploration of Surroundings
The journey of young animals as they take their first steps into their habitats is a captivating blend of instinctual behavior and parental guidance. From the moment they are born, the young ones of animals embark on a path of discovery that is crucial for their survival. This initial exploration is not just about physical movement but also about developing an understanding of the world around them.
Instinctual Behaviors in Newborn Animals
From the very start, instinct plays a pivotal role in how newborn animals begin to explore their surroundings. These innate behaviors are pre-programmed into their DNA, ensuring they perform essential actions that increase their chances of survival. For example, many mammal species, like deer or giraffes, exhibit the ability to stand and walk shortly after birth. This is an evolutionary adaptation that enables them to quickly escape potential predators.
In the wild, the necessity to adapt swiftly to the environment is evident. Take, for instance, the newborn sea turtles that instinctively head towards the sea immediately after hatching. This behavior, driven by their innate sense to follow the moonlight reflecting off the ocean, is crucial for their survival. Similarly, newborn birds such as ducklings are guided by their instinct to follow their mother, learning to swim and forage almost immediately.
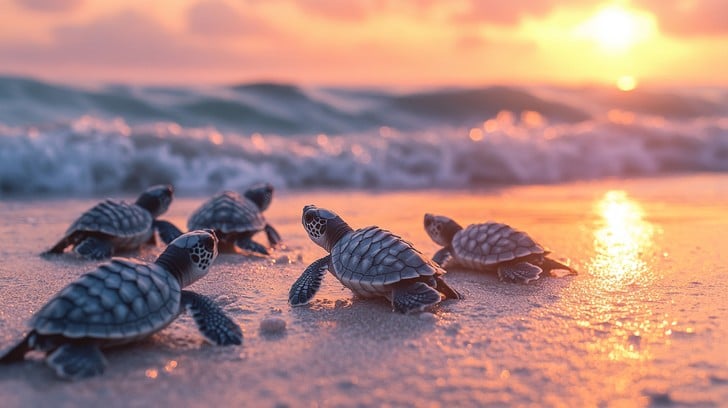

Newborn sea turtles instinctively heading towards the ocean
These instinctual behaviors are not just limited to physical movements. Young ones of animals also exhibit instinctual behaviors in their initial interactions with their environment. For instance, wolf pups engage in playful behavior that mimics hunting, which is a critical survival skill they need to learn.
Parental Guidance and Supervision
While instinct plays a significant role, parental guidance is equally crucial in the early stages of exploration. Many animal species invest considerable time and effort into guiding their young ones, providing them with both protection and education. This parental supervision is vital for teaching young animals the skills they need to thrive in their habitats.
In the animal kingdom, the role of parents is diverse and fascinating. For instance, elephant mothers are known for their protective nature, ensuring their calves are always within the safety of the herd. This not only provides a shield against predators but also serves as a learning platform for the calves to understand social structures and communication within the group.
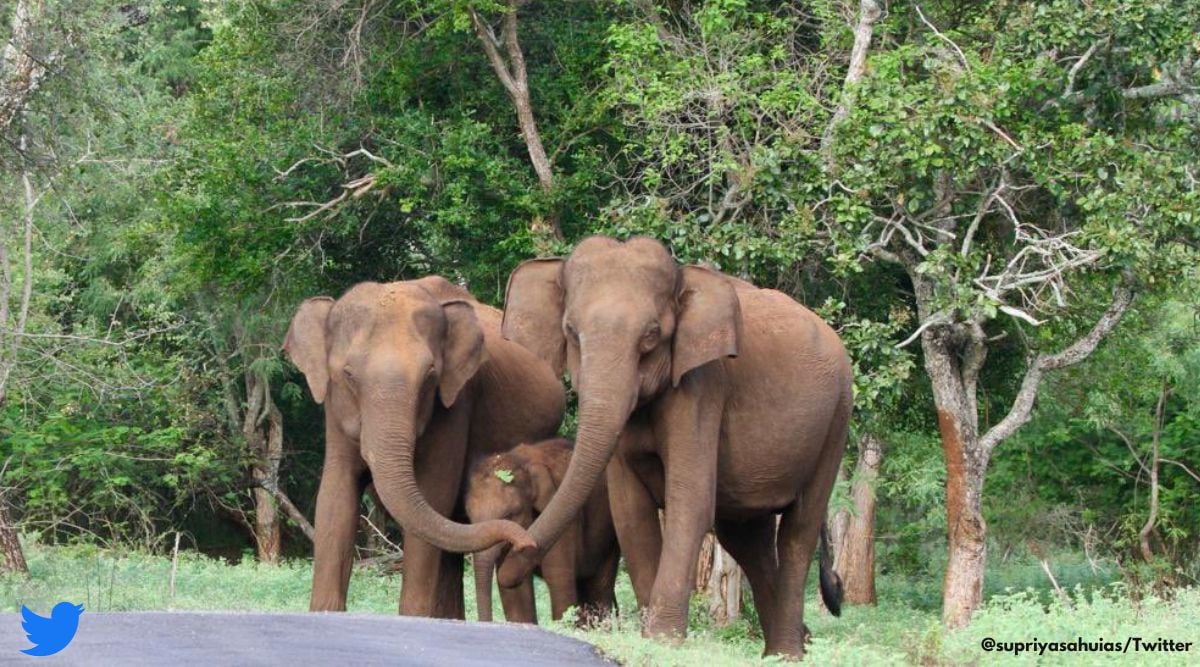

An elephant herd protecting a young calf
Similarly, in the case of lions, the pride acts as a nurturing environment. Lionesses work together to teach the cubs how to hunt, share, and interact with the pride members. This communal upbringing ensures that the young lions develop the necessary skills to eventually take on roles within the pride.
In aquatic environments, orca mothers are known to guide their calves through complex hunting techniques, highlighting the importance of parental teaching in ensuring the young ones’ survival. These mothers demonstrate coordinated hunting strategies, which are crucial for the calves to learn in their early stages of life.
Parental guidance is not just about survival skills but also about instilling confidence and independence in the young ones. By providing a balance of protection and freedom, parents enable their offspring to explore, make mistakes, and learn from them in a safe environment. This nurturing approach lays the groundwork for the development of complex behaviors and adaptations necessary for adult life.
In conclusion, the initial exploration of surroundings by young animals is a beautiful interplay of instinctual behaviors and parental guidance. This critical phase lays the foundation for their development, equipping them with the skills and confidence needed to navigate the challenges of their habitats. As we continue to study and understand these fascinating behaviors, we gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate processes that govern life in the animal kingdom.
The Role of Play in Learning About the Habitat
Play is not just a frivolous activity for the young ones of animals; it’s a critical part of their development and survival. Through play, these young creatures learn about their environments, develop necessary survival skills, and build social connections that are vital for their growth. Let’s delve into how play acts as an essential tool for young animals in exploring and understanding their habitats.
Social Play Among Siblings and Peers
Social play is a fascinating aspect of animal behavior, especially among the young ones of animals. It serves as a foundation for learning social norms, establishing bonds, and understanding the dynamics within their groups. For instance, lion cubs engage in playful wrestling and stalking games, which mimic the hunting techniques they will need as adults. These playful bouts are not merely about fun; they are structured interactions that teach cubs about hierarchy, cooperation, and competition within their pride.
In the world of dolphins, young calves often engage in synchronized swimming and leaping, which not only strengthens their physical abilities but also enhances their understanding of social cues and coordination within their pods. These playful interactions help them learn how to communicate and navigate the complex social structures of dolphin communities.
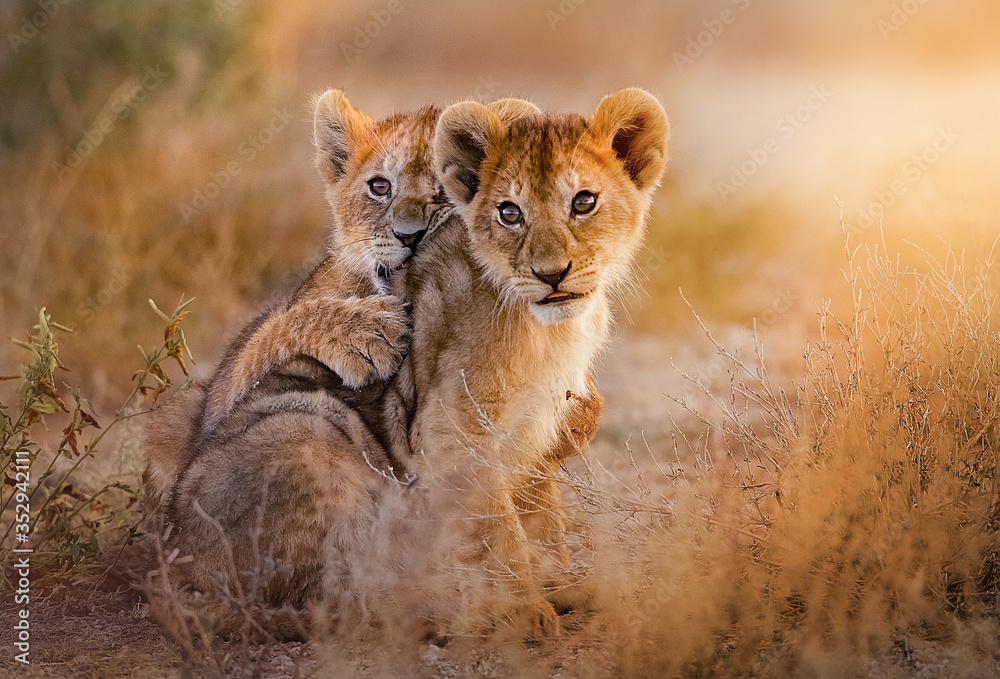

Lion cubs engage in playful wrestling in the savannah
Similarly, wolf pups participate in chase games and mock fights with their siblings. These activities help them develop coordination, strength, and social skills essential for pack life. By observing and mimicking the actions of older wolves, the pups learn how to hunt cooperatively and establish their roles within the pack’s hierarchy.
Through these social play activities, young animals not only hone their physical skills but also build the social networks necessary for survival in their respective habitats. These interactions lay the groundwork for complex social behaviors and relationships that will be crucial throughout their lives.
Developing Survival Skills Through Play
Beyond social interactions, play is a crucial mechanism through which young animals develop essential survival skills. These skills range from hunting techniques to escape strategies and resource gathering. For many species, play is the rehearsal ground for life’s challenges.
For example, young cheetahs engage in high-speed chases and pouncing games that mimic the hunting scenarios they will face as adults. These activities are not only exhilarating but also vital for developing the speed and precision required to bring down prey in the wild. Through these playful exercises, young cheetahs refine their stalking and sprinting techniques, enhancing their chances of survival in the harsh savannah environment.
In bear cubs, play takes the form of climbing trees and foraging for food. These activities are critical for developing agility and resource acquisition skills. Climbing strengthens their muscles and coordination, while foraging teaches them to identify edible plants and insects, vital for their sustenance and survival.
Moreover, young otters are often seen sliding down muddy banks into the water, a playful activity that doubles as a lesson in maneuvering through their aquatic environment. Through these repeated actions, they learn to swim efficiently, catch fish, and evade predators, ensuring they thrive in their riverine habitats.
Through play, the young ones of animals learn to adapt to their environments, developing both physical and cognitive skills that will ensure their survival. Play is not just an activity; it is a critical educational tool that prepares them for the myriad challenges they will face as they mature into adults.
Navigating Different Habitats: From Forests to Oceans
The journey of exploration for the young ones of animals is as vast and varied as the world itself. From the dense canopies of forests to the expansive blue of the oceans, each habitat presents unique challenges and learning opportunities. These environments shape the development of young animals, teaching them essential skills for survival.
Land Habitats: Forests, Deserts, and Grasslands
Forests, deserts, and grasslands each offer a distinct setting for young animals to explore. In forests, the dense foliage and towering trees provide a complex environment where young animals like chimpanzees learn to climb and navigate through the branches. They observe elders to understand the intricate art of finding food and recognizing territorial boundaries. In these lush habitats, the canopy often conceals hidden threats, making vigilance a crucial skill.
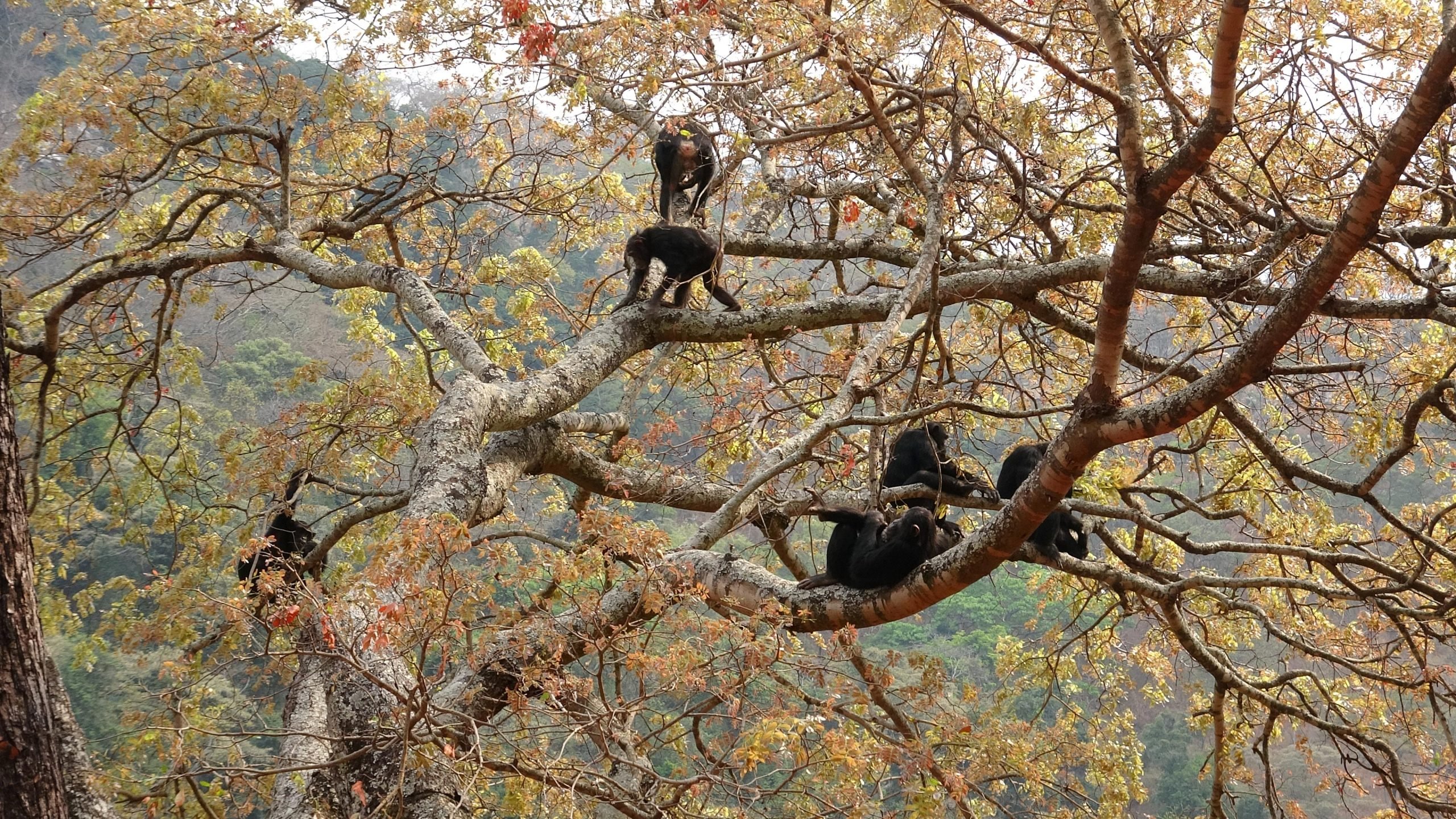

A young chimpanzee learning to climb in a dense forest
In the vast openness of deserts, young animals such as meerkat pups must quickly adapt to the harsh conditions. The searing heat and scarce water sources demand that they develop acute survival instincts. Under the watchful eyes of adults, they learn to dig for food and recognize the subtle signs of predators in the sandy landscape.
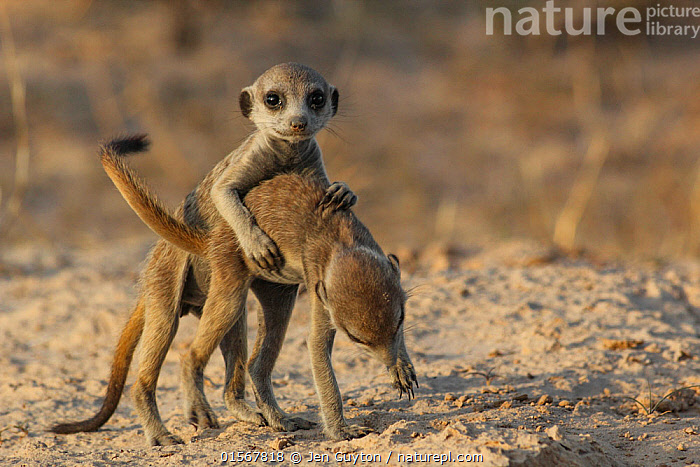

Meerkat pups exploring the harsh desert environment
Grasslands, on the other hand, present a different array of challenges. Here, young animals like lion cubs must master the art of stealth and coordination to hunt effectively. The open plains offer little cover, requiring them to rely on speed and strategy. Social interactions with siblings and other pride members are crucial for honing these essential survival skills.

Lion cubs practicing hunting techniques in the grassland
Aquatic Habitats: Rivers, Lakes, and Oceans
The aquatic world is equally diverse, with its own set of challenges for the young ones of animals. In rivers and lakes, creatures such as otter pups learn to swim and catch fish under the guidance of their parents. These bodies of water provide a relatively safe environment where young animals can practice essential skills without the immediate threat of ocean predators.
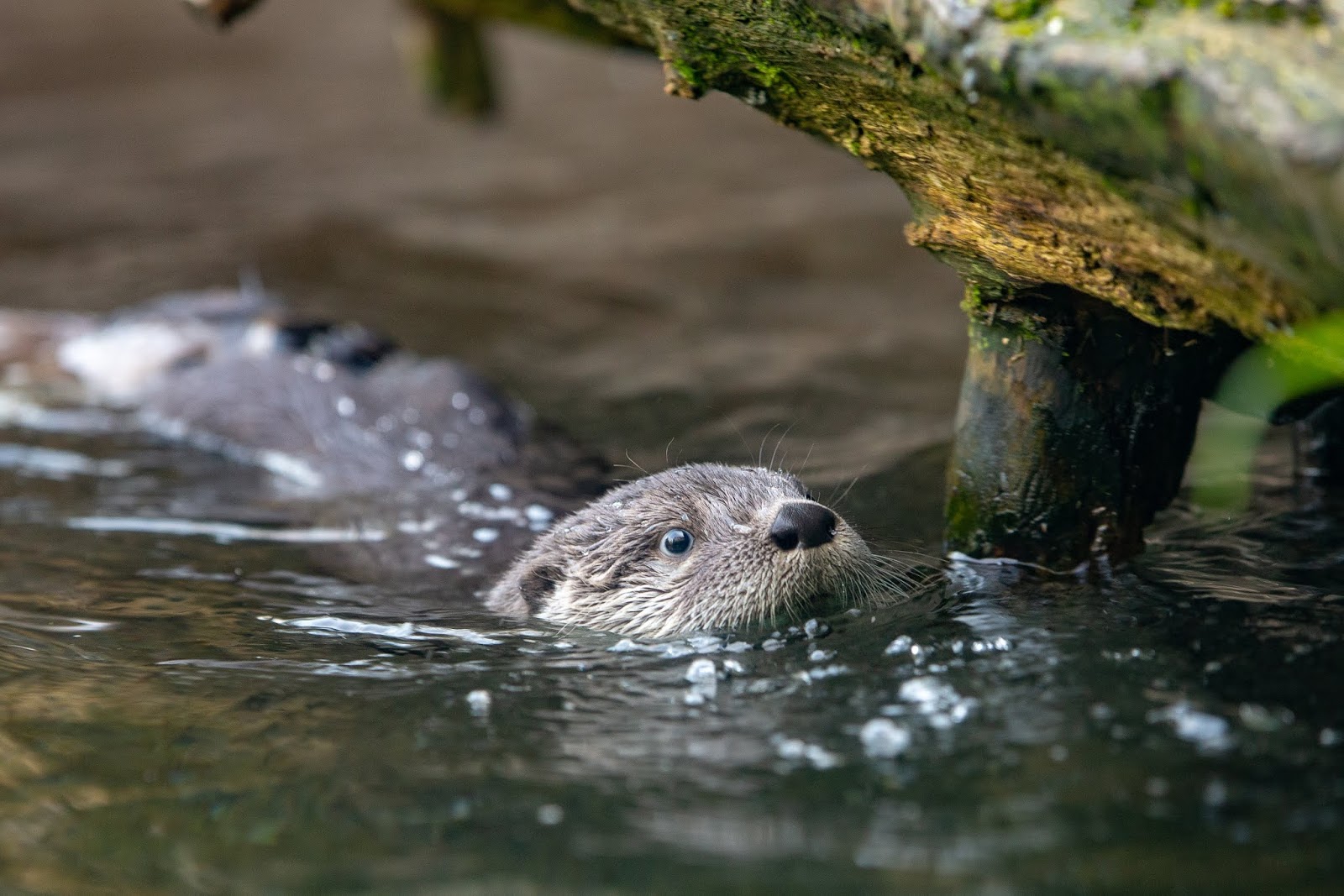

Otter pups learning to swim in a river
In the vast oceans, dolphin calves and young sea turtles face a more daunting challenge. The open ocean is a realm where navigation is key to survival. Dolphin calves, for instance, follow their mothers closely, learning the routes and social signals that are vital for their future independence. Similarly, young sea turtles must memorize the patterns of ocean currents to return to their nesting grounds as adults.

A dolphin calf learning to navigate the ocean with its mother
For every young animal, the experience of exploring different habitats is a critical part of their development. Whether traversing the dense forests or the deep blue seas, these young explorers acquire the knowledge and skills necessary to survive and thrive in the diverse environments of our planet.
The Challenges Young Animals Face in Exploration
Exploration is a crucial part of the development of young animals, often referred to as the young ones of animals. However, it is not without its challenges. As these creatures venture into the world, they encounter various obstacles that test their resilience and adaptability. These challenges range from natural threats like predators to the ever-changing environmental conditions.
Predators and Other Threats
For many young animals, the threat of predators looms large from the moment they take their first steps. The natural world is a delicate balance of predator and prey, and for the young ones of animals, learning to navigate this landscape is a matter of survival. Predators are constantly on the lookout for vulnerable prey, and young animals, with their lack of experience and smaller size, often find themselves at a disadvantage.
In the wild, lion cubs must learn to stay close to their pride for protection, while zebra foals quickly develop the ability to run alongside the herd to evade predators. The instincts of these young creatures play a crucial role in their survival. They learn to recognize the warning calls of their species and understand the importance of hiding or fleeing when danger is near.
Another significant threat to young animals is the presence of other competing species. In some ecosystems, competition for resources such as food and water can be fierce. Young animals must learn to identify safe sources of sustenance and how to access them without drawing the attention of predators or rivals.
Climate and Environmental Changes
Climate and environmental changes pose another set of challenges for young animals. As global temperatures rise and habitats are altered, the very landscapes that these creatures depend upon are shifting. For species whose survival is closely tied to specific environmental conditions, this can be particularly devastating.
Polar bear cubs, for instance, are born into a world where their icy habitat is melting at an alarming rate. These young ones of animals depend on the ice for hunting and resting, and as it diminishes, their chances of survival decrease. Similarly, young sea turtles face the challenge of changing ocean temperatures and rising sea levels, which can affect their nesting sites and food availability.
In addition to climate change, human activities such as deforestation, pollution, and urban expansion further threaten the habitats of young animals. These activities can lead to habitat fragmentation, making it difficult for young ones to find food, shelter, and mates.
Despite these challenges, many young animals exhibit remarkable resilience. They adapt to their changing environments by developing new behaviors and strategies for survival. For instance, some bird species have shifted their migration patterns in response to changing climates, while others have altered their breeding times to better align with food availability.

Polar bear cubs facing the challenges of a melting habitat
The exploration journey of young animals is fraught with challenges, yet it is through overcoming these obstacles that they develop the skills necessary for adult life. By understanding these challenges, we can better appreciate the complex interactions between young animals and their environments, as well as the importance of protecting these habitats for future generations.
The Impact of Exploration on Animal Development
Building Independence and Confidence
From the moment young animals, often referred to as young ones of animals, take their first tentative steps or venture into the unknown waters, they embark on a journey that is crucial for their survival. Exploration plays a pivotal role in building both independence and confidence, essential traits for their development. As these young creatures begin to explore their surroundings, they gradually detach from the constant supervision of their parents, learning to trust their instincts and abilities.
For instance, a young elephant calf, under the gentle yet firm guidance of its mother, learns to use its trunk not just for feeding but for sensing the world around it. This process of exploration allows the calf to build confidence in its abilities, gradually fostering a sense of independence. Similarly, lion cubs, as they engage in playful activities with their siblings, start honing their hunting skills. Initially, these activities might seem like mere play, but they are vital learning experiences that contribute to their growth.
As these young ones of animals venture further from the safety of their nests or dens, they encounter various challenges that test their newfound skills. Overcoming these hurdles, such as navigating difficult terrains or evading predators, reinforces their self-confidence and independence. This transformative journey from reliance to autonomy is a testament to the importance of exploration in animal development.
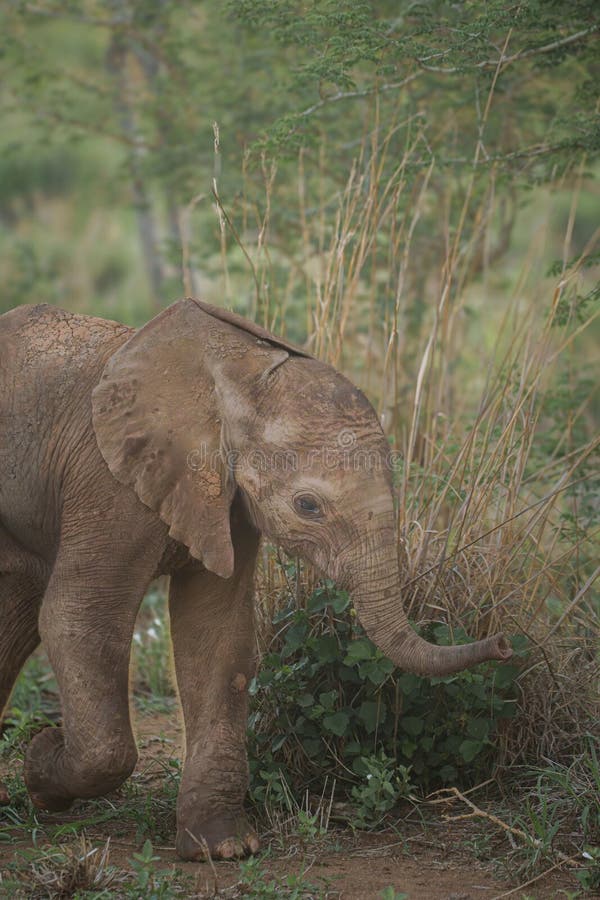

A young elephant calf exploring the savannah learning to use its trunk
Developing Complex Behaviors and Adaptations
The exploration of habitats by young animals is not just about gaining independence; it’s also about developing complex behaviors and adaptations crucial for survival. As they navigate their environments, these young creatures engage in a continuous learning process, adapting their behaviors to suit the challenges they face.
Consider young dolphins, who, under the watchful eyes of their mothers, learn intricate swimming techniques and social cues vital for their survival in the ocean’s vast expanse. Through exploration, these marine mammals develop sophisticated communication skills and the ability to work collaboratively, essential behaviors in their social structures.
In terrestrial environments, young meerkats participate in cooperative behaviors that are essential for the group’s survival. By observing and imitating adults, they learn to forage effectively and recognize potential threats. These complex behaviors are honed through repeated exploration and interaction with their environment and peers.
The adaptive skills learned by young animals during their explorations are critical in responding to changing environments. As climate change and human activities alter habitats, the ability of these animals to adapt becomes increasingly important. Exploring diverse environments equips them with the necessary tools to modify their behaviors and survive in a world where change is the only constant.
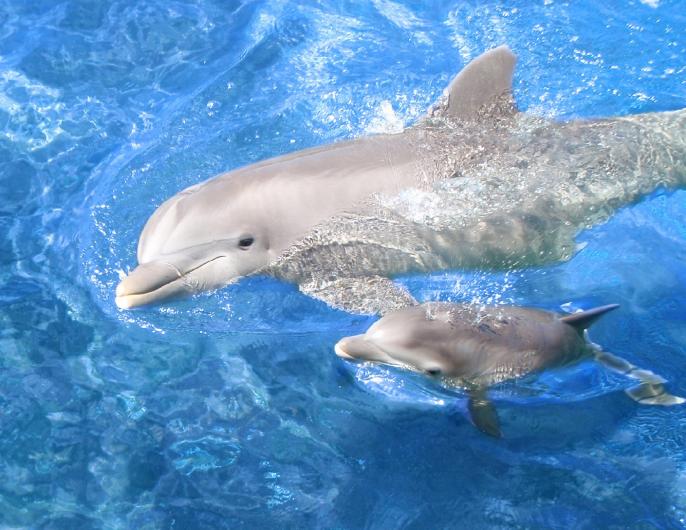

Young dolphins exploring the ocean learning swimming techniques and social cues
In essence, the exploration undertaken by young animals lays the foundation for a lifetime of learning and adaptation. As they grow and continue to explore, these creatures not only develop the skills necessary for survival but also contribute to the rich tapestry of life in their ecosystems, constantly evolving and adapting to the world around them.
Embracing the Journey of Growth and Discovery
The journey of young animals as they explore their habitats is not merely about survival; it is a beautiful saga of growth, discovery, and the deep-seated instinct to thrive. From the moment they open their eyes to the world, the young ones of animals embark on a lifelong adventure filled with curiosity, learning, and the development of unique adaptations that will serve them throughout their lives.
The Essence of Curiosity and Exploration
Curiosity is a powerful driver for young animals. It propels them to step beyond the safety of their nests or dens and venture into the unknown. This innate curiosity is not just a whimsical trait; it is crucial for their development. By exploring their surroundings, they learn about food sources, potential threats, and the intricacies of their environment. For instance, a young fox cub might venture out at dawn, its nose twitching with excitement as it uncovers the scent trails left by various creatures of the night.
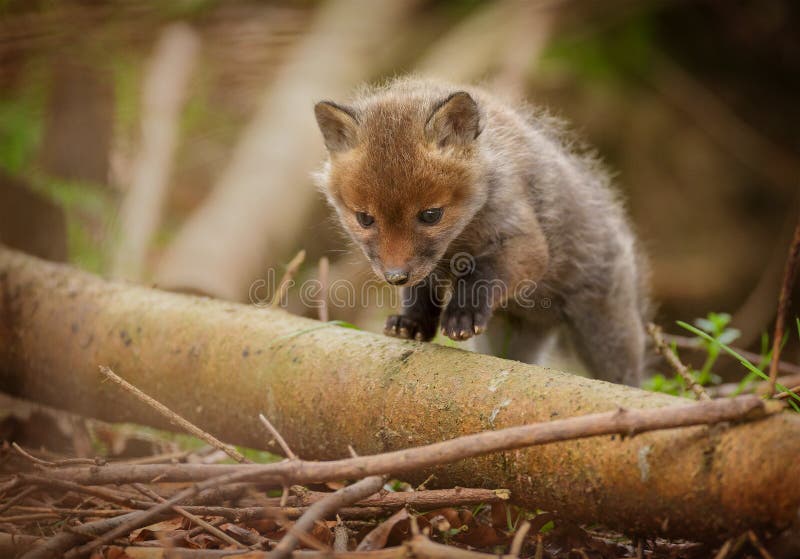

A curious fox cub exploring the forest at dawn
Building Independence and Confidence
Exploration plays a pivotal role in building independence and confidence in young animals. As they navigate through the complexities of their habitats, they gradually become less reliant on their parents. This transition is vital for species like the young ones of animals who need to fend for themselves in the wild. For example, a young lion cub, initially dependent on its mother, starts to engage in solo adventures. It learns to stalk and pounce, perfecting the art of hunting, which eventually becomes second nature.
Developing Complex Behaviors and Adaptations
The journey of discovery is not just about physical exploration but also about the development of complex behaviors and adaptations. Through interactions with their environment and peers, young animals learn vital survival skills. Play serves as a crucial tool in this learning process. Whether it’s a dolphin calf mimicking the leaps of its mother or a young otter mastering the skill of cracking open shells, these activities are fundamental in honing their abilities.
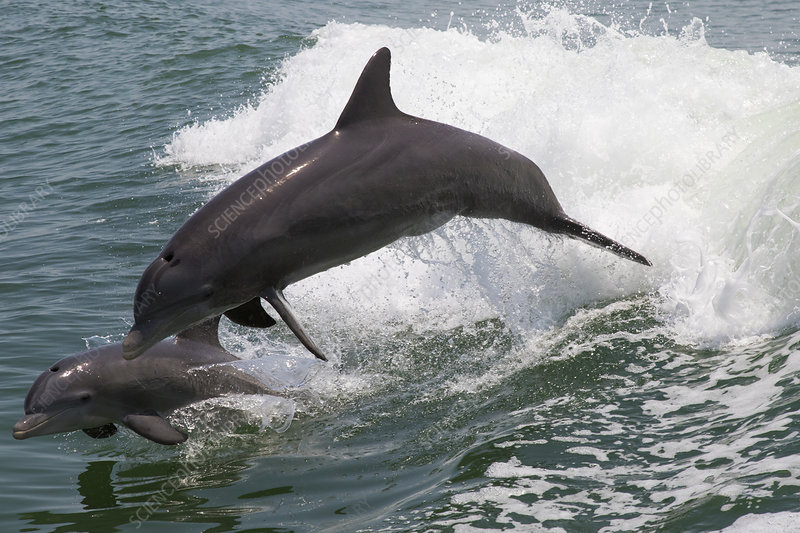

A dolphin calf learning by mimicking its mothers leaps
The Role of Environmental Challenges
The challenges posed by the environment further enrich the journey of discovery for young animals. Facing predators, harsh weather conditions, and finding food are part of their daily reality. Each challenge is a lesson, each survival a triumph that contributes to their growing repository of experiences and skills. These experiences foster resilience and adaptability, traits that are indispensable for survival in the wild.
A Lifelong Journey of Learning
While the early years are the most intense periods of learning and growth, the journey of exploration and discovery continues throughout the life of an animal. Each stage of life brings new challenges and opportunities for learning. A young elephant, for example, may spend years learning the migration routes from its older kin, understanding the nuances of social dynamics within the herd, and learning how to use its trunk with remarkable dexterity.

A young elephant learning the intricacies of using its trunk
The journey of young animals exploring their habitats is a testament to the wonders of nature and the incredible adaptability of life. It is through this journey that they become adept at surviving and thriving in the wild. By understanding and appreciating these journeys, we gain a deeper respect for the natural world and the remarkable creatures that inhabit it.
WildWhiskers is a dedicated news platform for animal lovers around the world. From heartwarming stories about pets to the wild journeys of animals in nature, we bring you fun, thoughtful, and adorable content every day. With the slogan “Tiny Tails, Big Stories!”, WildWhiskers is more than just a news site — it’s a community for animal enthusiasts, a place to discover, learn, and share your love for the animal kingdom. Join WildWhiskers and open your heart to the small but magical lives of animals around us!